Abstract
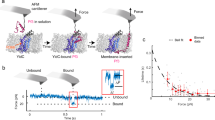
How chaperones, insertases and translocases facilitate insertion and folding of complex cytoplasmic proteins into cellular membranes is not fully understood. Here we utilize single-molecule force spectroscopy to observe YidC, a transmembrane chaperone and insertase, sculpting the folding trajectory of the polytopic α-helical membrane protein lactose permease (LacY). In the absence of YidC, unfolded LacY inserts individual structural segments into the membrane; however, misfolding dominates the process so that folding cannot be completed. YidC prevents LacY from misfolding by stabilizing the unfolded state from which LacY inserts structural segments stepwise into the membrane until folding is completed. During stepwise insertion, YidC and the membrane together stabilize the transient folds. Remarkably, the order of insertion of structural segments is stochastic, indicating that LacY can fold along variable pathways toward the native structure. Since YidC is essential in membrane protein biogenesis and LacY is a model for the major facilitator superfamily, our observations have general relevance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Driessen, A.J. & Nouwen, N. Protein translocation across the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 643–667 (2008).
Dalbey, R.E., Wang, P. & Kuhn, A. Assembly of bacterial inner membrane proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 80, 161–187 (2011).
Luirink, J., Yu, Z., Wagner, S. & de Gier, J.W. Biogenesis of inner membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1817, 965–976 (2012).
Stephenson, K. Sec-dependent protein translocation across biological membranes: evolutionary conservation of an essential protein transport pathway (review). Mol. Membr. Biol. 22, 17–28 (2005).
van Bloois, E. et al. The Sec-independent function of Escherichia coli YidC is evolutionary-conserved and essential. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 12996–13003 (2005).
Wang, P. & Dalbey, R.E. Inserting membrane proteins: the YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 machinery in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1808, 866–875 (2011).
Saller, M.J., Wu, Z.C., de Keyzer, J. & Driessen, A.J. The YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 protein family: common principles and distinct features. Biol. Chem. 393, 1279–1290 (2012).
Hartl, F.U., Bracher, A. & Hayer-Hartl, M. Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature 475, 324–332 (2011).
Engel, A. & Gaub, H.E. Structure and mechanics of membrane proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 127–148 (2008).
Kedrov, A., Janovjak, H., Ziegler, C., Kuhlbrandt, W. & Muller, D.J. Observing folding pathways and kinetics of a single sodium-proton antiporter from Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 355, 2–8 (2006).
Kessler, M., Gottschalk, K.E., Janovjak, H., Muller, D.J. & Gaub, H.E. Bacteriorhodopsin folds into the membrane against an external force. J. Mol. Biol. 357, 644–654 (2006).
Damaghi, M., Köster, S., Bippes, C.A., Yildiz, O. & Müller, D.J. One β hairpin follows the other: exploring refolding pathways and kinetics of the transmembrane β-barrel protein OmpG. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn Engl. 50, 7422–7424 (2011).
Bosshart, P.D. et al. The transmembrane protein KpOmpA anchoring the outer membrane of Klebsiella pneumoniae unfolds and refolds in response to tensile load. Structure 20, 121–127 (2012).
Bechtluft, P. et al. Direct observation of chaperone-induced changes in a protein folding pathway. Science 318, 1458–1461 (2007).
Kaiser, C.M. et al. Tracking UNC-45 chaperone-myosin interaction with a titin mechanical reporter. Biophys. J. 102, 2212–2219 (2012).
Nunes, J.M., Mayer-Hartl, M., Hartl, F.U. & Müller, D.J. Action of the Hsp70 chaperone system observed with single proteins. Nat. Commun. 6, 6307 (2015).
Thoma, J., Burmann, B.M., Hiller, S. & Müller, D.J. Impact of holdase chaperones Skp and SurA on the folding of β-barrel outer-membrane proteins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 22, 795–802 (2015).
