Abstract
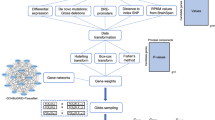
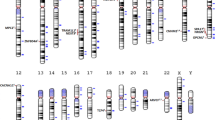
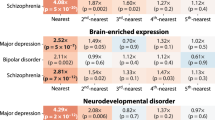
Schizophrenia is a major debilitating psychiatric disorder affecting ∼1% of the population worldwide. A tremendous amount of effort has been expended in the last two decades to identify genes influencing susceptibility to this disorder. Although there is a strong trend toward integrating data obtained from various genetic studies and their related biological information into a comprehensive resource for many complex diseases, we were unable to find such an effort for schizophrenia or for any other psychiatric disorder yet. In this study, we present Schizophrenia gene resource (SZGR), a comprehensive database with user-friendly web interface. SZGR deposits genetic data from all available sources, including those from association studies, linkage scans, gene expression, literature, gene ontology (GO) annotations, gene networks, cellular and regulatory pathways, as well as microRNAs and their target sites. Moreover, SZGR provides online tools for data browse and search, data integration, custom gene ranking and graphical presentation. This system can be easily applied to other complex diseases, especially to other psychiatric disorders. The SZGR database is available at http://bioinfo.mc.vanderbilt.edu/SZGR/.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Owen MJ, Craddock N, O’Donovan MC . Schizophrenia: genes at last? Trends Genet 2005; 21: 518–525.
Sullivan PF, Kendler KS, Neale MC . Schizophrenia as a complex trait: evidence from a meta-analysis of twin studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 1187–1192.
Burmeister M, McInnis MG, Zollner S . Psychiatric genetics: progress amid controversy. Nat Rev Genet 2008; 9: 527–540.
Konneker T, Barnes T, Furberg H, Losh M, Bulik CM, Sullivan PF . A searchable database of genetic evidence for psychiatric disorders. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2008; 147B: 671–675.
Allen NC, Bagade S, McQueen MB, Ioannidis JP, Kavvoura FK, Khoury MJ et al. Systematic meta-analyses and field synopsis of genetic association studies in schizophrenia: the SzGene database. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 827–834.
Sullivan PF, Lin D, Tzeng JY, van den Oord E, Perkins D, Stroup TS et al. Genomewide association for schizophrenia in the CATIE study: results of stage 1. Mol Psychiatry 2008; 13: 570–584.
Williams HJ, Owen MJ, O’Donovan MC . Schizophrenia genetics: new insights from new approaches. Br Med Bull 2009; 91: 61–74.
Purcell SM, Wray NR, Stone JL, Visscher PM, O’Donovan MC, Sullivan PF et al. Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature 2009; 460: 748–752.
Lewis CM, Levinson DF, Wise LH, DeLisi LE, Straub RE, Hovatta I et al. Genome scan meta-analysis of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, part II: Schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 34–48.
Ng MYM, Levinson DF, Faraone SV, Suarez BK, DeLisi LE, Arinami T et al. Meta-analysis of 32 genome-wide linkage studies of schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2009; 14: 774–785.
Higgs BW, Elashoff M, Richman S, Barci B . An online database for brain disease research. BMC Genomics 2006; 7: 70.
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 2000; 25: 25–29.
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M, Hirakawa M, Itoh M et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: D480–D484.
Zhou M, Zhuang YL, Xu Q, Li YD, Shen Y . VSD: a database for schizophrenia candidate genes focusing on variations. Hum Mutat 2004; 23: 1–7.
Sun J, Jia P, Fanous AH, Webb BT, van den Oord EJCG, Chen X et al. A multi-dimensional evidence-based candidate gene prioritization approach for complex diseases – schizophrenia as a case. Bioinformatics 2009; doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp428; published online 14 July 2009.
Sun J, Kuo PH, Riley BP, Kendler KS, Zhao Z . Candidate genes for schizophrenia: a survey of association studies and gene ranking. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2008; 147B: 1173–1181.
Peri S, Navarro JD, Amanchy R, Kristiansen TZ, Jonnalagadda CK, Surendranath V et al. Development of human protein reference database as an initial platform for approaching systems biology in humans. Genome Res 2003; 13: 2363–2371.
