Abstract
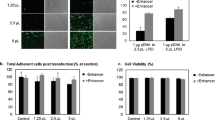
Gene delivery to stem cells holds great potential for tissue regeneration and delivery of therapeutic proteins. The major barrier is the lack of safe and efficient delivery methods. Here, we report enhanced gene delivery systems for human stem cells using biodegradable polymeric vectors. A library of poly (β-amino esters) end-modified derivatives was developed and optimized for high transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity for three human stem cell lines including human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) and human embryonic stem cell-derived cells (hESCds). In the presence of 10% serum, leading end-modified C32 polymeric vectors exhibited significantly high transfection efficiency in hMSCs (27±2%), hADSCs (24±3%) and hESCds (56±11%), with high cell viability (87–97%) achieved in all cell types. Our results show that poly(β-amino esters) as a class, and end-modified versions of C32 in particular, are efficient polymeric vectors for gene delivery to both adult and embryonic-derived stem cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999; 284: 143–147.
Shamblott MJ, Axelman J, Wang S, Bugg EM, Littlefield JW, Donovan PJ et al. Derivation of pluripotent stem cells from cultured human primordial germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 13726–13731.
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 1998; 282: 1145–1147.
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell JW, Katz AJ et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng 2001; 7: 211–228.
Wickham MQ, Erickson GR, Gimble JM, Vail TP, Guilak F . Multipotent stromal cells derived from the infrapatellar fat pad of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2003; 412: 196–212.
Reynolds BA, Weiss S . Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science 1992; 255: 1707–1710.
Song HJ, Stevens CF, Gage FH . Neural stem cells from adult hippocampus develop essential properties of functional CNS neurons. Nat Neurosci 2002; 5: 438–445.
Jankowski RJ, Deasy BM, Huard J . Muscle-derived stem cells. Gene therapy 2002; 9: 642–647.
Strulovici Y, Leopold PL, O’Connor TP, Pergolizzi RG, Crystal RG . Human embryonic stem cells and gene therapy. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 850–866.
Goessler UR, Riedel K, Hormann K, Riedel F . Perspectives of gene therapy in stem cell tissue engineering. Cells Tissues Organs 2006; 183: 169–179.
Kumar S, Chanda D, Ponnazhagan S . Therapeutic potential of genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Therapy 2008; 15: 711–715.
Zachos T, Diggs A, Weisbrode S, Bartlett J, Bertone A . Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated gene delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in an articular fracture model. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 1543–1550.
Betz VM, Betz OB, Harris MB, Vrahas MS, Evans CH . Bone tissue engineering and repair by gene therapy. Front Biosci 2008; 13: 833–841.
Conrad C, Gupta R, Mohan H, Niess H, Bruns CJ, Kopp R et al. Genetically engineered stem cells for therapeutic gene delivery. Curr Gene Ther 2007; 7: 249–260.
Sueblinvong V, Suratt BT, Weiss DJ . Novel therapies for the treatment of cystic fibrosis: new developments in gene and stem cell therapy. Clin Chest Med 2007; 28: 361–379.
Bigger BW, Siapati EK, Mistry A, Waddington SN, Nivsarkar MS, Jacobs L et al. Permanent partial phenotypic correction and tolerance in a mouse model of hemophilia B by stem cell gene delivery of human factor IX. Gene Therapy 2006; 13: 117–126.
Zhong L, Zhao W, Wu J, Maina N, Han Z, Srivastava A . Adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells as a therapeutic tool. Curr Gene Ther 2006; 6: 683–698.
Kobayashi N, Rivas-Carrillo JD, Soto-Gutierrez A, Fukazawa T, Chen Y, Navarro-Alvarez N et al. Gene delivery to embryonic stem cells. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 2005; 75: 10–18.
Park TG, Jeong JH, Kim SW . Current status of polymeric gene delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2006; 58: 467–486.
Pack DW, Hoffman AS, Pun S, Stayton PS . Design and development of polymers for gene delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2005; 4: 581–593.
Lakshmipathy U, Pelacho B, Sudo K, Linehan JL, Coucouvanis E, Kaufman DS et al. Efficient transfection of embryonic and adult stem cells. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2004; 22: 531–543.
Aslan H, Zilberman Y, Arbeli V, Sheyn D, Matan Y, Liebergall M et al. Nucleofection-based ex vivo nonviral gene delivery to human stem cells as a platform for tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng 2006; 12: 877–889.
