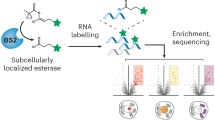
Abstract
Probes that form covalent bonds with RNA molecules on the basis of their chemical reactivity would advance our ability to study the transcriptome. We developed a set of electrophilic activity-based RNA probes designed to react with unusually nucleophilic RNAs. We used these probes to identify reactive genome-encoded RNAs, resulting in the discovery of a 42-nt catalytic RNA from an archaebacterium that reacts with a 2,3-disubstituted epoxide at N7 of a specific guanosine. Detailed characterization of the catalytic RNA revealed the structural requirements for reactivity. We developed this catalytic RNA into a general tool to selectively conjugate a small molecule to an RNA of interest. This strategy enabled up to 500-fold enrichment of target RNA from total mammalian RNA or from cell lysate. We demonstrated the utility of this approach by selectively capturing proteins in yeast cell lysate that bind the ASH1 mRNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Djebali, S. et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 489, 101–108 (2012).
Kowtoniuk, W.E. et al. A chemical screen for biological small molecule–RNA conjugates reveals CoA-linked RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 7768–7773 (2009).
Dumelin, C.E., Chen, Y., Leconte, A.M., Chen, Y.G. & Liu, D.R. Discovery and biological characterization of geranylated RNA in bacteria. Nat. Chem. Biol. 8, 913–919 (2012).
Doudna, J.A. & Cech, T.R. The chemical repertoire of natural ribozymes. Nature 418, 222–228 (2002).
Fedor, M.J. & Williamson, J.R. The catalytic diversity of RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 399–412 (2005).
Joyce, G.F. Forty years of in vitro evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 46, 6420–6436 (2007).
Cravatt, B.F., Wright, A.T. & Kozarich, J.W. Activity-based protein profiling: from enzyme chemistry to proteomic chemistry. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 383–414 (2008).
Sadaghiani, A.M., Verhelst, S.H. & Bogyo, M. Tagging and detection strategies for activity–based proteomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 11, 20–28 (2007).
Hinner, M.J. & Johnsson, K. How to obtain labeled proteins and what to do with them. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 21, 766–776 (2010).
Jing, C. & Cornish, V.W. Chemical tags for labeling proteins inside living cells. Acc. Chem. Res. 44, 784–792 (2011).
Low, J.T. & Weeks, K.M. SHAPE-directed RNA secondary structure prediction. Methods 52, 150–158 (2010).
Baruah, H., Puthenveetil, S., Choi, Y.A., Shah, S. & Ting, A.Y. An engineered aryl azide ligase for site-specific mapping of protein–protein interactions through photo–cross–linking. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 47, 7018–7021 (2008).
Rutkowska, A., Haering, C.H. & Schultz, C. A FlAsH–based cross-linker to study protein interactions in living cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 50, 12655–12658 (2011).
Chidley, C., Haruki, H., Pedersen, M.G., Muller, E. & Johnsson, K. A yeast-based screen reveals that sulfasalazine inhibits tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7, 375–383 (2011).
Ameta, S. & Jäschke, A. An RNA catalyst that reacts with a mechanistic inhibitor of serine proteases. Chem. Sci. 4, 957–964 (2013).
Sharma, A.K. et al. Fluorescent RNA labeling using self-alkylating ribozymes. ACS. Chem. Biol. 2014, 1680–1684 (2014).
Armitage, B.A. Imaging of RNA in live cells. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 15, 806–812 (2011).
Baker, M. RNA imaging in situ. Nat. Methods 9, 787–790 (2012).
Walker, S.C., Scott, F.H., Srisawat, C. & Engelke, D.R. RNA affinity tags for the rapid purification and investigation of RNAs and RNA-protein complexes. Methods Mol. Biol. 488, 23–40 (2008).
McHugh, C.A., Russell, P. & Guttman, M. Methods for comprehensive experimental identification of RNA-protein interactions. Genome Biol. 15, 203–212 (2014).
Doudna, J.A. & Lorsch, J.R. Ribozyme catalysis: not different, just worse. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12, 395–402 (2005).
Lilley, D.M.J. & Eckstein, F. Ribozymes and RNA Catalysis (RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2008).
Chen, Y.G., Kowtoniuk, W.E., Agarwal, I., Shen, Y. & Liu, D.R. LC/MS analysis of cellular RNA reveals NAD-linked RNA. Nat. Chem. Biol. 5, 879–881 (2009).
Thomas, J.M. & Perrin, D.M. Active site labeling of G8 in the hairpin ribozyme: implications for structure and mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 16540–16545 (2006).
Weerapana, E., Simon, G.M. & Cravatt, B.F. Disparate proteome reactivity profiles of carbon electrophiles. Nat. Chem. Biol. 4, 405–407 (2008).
Barglow, K.T. & Cravatt, B.F. Discovering disease-associated enzymes by proteome reactivity profiling. Chem. Biol. 11, 1523–1531 (2004).