Bader GD, Donaldson I, Wolting C, Ouellette BF, Pawson T, Hogue CW . BIND–The Biomolecular Interaction Network Database. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: 242–245.
Hermjakob H, Montecchi-Palazzi L, Lewington C, Mudali S, Kerrien S, Orchard S et al. IntAct: an open source molecular interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: D452–D455.
Zanzoni A, Montecchi-Palazzi L, Quondam M, Ausiello G, Helmer-Citterich M, Cesareni G . MINT: a Molecular INTeraction database. FEBS Lett 2002; 513: 135–140.
Matthews L, Gopinath G, Gillespie M, Caudy M, Croft D, de Bono B et al. Reactome knowledgebase of human biological pathways and processes. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: D619–D622.
Salwinski L, Miller CS, Smith AJ, Pettit FK, Bowie JU, Eisenberg D . The Database of Interacting Proteins: 2004 update. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: D449–D451.
Ross CA, Margolis RL, Reading SA, Pletnikov M, Coyle JT . Neurobiology of schizophrenia. Neuron 2006; 52: 139–153.
Witten TM, Bonchev D . Predicting aging/longevity-related genes in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Chem Biodivers 2007; 4: 2639–2655.
Managbanag JR, Witten TM, Bonchev D, Fox LA, Tsuchiya M, Kennedy BK et al. Shortest-path network analysis is a useful approach toward identifying genetic determinants of longevity. PLoS ONE 2008; 3: e3802.
Beveridge NJ, Tooney PA, Carroll AP, Gardiner E, Bowden N, Scott RJ et al. Dysregulation of miRNA 181b in the temporal cortex in schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 2008; 17: 1156–1168.
Perkins DO, Jeffries CD, Jarskog LF, Thomson JM, Woods K, Newman MA et al. microRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Genome Biol 2007; 8: R27.
Burmistrova OA, Goltsov AY, Abramova LI, Kaleda VG, Orlova VA, Rogaev EI . MicroRNA in schizophrenia: genetic and expression analysis of miR-130b (22q11). Biochemistry (Mosc) 2007; 72: 578–582.
Zhang R, Su B . MicroRNA regulation and the variability of human cortical gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: 4621–4628.
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007; 129: 1401–1414.
Liang Y, Ridzon D, Wong L, Chen C . Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal human tissues. BMC Genomics 2007; 8: 166.
Su AI, Wiltshire T, Batalov S, Lapp H, Ching KA, Block D et al. A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 6062–6067.
Wu X, Jiang R, Zhang MQ, Li S . Network-based global inference of human disease genes. Mol Syst Biol 2008; 4: 189.
Klein P, Ravi RA . Nearly best-possible approximation algorithm for node-weighted Steiner trees. J Algorithms 1995; 19: 104–115.
The International Schizophrenia Consortium. Rare chromosomal deletions and duplications increase risk of schizophrenia. Nature 2008; 455: 237–241.
Walsh T, McClellan JM, McCarthy SE, Addington AM, Pierce SB, Cooper GM et al. Rare structural variants disrupt multiple genes in neurodevelopmental pathways in schizophrenia. Science 2008; 320: 539–543.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Kenneth Kendler, Ayman Fanous, Brien Riley, and many other colleagues for their valuable discussions. This work was supported by grants (AA017437 and LM009598) from National Institute of Health, Thomas F and Kate Miller Jeffress Memorial Trust Fund and NARSAD Young Investigator Award to ZZ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, P., Sun, J., Guo, A. et al. SZGR: a comprehensive schizophrenia gene resource. Mol Psychiatry 15, 453–462 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2009.93
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2009.93
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A human forebrain organoid model of fragile X syndrome exhibits altered neurogenesis and highlights new treatment strategies
Nature Neuroscience (2021)
-
A new locus regulating MICALL2 expression was identified for association with executive inhibition in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Molecular Psychiatry (2018)
-
Analyzing the genes related to nicotine addiction or schizophrenia via a pathway and network based approach
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
DNA N6-methyladenine is dynamically regulated in the mouse brain following environmental stress
Nature Communications (2017)
-
DNA methylation in schizophrenia in different patient-derived cell types
npj Schizophrenia (2017)