Abstract
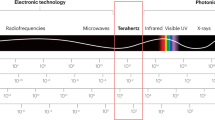
Electromagnetic radiation in the terahertz (THz) frequency range is a fascinating spectroscopic tool that provides resonant access to fundamental modes, including the motions of free electrons, the rotations of molecules, the vibrations of crystal lattices and the precessions of spins. Consequently, THz waves have been extensively used to probe such responses with high sensitivity. However, owing to recent developments in high-power sources, scientists have started to abandon the role of pure observers and are now exploiting intense THz radiation to engineer transient states of matter. This Review provides an overview and illustrative examples of how the electric and magnetic fields of intense THz transients can be used to control matter and light resonantly and nonresonantly.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chichkov, B. N., Momma, C., Nolte, S., von Alvensleben, F. & Tünnermann, A. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl. Phys. A 63, 109–115 (1996).
Christov, I. P., Murnane, M. M. & Kapteyn, H. C. High-harmonic generation of attosecond pulses in the “single-cycle” regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1251–1254 (1997).
Beard, M. C., Turner, G. M. & Schmuttenmaer, C. A. Terahertz spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 7146–7159 (2002).
Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nature Photon. 1, 97–105 (2007).
Ulbricht, R., Hendry, E., Shan, J., Heinz, T. F. & Bonn, M. Carrier dynamics in semiconductors studied with time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 543–586 (2011).
Jepsen, P. U., Cooke, D. G. & Koch, M. Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging — modern techniques and applications. Laser Photon. Rev. 5, 124–166 (2011).
Baxter, J. B. & Guglietta, G. W. Terahertz spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 83, 4342–4368 (2011).
Ganichev, S. D. & Prettl, W. Intense Terahertz Excitation of Semiconductors (Oxford Univ. Press, 2006).
Hoffmann, M. C. Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging (eds Peiponen, K.-E., Zeitler, A. & Kuwata-Gonokami, M.) Ch. 14 (Springer Series in Optical Sciences 171, Springer, 2013).
Hirori, H., Doi, A., Blanchard, F. & Tanaka, K. Single-cycle terahertz pulses with amplitudes exceeding 1 MV/cm generated by optical rectification in LiNbO3 . Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 091106 (2011).
Katayama, I. et al. Ferroelectric soft mode in a SrTiO3 thin film impulsively driven to the anharmonic regime using intense picosecond terahertz pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 097401 (2012).
Qi, T., Shin, Y.-H., Yeh, K.-L., Nelson, K. A. & Rappe, A. M. Collective coherent control: synchronization of polarization in ferroelectric PbTiO3 by shaped THz fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 247603 (2009).
Fritz, D. M. et al. Ultrafast bond softening in bismuth: mapping a solid's interatomic potential with X-rays. Science 315, 633–636 (2007).
Daranciang, D. et al. Ultrafast photovoltaic response in ferroelectric nanolayers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 087601 (2012).
Fausti, D. et al. Light-induced superconductivity in a stripe-ordered cuprate. Science 331, 189–191 (2011).
Caviglia, A. D. et al. Ultrafast strain engineering in complex oxide heterostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 136801 (2012).
Harde, H., Keiding, S. & Grischkowsky, D. THz commensurate echoes: periodic rephasing of molecular transitions in free-induction decay. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 1834–1837 (1991).
Bigourd, D. et al. Rotational spectroscopy and dynamics of carbonyl sulphide studied by terahertz free induction decays signals. Opt. Commun. 281, 3111–3119 (2008).
Fleischer, S., Zhou, Y., Field, R. W. & Nelson, K. A. Molecular orientation and alignment by intense single-cycle THz pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 163603 (2011).
Fleischer, S., Field, R. W. & Nelson, K. A. Commensurate two-quantum coherences induced by time-delayed THz fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 123603 (2012).
Stöhr, J. & Siegmann, H. C. Magnetism: From Fundamentals to Nanoscale Dynamics (Springer Series in Solid-State Sciences 152, Springer, 2006).
