Abstract
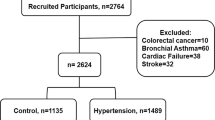
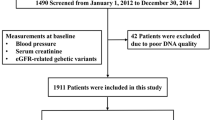
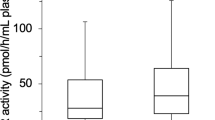
To investigate whether increased dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) activity predicts new-onset hypertension in Chinese patients. A prospective study was conducted for 1884 adults (804 men/1080 women) aged 18–70 years without hypertension. Participants were examined in 2007 (baseline) and 2011 (follow-up) and circulating DPP4 activity, mannose 6-phosphate receptor (M6P-R) concentration, inflammatory markers and oxidative stress parameters were measured. After a 4-year follow-up, 296 individuals developed hypertension with an incidence of 39 per 1000 patient years. In multiple linear regression analyses, baseline DPP4 activity was an independent predictor of an increase in M6P-R, inflammatory markers and oxidative stress parameters over a 4-year period (all P<0.01). Cox proportional hazards models revealed that DPP4 activity independently predicted the risk of developing hypertension (relative risk 2.68 (95% confidence interval 1.71–4.21) P<0.01). Our results indicate that DPP4 activity is an important predictor of hypertension onset in apparently healthy Chinese individuals. This finding may have important implications for understanding the effects of DPP4 in promoting inflammation and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of hypertension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao Y, Chen G, Tian H, Lin L, Lu J, Weng J et al. Prevalence of hypertension in China: a cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e65938.
Ryan MJ . An update on immune system activation in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Hypertension 2013; 62: 226–230.
Virdis A, Dell'Agnello U, Taddei S . Impact of inflammation on vascular disease in hypertension. Maturitas 2014; 78: 179–183.
Leibowitz A, Schiffrin EL . Immune mechanisms in hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 2011; 13: 465–472.
Rodrigo R, Gonzalez J, Paoletto F . The role of oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of hypertension. Hypertens Res 2011; 34: 431–440.
Zalba G, San Jose G, Moreno MU, Fortuno MA, Fortuno A, Beaumont FJ et al. Oxidative stress in arterial hypertension: role of nad(p)h oxidase. Hypertension 2001; 38: 1395–1399.
Matteucci E, Giampietro O . Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (cd26): knowing the function before inhibiting the enzyme. Curr Med Chem 2009; 16: 2943–2951.
Lamers D, Famulla S, Wronkowitz N, Hartwig S, Lehr S, Ouwens DM et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a novel adipokine potentially linking obesity to the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2011; 60: 1917–1925.
Itou M, Kawaguchi T, Taniguchi E, Sata M . Dipeptidyl peptidase-4: a key player in chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19: 2298–2306.
Zhong J, Rao X, Rajagopalan S . An emerging role of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (dpp4) beyond glucose control: potential implications in cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2013; 226: 305–314.
Cordero OJ, Salgado FJ, Vinuela JE, Nogueira M . Interleukin-12 enhances cd26 expression and dipeptidyl peptidase iv function on human activated lymphocytes. Immunobiology 1997; 197: 522–533.
Ikushima H, Munakata Y, Iwata S, Ohnuma K, Kobayashi S, Dang NH et al. Soluble cd26/dipeptidyl peptidase iv enhances transendothelial migration via its interaction with mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor ii receptor. Cell Immunol 2002; 215: 106–110.
Ishibashi Y, Matsui T, Maeda S, Higashimoto Y, Yamagishi S . Advanced glycation end products evoke endothelial cell damage by stimulating soluble dipeptidyl peptidase-4 production and its interaction with mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor ii receptor. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2013; 12: 125.
Mason RP, Jacob RF, Kubant R, Ciszewski A, Corbalan JJ, Malinski T . Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition with saxagliptin enhanced nitric oxide release and reduced blood pressure and sicam-1 levels in hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2012; 60: 467–473.
Ogawa S, Ishiki M, Nako K, Okamura M, Senda M, Mori T et al. Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, decreases systolic blood pressure in japanese hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes. Tohoku J Exp Med 2011; 223: 133–135.
Mistry GC, Maes AL, Lasseter KC, Davies MJ, Gottesdiener KM, Wagner JA et al. Effect of sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, on blood pressure in nondiabetic patients with mild to moderate hypertension. J Clin Pharmacol 2008; 48: 592–598.
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in china. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 1090–1101.
Alderman M, Arakawa K, Beilin L, Chalmers J, Erdine S, Fujishima M et al. 1999 world health organization–international society of hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension. Guidelines sub-committee. Blood Press Suppl 1999; 1: 9–43.
Rose GA, Blackburn H . Cardiovascular survey methods. Monogr Ser World Health Organ 1968; 56: 1–188.
Yang F, Zheng T, Gao Y, Baskota A, Chen T, Ran X et al. Increased plasma dpp4 activity is an independent predictor of the onset of metabolic syndrome in chinese over 4 years: result from the china national diabetes and metabolic disorders study. PLoS ONE 2014; 9: e92222.
Nelson KM, Boyko EJ, Koepsell T . All-cause mortality risk among a national sample of individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: 2360–2364.
Kirino Y, Sei M, Kawazoe K, Minakuchi K, Sato Y . Plasma dipeptidyl peptidase 4 activity correlates with body mass index and the plasma adiponectin concentration in healthy young people. Endocr J 2012; 59: 949–953.
Jeyaratnaganthan N, Hojlund K, Kroustrup JP, Larsen JF, Bjerre M et al. Circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-ii/mannose-6-phosphate receptor in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Growth Horm IGF Res 2010; 20: 185–191.
Jadzinsky M, Pfutzner A, Paz-Pacheco E, Xu Z, Allen E, Chen R et al. Saxagliptin given in combination with metformin as initial therapy improves glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with either monotherapy: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2009; 11: 611–622.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the residents and nurses of the Department of Endocrinology of Yulin Community Hospital, the First People’s Hospital of Longquan and the First People’s Hospital of Liangshan Yi Nationality Autonomy District for their diligent work in collecting demographic data and blood samples. This study was supported by grants from the Chinese Medical Association Foundation and Chinese Diabetes Society (No. 07020470055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, T., Chen, T., Liu, Y. et al. Increased plasma DPP4 activity predicts new-onset hypertension in Chinese over a 4-year period: possible associations with inflammation and oxidative stress. J Hum Hypertens 29, 424–429 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2014.111
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2014.111
This article is cited by
-
Prognostic value of plasma DPP4 activity in ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2017)