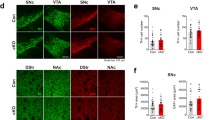
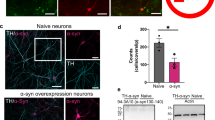
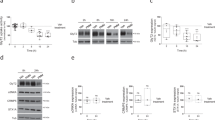
Abstract
Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) is a trophic factor that has an essential role in the nervous system by modulating neurodevelopment, neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity. Despite the evidence that NRG1 and its receptors, ErbB tyrosine kinases, are expressed in mesencephalic dopaminergic nuclei and their functional alterations are reported in schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease, the role of NRG1/ErbB signalling in dopaminergic neurons remains unclear. Here we found that NRG1 selectively increases the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1)-activated currents by inducing synthesis and trafficking to membrane of functional receptors and stimulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K-Akt-mTOR) pathway, which is required for mGluR1 function. Notably, an endogenous NRG1/ErbB tone is necessary to maintain mGluR1 function, by preserving its surface membrane expression in dopaminergic neurons. Consequently, it enables striatal mGluR1-induced dopamine outflow in in vivo conditions. Our results identify a novel role of NRG1 in the dopaminergic neurons, whose functional alteration might contribute to devastating diseases, such as schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burden S, Yarden Y . Neuregulins and their receptors: a versatile signaling module in organogenesis and oncogenesis. Neuron 1997; 18: 847–855.
Buonanno A, Fischbach GD . Neuregulin and ErbB receptor signaling pathways in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2001; 11: 287–296.
Falls DL . Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signalling strategies. Exp. Cell Res 2003; 284: 14–30.
Mei L, Xiong WC . Neuregulin 1 in neural development, synaptic plasticity and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci 2008; 9: 437–452.
Iwakura Y, Nawa H . ErbB1-4 dependent EGF/neuregulin signals and their crosstalk in the central nervous system: pathological implications in schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 2013; 7: 1–13.
Steiner H, Blum M, Kitai ST, Fedi P . Differential expression of ErbB3 and ErbB4 neuregulin receptors in dopamine neurons and forebrain areas of the adult rat. Exp Neurol 1999; 159: 494–503.
Kerber G, Streif R, Schwaiger FW, Kreutzberg GW, Hager G . Neuregulin-1 isoforms are differentially expressed in the intact and regenerating adult rat nervous system. J Mol Neurosci 2003; 21: 149–165.
Law AJ, Shannon Weickert C, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Harrison PJ . Neuregulin-1 (NRG-1) mRNA and protein in the adult human brain. Neuroscience 2004; 127: 125–136.
Abe Y, Namba H, Zheng Y, Nawa H . In situ hybridization reveals developmental regulation of ErbB1-4 mRNA expression in mouse midbrain: implication of ErbB receptors for dopaminergic neurons. Neuroscience 2009; 161: 95–110.
Stefansson H, Sigurdsson E, Steinthorsdottir V, Bjornsdottir S, Sigmundsson T, Ghosh S et al. Neuregulin 1 and susceptibility to schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 877–892.
Yang JZ, Si TM, Ruan Y, Ling YS, Han YH, Wang XL et al. Association study of neuregulin 1 gene with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2003; 8: 706–709.
Munafo’ MR, Thiselton DL, Clark TG, Flint J . Association of the NRG1 gene and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 2006; 11: 539–546.
Shi J, Levinson DF, Duan J, Sanders AR, Zheng Y, Pe'er I et al. Common variants on chromosome 6p22.1 are associated with schizophrenia. Nature 2009; 460: 753–757.
Hashimoto R, Straub RE, Weickert CS, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR . Expression analysis of neuregulin-1 in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 299–307.
Petryshen TL, Middleton FA, Kirby A, Aldinger KA, Purcell S, Tahl AR et al. Support for involvement of neuregulin 1 in schizophrenia pathophysiology. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 366–374.
Law AJ, Lipska BK, Weickert CS, Hyde TM, Straub RE, Hashimoto R et al. Neuregulin 1 transcripts are differentially expressed in schizophrenia and regulated by 5' SNPs associated with the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 6747–6752.
Hahn CG, Wang HY, Cho DS, Talbot K, Gur RE, Berrettini WH et al. Altered neuregulin 1-erbB4 signaling contributes to NMDA receptor hypofunction in schizophrenia. Nat Med 2006; 12: 824–828.
du Bois TM, Newell KA, Huang XF . Perinatal phencyclidine treatment alters neuregulin 1/erbB4 expression and activation in later life. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2012; 22: 356–363.
Radonjić NV, Jakovcevski I, Bumbaširević V, Petronijević ND . Perinatal phencyclidine administration decreases the density of cortical interneurons and increases the expression of neuregulin-1. Psycopharmacology 2013; 227: 673–683.
