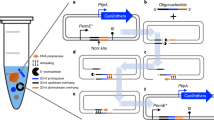
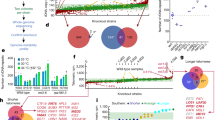
Abstract
We developed a CRISPR–Cas9- and homology-directed-repair-assisted genome-scale engineering method named CHAnGE that can rapidly output tens of thousands of specific genetic variants in yeast. More than 98% of target sequences were efficiently edited with an average frequency of 82%. We validate the single-nucleotide resolution genome-editing capability of this technology by creating a genome-wide gene disruption collection and apply our method to improve tolerance to growth inhibitors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Wang, H.H. et al. Nature 460, 894–898 (2009).
Warner, J.R., Reeder, P.J., Karimpour-Fard, A., Woodruff, L.B. & Gill, R.T. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 856–862 (2010).
Garst, A.D. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 35, 48–55 (2017).
Barbieri, E.M., Muir, P., Akhuetie-Oni, B.O., Yellman, C.M. & Isaacs, F.J. Cell 171, 1453–1467.e13 (2017).
Bao, Z. et al. ACS Synth. Biol. 4, 585–594 (2015).
Cong, L. et al. Science 339, 819–823 (2013).
Wang, T., Wei, J.J., Sabatini, D.M. & Lander, E.S. Science 343, 80–84 (2014).
Xiao, H. & Zhao, H. Biotechnol. Biofuels 7, 78 (2014).
Sandoval, N.R. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 10540–10545 (2012).
Streich, F.C. Jr. & Lima, C.D. Nature 536, 304–308 (2016).
Yunus, A.A. & Lima, C.D. Mol. Cell 35, 669–682 (2009).
Kim, H. & Kim, J.S. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15, 321–334 (2014).
Naito, Y., Hino, K., Bono, H. & Ui-Tei, K. Bioinformatics 31, 1120–1123 (2015).
Gietz, R.D. & Schiestl, R.H. Nat. Protoc. 2, 31–34 (2007).
Hegemann, J.H. & Heick, S.B. Methods Mol. Biol. 765, 189–206 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and the US Department of Energy (DE-SC0018260). We thank A. Hernandez and C. Wright for assistance with next-generation sequencing, J. Zadeh for assistance with NGS data processing and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.B. and H.Z. conceived this project. Z.B., M.H., and H.X. designed the CHAnGE cassettes. R.C. and J.L. generated the ORF list and all possible guide sequences. M.H. sorted and selected the guide and homology arm sequences. Z.B., P.X., and I.T. performed the experiments. Z.B. analyzed the data. H.Z. supervised the research. Z.B. and H.Z. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
A patent application has been filed on this technology, on which H.Z. and Z.B. are authors.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Notes 1 and 2, Supplementary Figures 1–18, and Supplementary Tables 1, 2, 4, 5, 7. (PDF 3306 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
A summary of 24865 CHAnGE cassette sequences. (XLS 7358 kb)
Supplementary Table 6
A summary of 580 SIZ1 CHAnGE cassette sequences. (XLSX 87 kb)
Supplementary Code
Supplementary Code (PDF 35 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, Z., HamediRad, M., Xue, P. et al. Genome-scale engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with single-nucleotide precision. Nat Biotechnol 36, 505–508 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4132
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4132
This article is cited by
-
High throughput mutagenesis and screening for yeast engineering
Journal of Biological Engineering (2022)
-
High-content CRISPR screening
Nature Reviews Methods Primers (2022)
-
Applications of CRISPR/Cas gene-editing technology in yeast and fungi
Archives of Microbiology (2022)
-
How adaptive laboratory evolution can boost yeast tolerance to lignocellulosic hydrolyses
Current Genetics (2022)
-
Recent advances in construction and regulation of yeast cell factories
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology (2022)