Hiebert, W. K., Stankiewicz, A. & Freeman, M. R. Direct observation of magnetic relaxation in a small permalloy disk by time-resolved scanning Kerr microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 1134–1137 (1997).
Wang, Z. et al. Spin dynamics triggered by subterahertz magnetic field pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 123905 (2008).
Ruchert, C. et al. Field-driven femtosecond magnetization dynamics induced by ultrastrong coupling to THz transients. Preprint at http://lanl.arxiv.org/abs/1209.1280 (2012).
Back, C. H. et al. Magnetization reversal in ultrashort magnetic field pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 3251–3254 (1998).
Kampfrath, T. et al. Coherent terahertz control of antiferromagnetic spin waves. Nature Photon. 5, 31–34 (2011).
Yamaguchi, K., Nakajima, M. & Suemoto, T. Coherent control of spin precession motion with impulsive magnetic fields of half-cycle terahertz radiation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 237201 (2010).
Arikawa, T. et al. Quantum control of a Landau-quantized two-dimensional electron gas in a GaAs quantum well using coherent terahertz pulses. Phys. Rev. B 84, 241307(R) (2011).
Jin, Z. et al. Single-pulse terahertz coherent control of spin resonance in the canted antiferromagnet YFeO3, mediated by dielectric anisotropy. Phys. Rev. B 87, 094422 (2013).
Liu, J. & Zhang, X.-C. Terahertz-radiation-enhanced emission of fluorescence from gas plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 235002 (2009).
Kampfrath, T. et al. Long- and short-lived electrons with anomalously high collision rates in laser-ionized gases. Phys. Rev. E 76, 066401 (2007).
Liu, J., Dai, J., Chin, S. L. & Zhang, X.-C. Broadband terahertz wave remote sensing using coherent manipulation of fluorescence from asymmetrically ionized gases. Nature Photon. 4, 627–631 (2010).
Clough, B., Dai, J. & Zhang, X.-C. Laser air photonics: beyond the terahertz gap. Mater. Today 15, 50–58 (2012).
Leinß, S. et al. Terahertz coherent control of optically dark paraexcitons in Cu2O. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 246401 (2008).
Wagner, M. et al. Observation of the intraexciton Autler–Townes effect in GaAs/AlGaAs semiconductor quantum wells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 167401 (2010).
Greenland, P. T. et al. Coherent control of Rydberg states in silicon. Nature 465, 1057–1061 (2010).
Luo, C. W. et al. Phase-resolved nonlinear response of a two-dimensional electron gas under femtosecond intersubband excitation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 047402 (2004).
Tomaino, J. L. et al. Terahertz excitation of a coherent Λ-type three-level system of exciton-polariton modes in a quantum-well microcavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 267402 (2012).
Junginger, F. et al. Nonperturbative interband response of a bulk InSb semiconductor driven off resonantly by terahertz electromagnetic few-cycle pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 147403 (2012).
Matsunaga, R. & Shimano, R. Nonequilibrium BCS state dynamics induced by intense terahertz pulses in a superconducting NbN film. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 187002 (2012).
Beck, M. et al. Energy-gap dynamics of superconducting NbN thin films studied by time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 177007 (2011).
Glossner, A. et al. Cooper pair breakup in YBCO under strong terahertz fields. Preprint at http://lanl.arxiv.org/abs/1205.1684 (2012).
Dienst, A. et al. Optical excitation of Josephson plasma solitons in a cuprate superconductor. Nature Mater. 12, 535–541 (2013).
Mukai, Y., Hirori, H. & Tanaka, K. Electric field ionization of gallium acceptors in germanium induced by single-cycle terahertz pulses. Phys. Rev. B 87, 201202(R) (2013).
Ewers, B. et al. Ionization of coherent excitons by strong terahertz fields. Phys. Rev. B 85, 075307 (2012).
Zaks, B., Liu, R. B. & Sherwin, M. S. Experimental observation of electron–hole recollisions. Nature 483, 580–583 (2012).
