Abstract
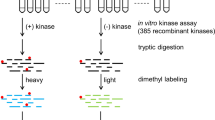
We introduce a mass spectrometry–based method that provides residue-resolved quantitative information about protein phosphorylation. In this assay we combined our full-length expressed stable isotope–labeled protein for quantification strategy (FLEXIQuant) with a traditional kinase assay to determine the mechanisms of multikinase substrate phosphorylation such as priming-dependent kinase activities. The assay monitors the decrease in signal intensity of the substrate peptides and the concomitant increase in the (n × 80 Da)-shifted phosphorylated peptide. We analyzed the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) activity on doublecortin (DCX) revealing mechanistic details about the role of phosphorylation cross-talk in GSK3β activity and permitting an advanced model for GSK3β-mediated signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hastie, C.J., McLauchlan, H.J. & Cohen, P. Assay of protein kinases using radiolabeled ATP: a protocol. Nat. Protoc. 1, 968–971 (2006).
Mok, J., Im, H. & Snyder, M. Global identification of protein kinase substrates by protein microarray analysis. Nat. Protoc. 4, 1820–1827 (2009).
Garcia, B.A. et al. Chemical derivatization of histones for facilitated analysis by mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2, 933–938 (2007).
Prabakaran, S. et al. Comparative analysis of Erk phosphorylation suggests a mixed strategy for measuring phospho-form distributions. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 482 (2011).
Kubota, K. et al. Sensitive multiplexed analysis of kinase activities and activity-based kinase identification. Nat. Biotechnol. 27, 933–940 (2009).
Yu, Y. et al. A site-specific, multiplexed kinase activity assay using stable-isotope dilution and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 11606–11611 (2009).
Singh, S., Springer, M., Steen, J., Kirschner, M.W. & Steen, H. FLEXIQuant: a novel tool for the absolute quantification of proteins, and the simultaneous identification and quantification of potentially modified peptides. J. Proteome Res. 8, 2201–2210 (2009).
Dickson, C. Protein techniques: immunoprecipitation, in vitro kinase assays, and Western blotting. Methods Mol. Biol. 461, 735–744 (2008).
Bilimoria, P.M. et al. A JIP3-regulated GSK3beta/DCX signaling pathway restricts axon branching. J. Neurosci. 30, 16766–16776 (2010).
Cohen, P. & Frame, S. The renaissance of GSK3. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 769–776 (2001).
Forde, J.E. & Dale, T.C. Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a key regulator of cellular fate. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 1930–1944 (2007).
Harwood, A.J. Signal transduction in development: holding the key. Dev. Cell 2, 384–385 (2002).
Gdalyahu, A. et al. DCX, a new mediator of the JNK pathway. EMBO J. 23, 823–832 (2004).
Cutillas, P.R. et al. Ultrasensitive and absolute quantification of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway by mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 8959–8964 (2006).
Olsen, J.V. et al. Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell 127, 635–648 (2006).
Gygi, S.P. et al. Quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures using isotope-coded affinity tags. Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 994–999 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Gunawardena for his thorough reading of our manuscript and for his advice. This work is funded in part by US National Institutes of Health grants NS066973, GM094844, GM096319 and GM081578 (H.S.) and NS041021 and NS047188 (A.B.), by the Tau Consortium (J.A.S.) and by the German Academic Exchange Service (D.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.S. contributed to devising the strategy and qualitative and quantitative mass spectrometry experiments, and wrote the initial manuscript; D.W. contributed qualitative mass spectrometry analysis; P.M.B. contributed in vitro kinase assays and revised the manuscript; P.M.B. and D.W. made equal contributions; A.B. contributed support and revisions to the manuscript. J.A.S. and H.S. contributed to devising the strategy and experimental design, provided support and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 393 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Winter, D., Bilimoria, P. et al. FLEXIQinase, a mass spectrometry–based assay, to unveil multikinase mechanisms. Nat Methods 9, 504–508 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1970
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1970
This article is cited by
-
Common mouse models of tauopathy reflect early but not late human disease
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2023)
-
Phosphoproteomics reveals rewiring of the insulin signaling network and multi-nodal defects in insulin resistance
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis of BR-defective mutant reveals a key role of GhSK13 in regulating cotton fiber development
Science China Life Sciences (2020)
-
Site-specific NMR mapping and time-resolved monitoring of serine and threonine phosphorylation in reconstituted kinase reactions and mammalian cell extracts
Nature Protocols (2013)