Abstract
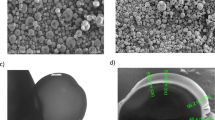
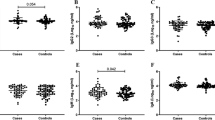
Immunity at mucosal surfaces, which are ports of entry for many pathogens, is essential in preventing infections. But most current strategies for passive immunization involve injection of antibodies for systemic, not mucosal, protection. We measured mucosal and systemic antibody levels after controlled topical delivery to the vagina. Poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) disks containing 125l-labeled monoclonal IgG or anti-lactate dehydrogenase-C4 antibodies were placed in the vaginas of mice. High antibody levels (0.26–12 μg/ml) were maintained at the mucosal surface for 7 days after disk insertion. Antibody molecules also penetrated into the vaginal epithelium, presumably by diffusing through the extracellular space, and entered the circulation. Biologically active antibodies were detected in the blood. The antibody concentration in the blood was approximately 1% of the concentration in the vagina. Although the permeability of the epithelium to macro-molecules is low, high concentrations were maintained at the luminal surface for an extended period, permitting substantial systemic uptake of antibody.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, J.K.-C. and Lehner, T. 1990. Prevention of colonization of Streptococcus mutans by topical application of monoclonal antibodies in human subjects. Arch. Oral Biol. 36:1158–1228
Tacket, C.O., Losonsky, G., Link, H., Hoang, Y, Guesry, P., Hilpert, H., and Levine, M.M. 1988.Protection by milk immunoglobulin concentrate against oral challenge with enterotoxigenic E. Co//. N. Eng. J. Med. 318:1240–1243
Whaley, K.J., Zeitlin, L.R., Barratt, R.A., Hoen, T.E., and Cone, R.A. 1994. Passive immunization of the vagina protects mice against vaginal transmission of genital herpes infections. J. Infect. Dis. 118:647–649
SherwoodV, J.K., ZeitlinV, L, Whaley, K.J., Cone, R.A., and Saltzman, W.M. 1996. Controlled release of antibodies for long-term topical passive immunoprotection of female mice against genital herpes. Bio/Technology 14:468–471
Castle, RE., Whaley, K.J., Hoen, I.E., Moench, T.R., and Cone, R.A. 1997. Contraceptive effect of sperm-agglutinating monoclonal antibodies in rabbits. Biol. Reprod. 56:153–159
Cone, R.A. and Whaley, K.J. 1994. Monoclonal antibodies for reproductive health: part I. Preventing sexual transmission of disease and pregnancy with topically applied antibodies. Am. J. Rephd. Immunol. 31:1–18
Saltzman, W.M. 1993. Antibodies for treating and preventing disease: the potential role of polymeric controlled release. Crit Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Sys. 10:111–142
Benziger, D. and Edelson, J. 1983. Absorption from the vagina. Drug Metabol. Rev. 14:137–168.
Okada, H. 1991. Vaginal route of peptide and protein drug delivery, pp. 633-666 in Peptide and protein drug delivery. Lee, V.H. (ed), Marcel Dekker, New York.
Schiff, I., Tulchinsky, D., and Ryan, K. 1977. Vaginal absorption of estrone and 17β-estradiol. Fertil. Steril. 28:1063–1066.
Apter, D., Cacciatore, B., Stenman, U. Alapiessa, U., and Assendorp, R. 1990. Clinical performance and endocrine profiles of contraceptive vaginal rings releasing 3-keto-desogestrel and ethinytestradiol. Contraception 42:285–295
Olsson, S. and Odlind, V. 1990. Contraception with vaginal ring releasing 3-keto-desogestrel and ethinylestradiol. Contraception 42:563–572
Schiff, I., Wentworth, B., Koos, B., Ryan, K., and Tulchinsky,D. 1978. Effect of estriol administration on the hypogonadal woman. Fertil. Steril. 30:278–282
Schiff, I., Tulchinsky, D., Ryan, K., Kadner, S., and Levitz,M.. 1980. Plasma estriol and its conjugates following oral and vaginal administration of estriol to postmenopausal women: Correlations with gonadotropin levels. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 138:1137–1141
Beck, L., Boots, L., and Stevens, V. 1975. Absorption of antibodies from the baboon vagina. Biol. Reprod. 13:10–16.