Zaks, B., Banks, H. & Sherwin, M. S. High-order sideband generation in bulk GaAs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 012104 (2013).
Kuehn, W. et al. Coherent ballistic motion of electrons in a periodic potential. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 146602 (2010).
Blanchard, F. et al. Effective mass anisotropy of hot electrons in nonparabolic conduction bands of n-doped InGaAs films using ultrafast terahertz pump–probe techniques. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 107401 (2011).
Gaal, P. et al. Internal motions of a quasiparticle governing its ultrafast nonlinear response. Nature 450, 1210–1213 (2007).
Bowlan, P. et al. High-field transport in an electron–hole plasma: transition from ballistic to drift motion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 256602 (2011).
Su, F. H. et al. Terahertz pulse induced intervalley scattering in photoexcited GaAs. Opt. Express 17, 9620–9629 (2009).
Razzari, L. et al. Nonlinear ultrafast modulation of the optical absorption of intense few-cycle terahertz pulses in n-doped semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 79, 193204 (2009).
Hebling, J., Hoffmann, M. C., Hwang, H. Y., Yeh, K.-L. & Nelson, K. A. Observation of nonequilibrium carrier distribution in Ge, Si, and GaAs by terahertz pump–terahertz probe measurements. Phys. Rev. B 81, 035201 (2010).
Ho, I.-C. & Zhang, X.-C. Driving intervalley scattering and impact ionization in InAs with intense terahertz pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 241908 (2011).
Wen, H., Wiczer, M. & Lindenberg, A. M. Ultrafast electron cascades in semiconductors driven by intense femtosecond terahertz pulses. Phys. Rev. B 78, 125203 (2008).
Hoffmann, M. C., Hebling, J., Hwang, H. Y., Yeh, K.-L. & Nelson, K. A. Impact ionization in InSb probed by terahertz pump–terahertz probe spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 79, 161201(R) (2009).
Liu, J., Kaur, G. & Zhang, X.-C. Photoluminescence quenching dynamics in cadmium telluride and gallium arsenide induced by ultrashort terahertz pulse. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 111103 (2010).
Hirori, H. et al. Extraordinary carrier multiplication gated by a picosecond electric field pulse. Nat. Commun. 2, 594 (2011).
Watanabe, S., Minami, N. & Shimano, R. Intense terahertz pulse induced exciton generation in carbon nanotubes. Opt. Express 19, 1528–1538 (2011).
Tani, S., Blanchard, F. & Tanaka, K. Ultrafast carrier dynamics in graphene under a high electric field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 166603 (2012).
Huang, S.-W. et al. High conversion efficiency, high energy terahertz pulses by optical rectification in cryogenically cooled lithium niobate. Opt. Lett. 38, 796–798 (2013).
Chen, H.-T., O'Hara, J. F., Azad, A. K. & Taylor, A. J. Manipulation of terahertz radiation using metamaterials. Laser Photon. Rev. 5, 513–533 (2011).
Seo, M. A. et al. Terahertz field enhancement by a metallic nano slit operating beyond the skin-depth limit. Nature Photon. 3, 152–156 (2009).
Shalaby, M. et al. Concurrent field enhancement and high transmission of THz radiation in nanoslit arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 041110 (2011).
Werley, C. A. et al. Time-resolved imaging of near-fields in THz antennas and direct quantitative measurement of field enhancements. Opt. Express 20, 8551–8567 (2012).
Blanchard, F., Doi, A., Tanaka, T. & Tanaka, K. Subwavelength terahertz imaging. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 43, 237–259 (2013).
Giannini, V., Berrier, A., Maier, S. A., Sánchez-Gil, J. A. & Gómez-Rivas, J. Scattering efficiency and near field enhancement of active semiconductor plasmonic antennas at terahertz frequencies. Opt. Express 18, 2797–2807 (2010).
Wimmer, L. et al. Controlling and streaking nanotip photoemission by enhanced single-cycle terahertz pulses. Preprint at http://lanl.arxiv.org/abs/1307.2581 (2013).
