Abstract
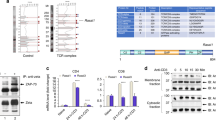
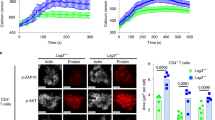
To investigate the role of the kinase Zap70 in T cells, we generated mice expressing a Zap70 mutant whose catalytic activity can be selectively blocked by a small-molecule inhibitor. We found that conventional naive, effector and memory T cells were dependent on the kinase activity of Zap70 for their activation, which demonstrated a nonredundant role for Zap70 in signals induced by the T cell antigen receptor (TCR). In contrast, the catalytic activity of Zap70 was not required for activation of the GTPase Rap1 and inside-out signals that promote integrin adhesion. This Zap70 kinase–independent pathway was sufficient for the suppressive activity of regulatory T cells (Treg cells), which was unperturbed by inhibition of the catalytic activity of Zap70. Our results indicate Zap70 is a likely therapeutic target.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 November 2010
In the version of this article initially published online, the key above Figure 5a was mislabeled. The correct label is Treg:Tconv. The error has been corrected for the print, PDF and HTML versions of this article.
References
Au-Yeung, B.B. et al. The structure, regulation, and function of ZAP-70. Immunol. Rev. 228, 41–57 (2009).
Koretzky, G.A., Abtahian, F. & Silverman, M.A. SLP76 and SLP65: complex regulation of signalling in lymphocytes and beyond. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 67–78 (2006).
Horejsi, V., Zhang, W. & Schraven, B. Transmembrane adaptor proteins: organizers of immunoreceptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 603–616 (2004).
Kadlecek, T.A. et al. Differential requirements for ZAP-70 in TCR signaling and T cell development. J. Immunol. 161, 4688–4694 (1998).
Negishi, I. et al. Essential role for ZAP-70 in both positive and negative selection of thymocytes. Nature 376, 435–438 (1995).
Chan, A.C. et al. ZAP-70 deficiency in an autosomal recessive form of severe combined immunodeficiency. Science 264, 1599–1601 (1994).
Elder, M.E. et al. Human severe combined immunodeficiency due to a defect in ZAP-70, a T cell tyrosine kinase. Science 264, 1596–1599 (1994).
Bishop, A.C. et al. Design of allele-specific inhibitors to probe protein kinase signaling. Curr. Biol. 8, 257–266 (1998).
Levin, S.E., Zhang, C., Kadlecek, T.A., Shokat, K.M. & Weiss, A. Inhibition of ZAP-70 kinase activity via an analog-sensitive allele blocks T cell receptor and CD28 superagonist signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 15419–15430 (2008).
Hsu, L.Y., Tan, Y.X., Xiao, Z., Malissen, M. & Weiss, A. A hypomorphic allele of ZAP-70 reveals a distinct thymic threshold for autoimmune disease versus autoimmune reactivity. J. Exp. Med. 206, 2527–2541 (2009).
Tanaka, S. et al. Graded attenuation of TCR signaling elicits distinct autoimmune diseases by altering thymic T Cell selection and regulatory T Cell function. J. Immunol. 185, 2295–2305 (2010).
Takahashi, T. et al. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by CD25+CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells: induction of autoimmune disease by breaking their anergic/suppressive state. Int. Immunol. 10, 1969–1980 (1998).
Thornton, A.M. & Shevach, E.M. CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production. J. Exp. Med. 188, 287–296 (1998).
Tang, Q. et al. In vitro-expanded antigen-specific regulatory T cells suppress autoimmune diabetes. J. Exp. Med. 199, 1455–1465 (2004).
Hickman, S.P., Yang, J., Thomas, R.M., Wells, A.D. & Turka, L.A. Defective activation of protein kinase C and Ras-ERK pathways limits IL-2 production and proliferation by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 177, 2186–2194 (2006).
Gavin, M.A., Clarke, S.R., Negrou, E., Gallegos, A. & Rudensky, A. Homeostasis and anergy of CD4+CD25+ suppressor T cells in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 3, 33–41 (2002).