Marger, M.D. & Saier, M.H. Jr. A major superfamily of transmembrane facilitators that catalyse uniport, symport and antiport. Trends Biochem. Sci. 18, 13–20 (1993).
Abramson, J. et al. Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Science 301, 610–615 (2003).
Guan, L., Mirza, O., Verner, G., Iwata, S. & Kaback, H.R. Structural determination of wild-type lactose permease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 15294–15298 (2007).
Nagamori, S., Smirnova, I.N. & Kaback, H.R. Role of YidC in folding of polytopic membrane proteins. J. Cell Biol. 165, 53–62 (2004).
Zhu, L., Kaback, H.R. & Dalbey, R.E. YidC protein, a molecular chaperone for LacY protein folding via the SecYEG protein machinery. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 28180–28194 (2013).
Serdiuk, T. et al. Substrate-induced changes in the structural properties of LacY. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, E1571–E1580 (2014).
Serdiuk, T., Sugihara, J., Mari, S.A., Kaback, H.R. & Müller, D.J. Observing a lipid-dependent alteration in single lactose permeases. Structure 23, 754–761 (2015).
Viitanen, P., Newman, M.J., Foster, D.L., Wilson, T.H. & Kaback, H.R. Purification, reconstitution, and characterization of the lac permease of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 125, 429–452 (1986).
Herzlinger, D., Viitanen, P., Carrasco, N. & Kaback, H.R. Monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. 2. Binding studies with membrane vesicles and proteoliposomes reconstituted with purified lac carrier protein. Biochemistry 23, 3688–3693 (1984).
Müller, D.J. & Engel, A. Atomic force microscopy and spectroscopy of native membrane proteins. Nat. Protoc. 2, 2191–2197 (2007).
Kedrov, A., Krieg, M., Ziegler, C., Kuhlbrandt, W. & Muller, D.J. Locating ligand binding and activation of a single antiporter. EMBO Rep. 6, 668–674 (2005).
Sapra, K.T., Besir, H., Oesterhelt, D. & Muller, D.J. Characterizing molecular interactions in different bacteriorhodopsin assemblies by single-molecule force spectroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 355, 640–650 (2006).
Ge, L., Perez, C., Waclawska, I., Ziegler, C. & Muller, D.J. Locating an extracellular K+-dependent interaction site that modulates betaine-binding of the Na+-coupled betaine symporter BetP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, E890–E898 (2011).
Bippes, C.A. et al. Peptide transporter DtpA has two alternate conformations, one of which is promoted by inhibitor binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, E3978–E3986 (2013).
Dowhan, W. & Bogdanov, M. Lipid-dependent membrane protein topogenesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 515–540 (2009).
Oesterhelt, F. et al. Unfolding pathways of individual bacteriorhodopsins. Science 288, 143–146 (2000).
Fanelli, F. & Seeber, M. Structural insights into retinitis pigmentosa from unfolding simulations of rhodopsin mutants. FASEB J. 24, 3196–3209 (2010).
Kappel, C. & Grubmüller, H. Velocity-dependent mechanical unfolding of bacteriorhodopsin is governed by a dynamic interaction network. Biophys. J. 100, 1109–1119 (2011).
Bibi, E. & Kaback, H.R. In vivo expression of the lacY gene in two segments leads to functional lac permease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 4325–4329 (1990).
Zen, K.H., McKenna, E., Bibi, E., Hardy, D. & Kaback, H.R. Expression of lactose permease in contiguous fragments as a probe for membrane-spanning domains. Biochemistry 33, 8198–8206 (1994).
Cymer, F., von Heijne, G. & White, S.H. Mechanisms of integral membrane protein insertion and folding. J. Mol. Biol. 427, 999–1022 (2015).
Müller, D.J. et al. Observing membrane protein diffusion at subnanometer resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 327, 925–930 (2003).
Bogdanov, M., Xie, J., Heacock, P. & Dowhan, W. To flip or not to flip: lipid-protein charge interactions are a determinant of final membrane protein topology. J. Cell Biol. 182, 925–935 (2008).