Burresi, M. et al. Magnetic light–matter interactions in a photonic crystal nanocavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 123901 (2010).
Liu, M. et al. Terahertz-field-induced insulator-to-metal transition in vanadium dioxide metamaterial. Nature 487, 345–348 (2012).
Shen, Y. et al. Nonlinear cross-phase modulation with intense single-cycle terahertz pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 043901 (2007).
Novelli, F., Fausti, D., Giusti, F., Parmigiani, F. & Hoffmann, M. Mixed regime of light-matter interaction revealed by phase sensitive measurements of the dynamical Franz-Keldysh effect. Sci. Rep. 3, 1227 (2013).
Shen, Y. et al. Electro-optic time lensing with an intense single-cycle terahertz pulse. Phys. Rev. A 81, 053835 (2010).
Foster, M. A. et al. Silicon-chip-based ultrafast optical oscilloscope. Nature 456, 81–84 (2008).
Beggs, D. M., Krauss, T. F., Kuipers, L. & Kampfrath, T. Ultrafast tilting of the dispersion of a photonic crystal and adiabatic spectral compression of light pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 033902 (2012).
Schubert, O. et al. Ultrashort pulse characterization with a terahertz streak camera. Opt. Lett. 36, 4458–4460 (2011).
Hoffmann, M. C., Brandt, N. C., Hwang, H. Y., Yeh, K.-L. & Nelson, K. A. Terahertz Kerr effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 231105 (2009).
Turchinovich, D., Hvam, J. M. & Hoffmann, M. C. Self-phase modulation of a single-cycle terahertz pulse by nonlinear free-carrier response in a semiconductor. Phys. Rev. B 85, 201304(R) (2012).
Zhang, C. et al. Terahertz nonlinear superconducting metamaterials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 081121 (2013).
Fan, K. et al. Nonlinear terahertz metamaterials via field-enhanced carrier dynamics in GaAs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 217404 (2013).
Jewariya, M., Nagai, M. & Tanaka, K. Ladder climbing on the anharmonic intermolecular potential in an amino acid microcrystal via an intense monocycle terahertz pulse. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 203003 (2010).
Eickemeyer, F., Kaindl, R. A., Woerner, M., Elsaesser, T. & Weiner, A. M. Controlled shaping of ultrafast electric field transients in the mid-infrared spectral range. Opt. Lett. 25, 1472–1474 (2000).
Ahn, J., Efimov, A., Averitt, R. & Taylor, A. Terahertz waveform synthesis via optical rectification of shaped ultrafast laser pulses. Opt. Express 11, 2486–2496 (2003).
Chen, Z., Zhou, X., Werley, C. A. & Nelson, K. A. Generation of high power tunable multicycle terahertz pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 071102 (2011).
Feurer, T., Vaughan, J. C. & Nelson, K. A. Spatiotemporal coherent control of lattice vibrational waves. Science 299, 374–377 (2003).
Feurer, T. et al. Terahertz polaritonics. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 37, 317–350 (2007).
Knippels, G. M. H., Mols, R. F. X. A. M., van der Meer, A. F. G., Oepts, D. & van Amersfoort, P. W. Intense far-infrared free-electron laser pulses with a length of six optical cycles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 1755–1758 (1995).
Zvyagin, S. A. et al. Terahertz-range free-electron laser electron spin resonance spectroscopy: techniques and applications in high magnetic fields. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80, 073102 (2009).
Först, M et al. in Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging (eds Peiponen, K.-E., Zeitler, A. & Kuwata-Gonokami, M.) Ch. 23 (Springer Series in Optical Sciences 171, Springer, 2013).
Gensch, M. et al. New infrared undulator beamline at FLASH. Infrared Phys. Technol. 51, 423–425 (2008).
Elias, L. R., Hu, J. & Ramian, G. The UCSB electrostatic accelerator free electron laser: first operation. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. A 237, 203–206 (1985).