Simon, G.M. & Cravatt, B.F. Activity-based proteomics of enzyme superfamilies: serine hydrolases as a case study. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 11051–11055 (2010).
Kawarabayasi, Y. et al. Complete genome sequence of an aerobic hyper-thermophilic crenarchaeon, Aeropyrum pernix K1. DNA Res. 6, 83–101 (1999).
Lee, N., Bessho, Y., Wei, K., Szostak, J.W. & Suga, H. Ribozyme-catalyzed tRNA aminoacylation. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7, 28–33 (2000).
Sengle, G. et al. Novel RNA catalysts for the Michael reaction. Chem. Biol. 8, 459–473 (2001).
Fusz, S., Eisenführ, A., Srivatsan, S.G., Heckel, A. & Famulok, M. A ribozyme for the aldol reaction. Chem. Biol. 12, 941–950 (2005).
Saran, D., Nickens, D.G. & Burke, D.H. A trans acting ribozyme that phosphorylates exogenous RNA. Biochemistry 44, 15007–15016 (2005).
Boysen, G., Pachkowski, B.F., Nakamura, J. & Swenberg, J.A. The formation and biological significance of N7-guanine adducts. Mutat. Res. 678, 76–94 (2009).
Hansen, M.R. & Hurley, L.H. Old drugs having modern friends in structural biology. Acc. Chem. Res. 29, 249–258 (1996).
Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3406–3415 (2003).
Machanick, P. & Bailey, T.L. MEME-ChIP: motif analysis of large DNA datasets. Bioinformatics 27, 1696–1697 (2011).
Bao, G., Rhee, W.J. & Tsourkas, A. Fluorescent probes for live-cell RNA detection. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 11, 25–47 (2009).
Jao, C.Y. & Salic, A. Exploring RNA transcription and turnover in vivo by using click chemistry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 15779–15784 (2008).
Trcek, T., Larson, D.R., Moldón, A., Query, C.C. & Singer, R.H. Single molecule mRNA decay measurements reveal promoter-regulated mRNA stability in yeast. Cell 147, 1484–1497 (2011).
Rabani, M. et al. Metabolic labeling of RNA uncovers principles of RNA production and degradation dynamics in mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 436–442 (2011).
Cosma, M.P. Daughter-specific repression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae HO: Ash1 is the commander. EMBO Rep. 5, 953–957 (2004).
Langer, P.R., Waldrop, A.A. & Ward, D.C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 6633–6637 (1981).
Curtis, E.A. & Liu, D.R. Discovery of widespread GTP-binding motifs in genomic DNA and RNA. Chem. Biol. 20, 521–532 (2013).
Tretyakova, N.Y., Sangaiah, R., Yen, T.Y. & Swenberg, J.A. Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro quantitation of N-7-guanine adducts of diepoxybutane. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 10, 779–785 (1997).
Ponchon, L. & Dardel, F. Recombinant RNA technology: the tRNA scaffold. Nat. Methods 4, 571–576 (2007).
Paul, C.P. et al. Localized expression of small RNA inhibitors in human cells. Mol. Ther. 7, 237–247 (2003).
Paige, J.S., Wu, K.Y. & Jaffrey, S.R. RNA mimics of green fluorescent protein. Science 333, 642–646 (2011).
Ghaemmaghami, S. et al. Global analysis of protein expression in yeast. Nature 425, 737–741 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health (NIH)/ National Institute of General Medical Sciences R01 GM065865 and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. R.I.M. and S.M. were supported by a NIH National Research Service Award Postdoctoral Fellowship (F32GM099359 and F32GM101751). We thank L. Goff for assistance with bioinformatics analysis, D. Engelke (University of Michigan, Ann Arbor) for providing the 5S rRNA plasmid and E. Weerapana (Boston College) for providing the fluorophosphonate probe. We are also grateful to C. Dumelin, A. Leconte, L. McGregor, D. Thompson and D. Usanov for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.I.M. designed the research, prepared materials and performed experiments. J.P.G. and S.M. prepared materials and performed research. E.A.C. and W.I.L. prepared materials. D.R.L. designed and supervised the research. R.I.M. and D.R.L. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Results, Supplementary Figures 1–15, Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 and Supplementary Note. (PDF 5739 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDonald, R., Guilinger, J., Mukherji, S. et al. Electrophilic activity-based RNA probes reveal a self-alkylating RNA for RNA labeling. Nat Chem Biol 10, 1049–1054 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1655
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1655
This article is cited by
-
A SAM analogue-utilizing ribozyme for site-specific RNA alkylation in living cells
Nature Chemistry (2023)
-
Structural basis for substrate binding and catalysis by a self-alkylating ribozyme
Nature Chemical Biology (2022)
-
Total RNA Synthesis and its Covalent Labeling Innovation
Topics in Current Chemistry (2022)
-
Programmable site-selective labeling of oligonucleotides based on carbene catalysis
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Site-specific RNA methylation by a methyltransferase ribozyme
Nature (2020)