Gerlai R, Pisacane P, Erickson S . Heregulin, but not ErbB2 or ErbB3, heterozygous mutant mice exhibit hyperactivity in multiple behavioral tasks. Behav Brain Res 2000; 109: 219–227.
Golub MS, Germann SL, Lloyd KC . Behavioral characteristics of a nervous system-specific erbB4 knock-out mouse. Behav Brain Res 2004; 153: 159–170.
Deakin IH, Law AJ, Oliver PL, Schwab MH, Nave KA, Harrison PJ, Bannerman DM . Behavioural characterization of neuregulin 1 type I overexpressing transgenic mice. Neuroreport 2009; 20: 1523–1528.
Deakin IH, Nissen W, Law AJ, Lane T, Kanso R, Schwab MH et al. Transgenic overexpression of the type I isoform of neuregulin 1 affects working memory and hippocampal oscillations but not long-term potentiation. Cereb Cortex 2012; 22: 1520–1529.
Kato T, Kasai A, Mizuno M, Fengyi L, Shintani N, Maeda S et al. Phenotypic characterization of transgenic mice overexpressing neuregulin-1. PLoS One 2010; 5: 1–13.
Yin DM, Chen YJ, Lu YS, Bean JC, Sathyamurthy A, Shen C et al. Reversal of behavioral deficits and synaptic dysfunction in mice overexpressing neuregulin 1. Neuron 2013; 78: 644–657.
Zhang L, Fletcher-Turner A, Marchionni MA, Apparsundaram S, Lundgren KH, Yurek DM et al. Neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects of the neuregulin glial growth factor-2 on dopaminergic neurons in rat primary midbrain cultures. J Neurochem 2004; 91: 1358–1368.
Carlsson T, Schindler FR, Höllerhage M, Depboylu C, Arias-Carrión O, Schnurrbusch S et al. Systemic administration of neuregulin-1β1 protects dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 2011; 117: 1066–1074.
Depboylu C, Höllerhage M, Schnurrbusch S, Brundin P, Oertel WH, Schrattenholz A et al. Neuregulin-1 receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 is upregulated in midbrain dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson disease. Neurosci Lett 2012; 531: 209–214.
Kato T, Abe Y, Sotoyama H, Kakita A, Kominami R, Hirokawa S et al. Transient exposure of neonatal mice to neuregulin-1 results in hyperdopaminergic states in adulthood: implication in neurodevelopmental hypothesis for schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2011; 16: 307–320.
Newell KA, Karl T, Huang XF . A neuregulin 1 transmembrane domain mutation causes imbalanced glutamatergic and dopaminergic receptor expression in mice. Neuroscience 2013; 248: 670–680.
Yurek DM, Zhang L, Fletcher-Turner A, Seroogy KB . Supranigral injection of neuregulin1-beta induces striatal dopamine overflow. Brain Res 2004; 1028: 116–119.
Kwon OB, Paredes D, Gonzalez CM, Neddens J, Hernandez L, Vullhorst D et al. Neuregulin-1 regulates LTP at CA1 hippocampal synapses through activation of dopamine D4 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 15587–15592.
Tansey MG, Chu GC, Merlie JP . ARIA/HRG regulates AChR epsilon subunit gene expression at the neuromuscular synapse via activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Ras/MAPK pathway. J Cell Biol 1996; 134: 465–476.
Ozaki M, Sasner M, Yano R, Lu HS, Buonanno A . Neuregulin-beta induces expression of an NMDA-receptor subunit. Nature 1997; 390: 691–694.
Rieff HI, Raetzman LT, Sapp DW, Yeh HH, Siegel RE, Corfas G . et al. Neuregulin induces GABAA receptor subunit expression and neurite outgrowth in cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 10757–10766.
Okada M, Corfas G . Neuregulin 1 downregulates postsynaptic GABAA receptors at the hippocampal inhibitory synapse. Hippocampus 2004; 14: 337–344.
Gu Z, Jiang Q, Fu AKY, Ip NY, Yan Z . Regulation of NMDA receptors by neuregulin signaling in prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 4974–4984.
Abe Y, Namba H, Kato T, Iwakura Y, Nawa H . Neuregulin-1 signals from the periphery regulate AMPA receptor sensitivity and expression in GABAergic interneurons in developing neocortex. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 5699–5709.
Li B, Woo RS, Mei L, Malinow R . The neuregulin-1 receptor erbB4 controls glutamatergic synapse maturation and plasticity. Neuron 2007; 54: 583–597.
Schapansky J, Morissette M, Odero G, Albensi B, Glazner G . Neuregulin beta1 enhances peak glutamate-induced intracellular calcium levels through endoplasmic reticulum calcium release in cultured hippocampal neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2009; 87: 883–891.