Sherwood, J.K., Zeitlin, L, Chen, X., Whaley, K.J., Cone, R.A., and Saltzman, W.M . 1996. Residence half-life of IgG administered topically to the mouse vagina. Biol. Reprod. 54:264–269
Radomsky, M.L, Whaley, K.J., Cone, R.A., and Saltzman, W.M. 1992. Controlled vaginal delivery of antibodies in the mouse. Biol. Reprod. 47:133–140
O'Hern, PA, Bambra, C.S., Isahakia, M., and Goldberg, E. 1995. Reversible contraception in female baboons immunized with a synthetic epitope of sperm-specific lactate dehydrogenase. Biol. Reprod. 52:331–339
Saltzman, W.M. and Langer, R. 1989. Transport rates of proteins in porous polymers with known microgeometry. Biophys. J. 55:163–171
Sherwood, J.K. Long-term delwery of antibodies using controlled release polymers. (Ph.D. dissertation, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, 1996
Kuo,P.Y-R Enhancing antibody availability at the vaginal mucosa with controlled-release polymers. (Master's thesis, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD,1996
Kuo,P.Y.P and Saltzman, W.M. 1996. Novel systems for controlled delivery of macromolecules. Crit. Rev. Euk Gene Expr. 6:59–73.
Parr,M.B. and Parr, E.L. 1994. Mucosal immunity in the female and male reproductive tracts. 677–689 Handbook of mucosal immunology. Ogra, PL., Mestecky, J., Lamm, M.E., Strober, W, McGhee, J.R., and Bienenstock, J. (eds.), Academic Press, Inc., San Diego
Wira,C.R ., Richardson, J., and Prabhala, R. 1994. Endocrine regulation of mucosal immunity: effect of sex hormones and cytokines on the afferent and efferent arms of the immune system in the female reproductive tract, 705–718 in Handbook of mucosal immunology. Ogra, RL, Mestecky, J., Lamm, M.E., Strober, W., McGhee, J.R., and Bienenstock, J. (eds.), Academic Press, Inc., San Diego.
Snell,G.D. 1941. Reproduction. 55–88 in Biology of the laboratory mouse Snell, G.D. (ed.), Blakiston Company, Philadelphia.
Gude,W.D., Cosgrove, G.E., and Hirsch, G.P. 1982. Histological atlas of the laboratory mouse. Plenum Press, New York.
Sherwood,J.K. Controlled release of antibodies and antibody fragments for immunoprotection of the mucus epithelia. (Master's thesis, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, 1993).
Clauss,M.A. and Jain, R.K. 1990. Interstitial transport of rabbit and sheep antibodies in normal and neoplastic tissues. Cancer Res. 50:3487–3492
Baxter,L.T., Zhu, H., Mackensun, D.G., and Jain, R.K. 1994. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for specific and nonspecific monoclonal antibodies and fragments in normal tissues and human tumor xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Res. 54:1517–1528.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, P., Sherwood, J. & Saltzman, W. Topical antibody delivery systems produce sustained levels in mucosal tissue and blood. Nat Biotechnol 16, 163–167 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0298-163
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0298-163
This article is cited by
-
Clinical trial considerations on male contraception and collection of pregnancy information from female partner: update
Clinical and Translational Medicine (2016)
-
Protein and oligonucleotide delivery systems for vaginal microbicides against viral STIs
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2015)
-
Clinical trial considerations on male contraception and collection of pregnancy information from female partners
Journal of Translational Medicine (2012)
-
Building drug delivery into tissue engineering design
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2002)