Gelkop, S., Gish, G.D., Babichev, Y., Pawson, T. & Isakov, N. T cell activation-induced CrkII binding to the Zap70 protein tyrosine kinase is mediated by Lck-dependent phosphorylation of Zap70 tyrosine 315. J. Immunol. 175, 8123–8132 (2005).
Zhang, W. et al. Negative regulation of T cell antigen receptor-mediated Crk-L-C3G signaling and cell adhesion by Cbl-b. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 23978–23983 (2003).
Gelkop, S. & Isakov, N. T cell activation stimulates the association of enzymatically active tyrosine-phosphorylated ZAP-70 with the Crk adapter proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21519–21527 (1999).
Sasahara, Y. et al. Mechanism of recruitment of WASP to the immunological synapse and of its activation following TCR ligation. Mol. Cell 10, 1269–1281 (2002).
Sakaguchi, S., Wing, K., Onishi, Y., Prieto-Martin, P. & Yamaguchi, T. Regulatory T cells: how do they suppress immune responses? Int. Immunol. 21, 1105–1111 (2009).
Shevach, E.M. Mechanisms of foxp3+ T regulatory cell-mediated suppression. Immunity 30, 636–645 (2009).
Busse, D. et al. Competing feedback loops shape IL-2 signaling between helper and regulatory T lymphocytes in cellular microenvironments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 3058–3063 (2010).
Marski, M., Kandula, S., Turner, J.R. & Abraham, C. CD18 is required for optimal development and function of CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. J. Immunol. 175, 7889–7897 (2005).
Tran, D.Q. et al. Analysis of adhesion molecules, target cells, and role of IL-2 in human FOXP3+ regulatory T cell suppressor function. J. Immunol. 182, 2929–2938 (2009).
Li, L. et al. Rap1-GTP is a negative regulator of Th cell function and promotes the generation of CD4+CD103+ regulatory T cells in vivo. J. Immunol. 175, 3133–3139 (2005).
Kim, J.K. et al. Impact of the TCR signal on regulatory T cell homeostasis, function, and trafficking. PLoS One 4, e6580 (2009).
Iwashima, M., Irving, B.A., van Oers, N.S., Chan, A.C. & Weiss, A. Sequential interactions of the TCR with two distinct cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. Science 263, 1136–1139 (1994).
Chu, D.H. et al. Pre-T cell receptor signals are responsible for the down-regulation of Syk protein tyrosine kinase expression. J. Immunol. 163, 2610–2620 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Gately (Hoffmann–La Roche) for recombinant human IL-2; A. Roque for assistance in animal husbandry; C. MacArthur for cell sorting; and J. Wei for generating the Zap70(AS) BAC transgene construct. Supported by the National Institute of Arthritis, Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, National Institutes of Health (RC2AR058947 to A.W. and F32AR056174 to L.-Y.H.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.B.A.-Y. did most of the experiments and wrote the paper; S.E.L. did the initial characterization of Zap70(AS) mice; N.K. designed the strategy for generating Zap70(AS) mice; D.A.C. assisted with the ICAM-1 adhesion assays and calcium-flux assays; L.-Y.H. helped with the Zap70(YYAA) Treg cell–suppression assay; K.M.S. and C.Z. provided advice and synthesized 3-MB-PP1; and A.W. directed the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–7 (PDF 2262 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Au-Yeung, B., Levin, S., Zhang, C. et al. A genetically selective inhibitor demonstrates a function for the kinase Zap70 in regulatory T cells independent of its catalytic activity. Nat Immunol 11, 1085–1092 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1955
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1955
This article is cited by
-
Rapid increase in transferrin receptor recycling promotes adhesion during T cell activation
BMC Biology (2022)
-
Altered thymic differentiation and modulation of arthritis by invariant NKT cells expressing mutant ZAP70
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Non-kinase targets of protein kinase inhibitors
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2017)
-
Recruitment of calcineurin to the TCR positively regulates T cell activation
Nature Immunology (2017)
-
T cell receptor signalling in the control of regulatory T cell differentiation and function
Nature Reviews Immunology (2016)