Hoffmann, M. C. et al. Coherent single-cycle pulses with MV/cm field strengths from a relativistic transition radiation light source. Opt. Lett. 36, 4473–4475 (2011).
Wu, Z. et al. Intense terahertz pulses from SLAC electron beams using coherent transition radiation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84, 022701 (2013).
Reimann, K. Table-top sources of ultrashort THz pulses. Rep. Prog. Phys. 70, 1597 (2007).
Kitaeva, G. Kh. Terahertz generation by means of optical lasers. Laser Phys. Lett. 5, 559–576 (2008).
Hebling, J., Yeh, K.-L., Hoffmann, M. C., Bartal, B. & Nelson, K. A. Generation of high-power terahertz pulses by tilted-pulse-front excitation and their application possibilities. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 25, 6–19 (2008).
Fülöp, J. A. et al. Generation of sub-mJ terahertz pulses by optical rectification. Opt. Lett. 37, 557–559 (2012).
Blanchard, F. et al. Generation of 1.5 μJ single-cycle terahertz pulses by optical rectification from a large aperture ZnTe crystal. Opt. Express 15, 13212–13220 (2007).
Hauri, C. P., Ruchert, C., Vicario, C. & Ardana, F. Strong-field single-cycle THz pulses generated in an organic crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 161116 (2011).
Ruchert, C., Vicario, C. & Hauri, C. P. Scaling submillimeter single-cycle transients toward megavolts per centimeter field strength via optical rectification in the organic crystal OH1. Opt. Lett. 37, 899–901 (2012).
Reimann, K., Smith, R. P., Weiner, A. M., Elsaesser, T. & Woerner, M. Direct field-resolved detection of terahertz transients with amplitudes of megavolts per centimeter. Opt. Lett. 28, 471–473 (2003).
Sell, A., Leitenstorfer, A. & Huber, R. Phase-locked generation and field-resolved detection of widely tunable terahertz pulses with amplitudes exceeding 100 MV/cm. Opt. Lett. 33, 2767–2769 (2008).
You, D., Jones, R. R., Bucksbaum, P. H. & Dykaar, D. R. Generation of high-power sub-single-cycle 500-fs electromagnetic pulses. Opt. Lett. 18, 290–292 (1993).
Kim, K.-Y., Glownia, J. H., Taylor, A. J. & Rodriguez, G. High-power broadband terahertz generation via two-color photoionization in gases. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 48, 797–805 (2012).
Wu, Q. & Zhang, X.-C. Free-space electro-optic sampling of terahertz beams. Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 3523–3525 (1995).
Leitenstorfer, A., Hunsche, S., Shah, J., Nuss, M. C. & Knox, W. H. Detectors and sources for ultrabroadband electro-optic sampling: experiment and theory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 1516–1518 (1999).
Acknowledgements
T.K. acknowledges support from the DFG grant KA 3305/2-1 and thanks G. Kampfrath, L. Braun, R. K. Campen, M. Gensch, R. Huber, A. Leitenstorfer, S. Mährlein and M. Wolf for support and discussions. K.T. acknowledges support by KAKENHI (no. 23244065 and no. 20104007) from JSPS and MEXT of Japan and thanks M. Nagai, H. Hirori, F. Blanchard, S. Tani, A. Doi and T. Tanaka for collaborations and discussions. K.A.N. acknowledges support from Office of Naval Research grants N00014-09-1-1103 and N00014-06-1-0463.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kampfrath, T., Tanaka, K. & Nelson, K. Resonant and nonresonant control over matter and light by intense terahertz transients. Nature Photon 7, 680–690 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.184
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.184
This article is cited by
-
Ultrafast entropy production in pump-probe experiments
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Terahertz-induced martensitic transformation in partially stabilized zirconia
Communications Physics (2023)
-
Multi-millijoule terahertz emission from laser-wakefield-accelerated electrons
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Terahertz radiation by quantum interference of excitons in a one-dimensional Mott insulator
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Recent advances and research progress on microsystems and bioeffects of terahertz neuromodulation
Microsystems & Nanoengineering (2023)