Abstract
Objective:
The objective of this study was to examine the impact of Coagulase-negative staphylococcus (CoNS) sepsis in preterm infants on the neurodevelopmental outcomes at 30 to 42 months corrected age (CA).
Study Design:
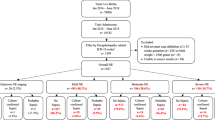
This is a retrospective cohort study. All preterm infants born at <29 weeks gestational age between 1995 and 2008 and had a neurodevelopmetnal assessment at 30 to 42 months CA were eligible. The neurodevelopmetnal outcomes of infants exposed to CoNS sepsis were compared with infants unexposed to any type of neonatal sepsis.
Result:
A total of 105 eligible infants who were exposed to CoNS sepsis were compared with 227 infants with no neonatal sepsis. In univariate analysis, infants with CoNS sepsis were more likely to have total major disability (odds ratio (OR)=1.9; 95% CI: 1.07 to 3.38) and cognitive delay (OR=2.53; 1.26 to 5.14).There was no significant difference in the incidence of cerebral palsy, blindness and deafness between the two groups. After correcting for potential confounders, CoNS sepsis was associated with increased risk of cognitive delay (adjusted odds ratio (aOR)= 2.23; 95% CI 1.01 to 4.9), but not with the total major disability (aOR=1.14; 95% CI: 0.55 to 2.34).
Conclusion:
Our study suggests that CoNS sepsis in preterm infants might be associated with increased risk for cognitive delay at 36 months CA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hack M, Wilson-Costello D, Friedman H, Taylor GH, Schluchter M, Fanaroff AA . Neurodevelopment and predictors of outcomes of children with birth weights of less than 1000 g: 1992-1995. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000; 154 (7): 725–731.
Pinto-Martin JA, Riolo S, Cnaan A, Holzman C, Susser MW, Paneth N . Cranial ultrasound prediction of disabling and nondisabling cerebral palsy at age two in a low birth weight population. Pediatrics 1995; 95 (2): 249–254.
Volpe JJ . Cerebral white matter injury of the premature infant-more common than you think. Pediatrics 2003; 112 (1 Pt 1): 176–180.
Volpe JJ . Postnatal sepsis, necrotizing entercolitis, and the critical role of systemic inflammation in white matter injury in premature infants. J Pediatr 2008; 153 (2): 160–163.
Volpe JJ . Neonatal encephalitis and white matter injury: more than just inflammation? Ann Neurol 2008; 64 (3): 232–236.
Stoll BJ, Gordon T, Korones SB, Shankaran S, Tyson JE, Bauer CR et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: a report from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. J Pediatr 1996; 129 (1): 63–71.
Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: the experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 2002; 110 (2 Pt 1): 285–291.
Klein JO . Bacteriology of neonatal sepsis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1990; 9 (10): 778–779.
Orsi GB, d'Ettorre G, Panero A, Chiarini F, Vullo V, Venditti M . Hospital-acquired infection surveillance in a neonatal intensive care unit. Am J Infect Control 2009; 37 (3): 201–203.
Van der Lugt NM, Steggerda SJ, Walther FJ . Use of rifampin in persistent coagulase negative staphylococcal bacteremia in neonates. BMC Pediatr 2010; 10: 84–89.
Isaacs D Australasian Study Group For Neonatal I. A ten year, multicentre study of coagulase negative staphylococcal infections in Australasian neonatal units. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2003; 88 (2): F89–F93.
Shah DK, Doyle LW, Anderson PJ, Bear M, Daley AJ, Hunt RW et al. Adverse neurodevelopment in preterm infants with postnatal sepsis or necrotizing enterocolitis is mediated by white matter abnormalities on magnetic resonance imaging at term. J Pediatr 2008; 153 (2): 170–175.
Schlapbach LJ, Aebischer M, Adams M, Natalucci G, Bonhoeffer J, Latzin P et al. Impact of sepsis on neurodevelopmental outcome in a Swiss National Cohort of extremely premature infants. Pediatrics 2011; 128 (2): e348–e357.
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Adams-Chapman I, Fanaroff AA, Hintz SR, Vohr B et al. Neurodevelopmental and growth impairment among extremely low-birth-weight infants with neonatal infection. JAMA 2004; 292 (19): 2357–2365.
Khashu M, Osiovich H, Henry D, Al Khotani A, Solimano A, Speert DP . Persistent bacteremia and severe thrombocytopenia caused by coagulase-negative Staphylococcus in a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatrics 2006; 117 (2): 340–348.
Dimitriou G, Fouzas S, Giormezis N, Giannakopoulos I, Tzifas S, Foka A et al. Clinical and microbiological profile of persistent coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteraemia in neonates. Clin Microbiol Infect 2011; 17 (11): 1684–1690.
Papile LA, Munsick-Bruno G, Schaefer A . Relationship of cerebral intraventricular hemorrhage and early childhood neurologic handicaps. J Pediatr 1983; 103 (2): 273–277.
Shennan AT, Dunn MS, Ohlsson A, Lennox K, Hoskins EM . Abnormal pulmonary outcomes in premature infants: prediction from oxygen requirement in the neonatal period. Pediatrics 1988; 82 (4): 527–532.
Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L et al. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg 1978; 187 (1): 1–7.