Guatteo E, Mercuri NB, Bernardi G, Knöpfel T . Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors mediate an inward current in rat substantianigra dopamine neurons that is independent from calcium mobilization. J Neurophysiol 1999; 82: 1974–1981.
Tozzi A, Bengtson CP, Longone P, Carignani C, Fusco FR, Bernardi G et al. Involvement of transient receptor potential-like channels in responses to mGluR-I activation in midbrain dopamine neurons. Eur J Neurosci 2003; 18: 2133–2145.
Prisco S, Natoli S, Bernardi G, Mercuri NB . Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors activate burst firing in rat midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Neuropharmacology 2002; 42: 289–296.
Renoldi G, Calcagno E, Borsini F, Invernizzi RW . Stimulation of group I mGlu receptors in the ventrotegmental area enhances extracellular dopamine in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurochem 2007; 100: 1658–1666.
Catania MV, D'Antoni S, Bonaccorso CM, Aronica E, Bear MF, Nicoletti F et al. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors: a role in neurodevelopmental disorders? Mol Neurobiol 2007; 35: 298–307.
Aiba A, Kano M, Chen C, Stanton ME, Fox GD, Herrup K et al. Deficient cerebellar long-term depression and impaired motor learning in mGluR1 mutant mice. Cell 1994; 79: 377–388.
Aiba A, Chen C, Herrup K, Rosenmund C, Stevens CF, Tonegawa S . (1994). Reduced hippocampal long-term potentiation and context-specific deficit in associative learning in mGluR1 mutant mice. Cell 1994; 79: 365–375.
Lüscher C, Huber KM . Group 1 mGluR-dependent synaptic long-term depression (mGluR-LTD): mechanisms and implications for circuitry & disease. Neuron 2010; 65: 445–459.
Ferraguti F, Crepaldi L, Nicoletti F . Metabotropic glutamate 1 receptor: current concepts and perspectives. Pharmacol Rev 2008; 60: 536–581.
Mercuri NB, Bonci A, Calabresi P, Stefani A, Bernardi G . Properties of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current Ih in rat midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 1995; 7: 462–469.
Gladding CM, Collett VJ, Jia Z, Bashir ZI, Collingridge GL, Molnár E et al. Tyrosine dephosphorylation regulates AMPAR internalisation in mGluR-LTD. Mol Cell Neurosci 2009; 40: 267–279.
Paxison G, Watson C . The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 5th edn. Academic Press, 2005.
Federici M, Latagliata EC, Ledonne A, Rizzo FR, Feligioni M, Sulzer D et al. Paradoxical abatement of striatal dopaminergic transmission by cocaine and methylphenidate. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 264–274.
Schoepp DD, Goldsworthy J, Johnson BG, Salhoff CR, Baker SR . 3,5-Dihydroxyphenylglycine is a highly selective agonist for phosphoinositide-linked metabotropic glutamate receptors in the rat hippocampus. J Neurochem 1994; 63: 769–772.
Shimizu S, Wakamori M, Maeda A, Kurosaki T, Takada N et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel receptor-activated TRP Ca2+ channel from mouse brain. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 10279–10287.
Subramony P, Dryer SE . Neuregulins stimulate the functional expression of Ca21-activated K1 channels in developing chicken parasympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 5934–5938.
Canetta SE, Luca E, Pertot E, Role LW, Talmage DA . Type III Nrg1 back signaling enhances functional TRPV1 along sensory axons contributing to basal and inflammatory thermal pain sensation. PLoS One 2011; 6: 1–16.
Yao JJ, Sun J, Zhao QR, Wang CY, Mei YA . Neuregulin-1 /ErbB4 signaling regulates Kv4.2-mediated transient 2 outward K+ current through the Akt/mTOR pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2013; 305: 197–206.
Magalhaes AC, Dunn H, Ferguson SS . Regulation of GPCR activity, trafficking and localization by GPCR-interacting proteins. Br J Pharmacol 2012; 165: 1717–1736.
Mundell SJ, Matharu AL, Pula G, Roberts PJ, Kelly E . Agonist-induced internalization of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1a is arrestin- and dynamin-dependent. J Neurochem 2001; 78: 546–551.
Dhami GK, Ferguson SS . Regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling, desensitization and endocytosis. Pharmacol Ther 2006; 111: 260–271.
Dale LB, Bhattacharya M, Seachrist JL, Anborgh PH, Ferguson SS . Agonist-stimulated and tonic internalization of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1a in human embryonic kidney 293 cells: agonist-stimulated endocytosis is beta-arrestin1 isoform-specific. Mol Pharmacol 2001; 60: 1243–1253.
Cenci MA . Dopamine dysregulation of movement control in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Trends Neurosci 2007; 30: 236–243.
Simpson EH, Kellendonk C, Kandel E . A possible role for the striatum in the pathogenesis of the cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Neuron 2010; 65: 585–596.