Guan, L. & Kaback, H.R. Properties of a LacY efflux mutant. Biochemistry 48, 9250–9255 (2009).
Bowie, J.U. Solving the membrane protein folding problem. Nature 438, 581–589 (2005).
Harris, N.J. & Booth, P.J. Folding and stability of membrane transport proteins in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1818, 1055–1066 (2012).
Engelman, D.M. et al. Membrane protein folding: beyond the two stage model. FEBS Lett. 555, 122–125 (2003).
Kumazaki, K. et al. Structural basis of Sec-independent membrane protein insertion by YidC. Nature 509, 516–520 (2014).
Shimokawa-Chiba, N. et al. Hydrophilic microenvironment required for the channel-independent insertase function of YidC protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 5063–5068 (2015).
Kumazaki, K. et al. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli YidC, a membrane protein chaperone and insertase. Sci. Rep. 4, 7299 (2014).
Rapoport, T.A., Goder, V., Heinrich, S.U. & Matlack, K.E. Membrane-protein integration and the role of the translocation channel. Trends Cell Biol. 14, 568–575 (2004).
Van Lehn, R.C., Zhang, B. & Miller, T.F., III. Regulation of multispanning membrane protein topology via post-translational annealing. eLife 4, e08697 (2015).
White, S.H. The messy process of guiding proteins into membranes. eLife 4, e12100 (2015).
Smirnova, I. et al. Sugar binding induces an outward facing conformation of LacY. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 16504–16509 (2007).
Bustamante, C., Marko, J.F., Siggia, E.D. & Smith, S. Entropic elasticity of lambda-phage DNA. Science 265, 1599–1600 (1994).
Kawamura, S. et al. Kinetic, energetic, and mechanical differences between dark-state rhodopsin and opsin. Structure 21, 426–437 (2013).
Acknowledgements
We thank R.E. Dalbey (The Ohio State University) for providing plasmid pT7-7 encoding YidC with a His10 tag at the C terminus; R. Newton, J. Thoma, S. Hiller and R.E. Dalbey for encouraging and constructive comments; and S. Weiser for assistance. This work was supported by the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich (to D.J.M.), the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant 205320_160199 to D.J.M.), the Swiss National Center of Competence in Research “NCCR Molecular Systems Engineering” (to D.J.M.), the European Union Marie Curie Actions program through the ACRITAS Initial Training Network (FP7-PEOPLE-2012-ITN, project 317348 to D.J.M.), U.S. National Institutes of Health grants DK51131, DK069463 and GM073210 (to H.R.K.), and U.S. National Science Foundation grant MCB-1129551 (to H.R.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.S., D.J.M. and H.R.K. designed the experiments. J.S. and D.B. cloned, expressed, purified and reconstituted LacY and YidC. T.S. performed the SMFS experiments. S.A.M. recorded AFM images. All authors analyzed experimental data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Results, Supplementary Figures 1–10 and Supplementary Tables 1–4. (PDF 1501 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serdiuk, T., Balasubramaniam, D., Sugihara, J. et al. YidC assists the stepwise and stochastic folding of membrane proteins. Nat Chem Biol 12, 911–917 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2169
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2169
This article is cited by
-
Evolutionary balance between foldability and functionality of a glucose transporter
Nature Chemical Biology (2022)
-
Towards a Quantitative Understanding of Protein–Lipid Bilayer Interactions at the Single Molecule Level: Opportunities and Challenges
The Journal of Membrane Biology (2021)
-
The Role of a Crystallographically Unresolved Cytoplasmic Loop in Stabilizing the Bacterial Membrane Insertase YidC2
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
The WRB Subunit of the Get3 Receptor is Required for the Correct Integration of its Partner CAML into the ER
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Structural Basis of the Sec Translocon and YidC Revealed Through X-ray Crystallography
The Protein Journal (2019)