The International Committee for the Classification of the Late Stages of Retinopathy of Prematurity. An international classification of retinopathy of prematurity. II. The classification of retinal detachment. Arch Ophthalmol 1987; 105 (7): 906–912.
Levine MS . Cerebral palsy diagnosis in children over age 1 year: standard criteria. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1980; 61 (9): 385–389.
Thorndike RHE, Sattler J . The Stanford-Binet intelligence scale fourth edition Guide for administering and scoring. Riverside Pub. Co: Chicago, IL, 1986; 192 p.
Beaino G, Khoshnood B, Kaminski M, Pierrat V, Marret S, Matis J et al. Predictors of cerebral palsy in very preterm infants: the EPIPAGE prospective population-based cohort study. Dev Med Child Neurol 2010; 52 (6): e119–e125.
Silveira RC, Procianoy RS, Dill JC, da Costa CS . Periventricular leukomalacia in very low birth weight preterm neonates with high risk for neonatal sepsis. J Pediatr 2008; 84 (3): 211–216.
Hack M, Taylor HG, Drotar D, Schluchter M, Cartar L, Wilson-Costello D et al. Poor predictive validity of the Bayley Scales of Infant Development for cognitive function of extremely low birth weight children at school age. Pediatrics 2005; 116 (2): 333–341.
Alshaikh B, Yusuf K, Sauve R . Neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants with neonatal sepsis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Perinatol 2013; 33 (7): 558–564.
Vella-Brincat JW, Begg EJ, Robertshawe BJ, Lynn AM, Borrie TL, Darlow BA . Are gentamicin and/or vancomycin associated with ototoxicity in the neonate? A retrospective audit. Neonatology 2011; 100 (2): 186–193.
Coenraad S, Goedegebure A, van Goudoever JB, Hoeve LJ . Risk factors for auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder in NICU infants compared to normal-hearing NICU controls. Laryngoscope 2011; 121 (4): 852–855.
Woodward LJ, Moor S, Hood KM, Champion PR, Foster-Cohen S, Inder TE et al. Very preterm children show impairments across multiple neurodevelopmental domains by age 4 years. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2009; 94 (5): F339–F344.
Litt J, Taylor HG, Klein N, Hack M . Learning disabilities in children with very low birthweight: prevalence, neuropsychological correlates, and educational interventions. J Learn Disabil 2005; 38 (2): 130–141.
Woodward LJ, Clark CA, Bora S, Inder TE . Neonatal white matter abnormalities an important predictor of neurocognitive outcome for very preterm children. PLoS One 2012; 7 (12): e51879.
Leijser LM, de Bruine FT, van der Grond J, Steggerda SJ, Walther FJ, van Wezel-Meijler G . Is sequential cranial ultrasound reliable for detection of white matter injury in very preterm infants? Neuroradiology 2010; 52 (5): 397–406.
Khwaja O, Volpe JJ . Pathogenesis of cerebral white matter injury of prematurity. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2008; 93 (2): F153–F161.
Graham EM, Holcroft CJ, Rai KK, Donohue PK, Allen MC . Neonatal cerebral white matter injury in preterm infants is associated with culture positive infections and only rarely with metabolic acidosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004; 191 (4): 1305–1310.
Procianoy RS, Silveira RC . Association between high cytokine levels with white matter injury in preterm infants with sepsis. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2012; 13 (2): 183–187.
Chau TA, McCully ML, Brintnell W, An G, Kasper KJ, Vines ED et al. Toll-like receptor 2 ligands on the staphylococcal cell wall downregulate superantigen-induced T cell activation and prevent toxic shock syndrome. Nat Med 2009; 15 (6): 641–648.
Semmler A, Widmann CN, Okulla T, Urbach H, Kaiser M, Widman G et al. Persistent cognitive impairment, hippocampal atrophy and EEG changes in sepsis survivors. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2013; 84 (1): 62–69.
Iwashyna TJ, Ely EW, Smith DM, Langa KM . Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA 2010; 304 (16): 1787–1794.
Chavan SS, Huerta PT, Robbiati S, Valdes-Ferrer SI, Ochani M, Dancho M et al. HMGB1 mediates cognitive impairment in sepsis survivors. Mol Med 2012; 18: 930–937.
Klingenberg C, Aarag E, Ronnestad A, Sollid JE, Abrahamsen TG, Kjeldsen G et al. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal sepsis in neonates. Association between antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation and the host inflammatory response. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2005; 24 (9): 817–822.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshaikh, B., Yee, W., Lodha, A. et al. Coagulase-negative staphylococcus sepsis in preterm infants and long-term neurodevelopmental outcome. J Perinatol 34, 125–129 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2013.155
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2013.155
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Commensal Staphylococci Including Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Dogs and Cats in Remote New South Wales, Australia
Microbial Ecology (2020)
-
Neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years of age in preterm infants with late-onset sepsis
European Journal of Pediatrics (2019)
-
Suspected or known neonatal sepsis and neurodevelopmental delay by 5 years
Journal of Perinatology (2018)
-
Long-term outcome in survivors of neonatal tetanus following specialist intensive care in Vietnam
BMC Infectious Diseases (2017)
-
Early postnatal illness severity scores predict neurodevelopmental impairments at 10 years of age in children born extremely preterm
Journal of Perinatology (2017)