Swanson CJ, Kalivas PW . Regulation of locomotor activity by metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area. J Pharm Exp Ther 2000; 292: 406–414.
Hodgson RA, Hyde LA, Guthrie DH, Cohen-Williams ME, Leach PT, Kazdoba TM et al. Characterization of the selective mGluR1 antagonist, JNJ16259685, in rodent models of movement and coordination. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2011; 98: 181–187.
Balu DT, Coyle JT . Neuroplasticity signaling pathways linked to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2011; 35: 848–870.
Laruelle M, Kegeles LS, Abi-Dargham A . Glutamate, dopamine, and schizophrenia: from pathophysiology to treatment. Ann NY Acad Sci 2003; 1003: 138–158.
Perez-Costas E, Melendez-Ferro M, Roberts RC . Basal ganglia pathology in schizophrenia: dopamine connections and anomalies. J Neurochem 2010; 113: 287–302.
Perez-Costas E, Melendez-Ferro M, Rice MW, Conley RR, Roberts RC . Dopamine pathology in schizophrenia: analysis of total and phosphorylated tyrosine hydroxylase in the substantia nigra. Front Psychiatry 2012; 3: 1–14.
Yoon JH, Minzenberg MJ, Raouf S, D’Esposito M, Carter CS . Impaired prefrontal-basal ganglia functional connectivity and substantia nigra hyperactivity in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2013; 74: 122–129.
Heckers S, Konradi C . Substantia nigra hyperactivity in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2013; 74: 82–83.
Reid MA, Kraguljac NV, Avsar KB, White DM, den Hollander JA, Lahti AC . Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the substantia nigra in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2013; 147: 348–354.
Miyake N, Thompson J, Skinbjerg M, Abi-Dargham A . Presynaptic dopamine in schizophrenia. CNS Neurosci Ther 2011; 17: 104–109.
Lesage A, Steckler T . Metabotropic glutamate mGlu1 receptor stimulation and blockade: therapeutic opportunities in psychiatric illness. Eur J Pharmacol 2010; 639: 2–16.
Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N . Distribution of the mRNA for a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1) in the central nervous system: an in situ hybridization study in adult and developing rat. J Comp Neurol 1992; 322: 121–135.
Martin LJ, Blackstone CD, Huganir RL, Price DL . Cellular localization of a metabotropic glutamate receptor in rat brain. Neuron 1992; 9: 259–270.
Lavreysen H, Pereira SN, Leysen JE, Langlois X, Lesage AS . Metabotropic glutamate 1 receptor distribution and occupancy in the rat brain: a quantitative autoradiographic study using [3H]R214127. Neuropharmacology 2004; 46: 609–619.
Ayoub MA, Angelicheva D, Vile D, Chandler D, Morar B, Cavanaugh JA et al. Deleterious GRM1 mutations in schizophrenia. PLoS One 2012; 7: 1–8.
Gupta DS, McCullumsmith RE, Beneyto M, Haroutunian V, Davis KL, Meador-Woodruff JH . Metabotropic glutamate receptor protein expression in the prefrontal cortex and striatum in schizophrenia. Synapse 2005; 57: 123–131.
Volk DW, Egganm SM, Lewism DA . Alterations in metabotropic glutamate receptor 1α and regulator of G protein signaling 4 in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2010; 167: 1489–1498.
Brody SA, Conquet F, Geyer MA . Disruption of prepulse inhibition in mice lacking mGluR1. Eur J Neurosci 2003; 8: 2261–3366.
Selvaraj S, Sun Y, Watt JA, Wang S, Lei S, Birnbaumer L et al. Neurotoxin-induced ER stress in mouse dopaminergic neurons involves downregulation of TRPC1 and inhibition of AKT/mTOR signaling. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 1354–1367.
Acknowledgements
This work has been financed by Grants from the Minister of Health to NBM, Alzheimer’s Association (NIRG-11-204588) to MDA and the Italian Ministry of University and Research (PRIN 2009) to MDA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ledonne, A., Nobili, A., Latagliata, E. et al. Neuregulin 1 signalling modulates mGluR1 function in mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons. Mol Psychiatry 20, 959–973 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.109
This article is cited by
-
The laterodorsal tegmentum-ventral tegmental area circuit controls depression-like behaviors by activating ErbB4 in DA neurons
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
A new aspect on the correlation of ten SNPs in MIR and their target genes in dopaminergic pathways in schizophrenia
Bulletin of the National Research Centre (2022)
-
BACE1 controls synaptic function through modulating release of synaptic vesicles
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Neuregulin-2 ablation results in dopamine dysregulation and severe behavioral phenotypes relevant to psychiatric disorders
Molecular Psychiatry (2018)
-
ErbB4 signaling in dopaminergic axonal projections increases extracellular dopamine levels and regulates spatial/working memory behaviors
Molecular Psychiatry (2018)