Lynn D, Langer R . Degradable poly(beta-amino esters): Synthesis, characterization, and self-assembly with plasmid DNA. J Am Chem Soc 2000; 122: 10761–10768.
Lynn DM, Anderson DG, Putnam D, Langer R . Accelerated discovery of synthetic transfection vectors: parallel synthesis and screening of a degradable polymer library. J Am Chem Soc 2001; 123: 8155–8156.
Lim YB, Kim SM, Suh H, Park JS . Biodegradable, endosome disruptive, and cationic network-type polymer as a highly efficient and nontoxic gene delivery carrier. Bioconjug Chem 2002; 13: 952–957.
Akinc A, Anderson DG, Lynn DM, Langer R . Synthesis of poly(beta-amino ester)s optimized for highly effective gene delivery. Bioconjug Chem 2003; 14: 979–988.
Anderson DG, Peng W, Akinc A, Hossain N, Kohn A, Padera R et al. A polymer library approach to suicide gene therapy for cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 16028–16033.
Kim TI, Seo HJ, Choi JS, Yoon JK, Baek JU, Kim K et al. Synthesis of biodegradable cross-linked poly(beta-amino ester) for gene delivery and its modification, inducing enhanced transfection efficiency and stepwise degradation. Bioconjug Chem 2005; 16: 1140–1148.
Anderson DG, Lynn DM, Langer R . Semi-automated synthesis and screening of a large library of degradable cationic polymers for gene delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2003; 42: 3153–3158.
Anderson DG, Akinc A, Hossain N, Langer R . Structure/property studies of polymeric gene delivery using a library of poly(beta-amino esters). Mol Ther 2005; 11: 426–434.
Green J, Zugates G, Tedford N, Huang Y, Griffith L, Lauffenburger D et al. Combinatorial modification of degradable polymers enables transfection of human cells comparable to adenovirus. Adv Mater 2007; 19: 7.
Zugates GT, Peng W, Zumbuehl A, Jhunjhunwala S, Huang YH, Langer R et al. Rapid optimization of gene delivery by parallel end-modification of poly(beta-amino ester)s. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 1306–1312.
Peister A, Mellad JA, Wang M, Tucker HA, Prockop DJ . Stable transfection of MSCs by electroporation. Gene Therapy 2004; 11: 224–228.
Farrell LL, Pepin J, Kucharski C, Lin X, Xu Z, Uludag H . A comparison of the effectiveness of cationic polymers poly-L-lysine (PLL) and polyethylenimine (PEI) for non-viral delivery of plasmid DNA to bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC). Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2007; 65: 388–397.
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD . Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 1996; 87: 1171–1180.
Baldwin HS, Shen HM, Yan HC, DeLisser HM, Chung A, Mickanin C, Trask T, Kirschbaum NE, Newman PJ, Albelda SM, Buck CA . Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1/CD31): alternatively spliced, functionally distinct isoforms expressed during mammalian cardiovascular development. Development 1994; 120: 2539–2553.
Denis CV . Molecular and cellular biology of von Willebrand factor. Int J Hematol 2002; 75: 3–8.
Hwang NS, Varghese S, Zhang Z, Elisseeff J . Chondrogenic differentiation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cells in arginine-glycine-aspartate-modified hydrogels. Tissue Eng 2006; 12: 2695–2706.
Ogris M, Steinlein P, Kursa M, Mechtler K, Kircheis R, Wagner E . The size of DNA/transferrin-PEI complexes is an important factor for gene expression in cultured cells. Gene Therapy 1998; 5: 1425–1433.
Thomas M, Klibanov AM . Non-viral gene therapy: polycation-mediated DNA delivery. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2003; 62: 27–34.
Green JJ, Shi J, Chiu E, Leshchiner ES, Langer R, Anderson DG . Biodegradable polymeric vectors for gene delivery to human endothelial cells. Bioconjug Chem 2006; 17: 1162–1169.
Acknowledgements
We thank the NIH (R01-EB000244-27 and R01-DE016516-03) for funding. FY gratefully acknowledge the National Institutes of Health for National Research Service Award postdoctoral fellowship (1F32 AR056567-01). We also thank the laboratory of Professor Johnny Huard at the University of Pittsburgh for kindly providing us the DNA plasmid-encoding human vascular endothelial growth factor 165 used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Gene Therapy website (http://www.nature.com/gt)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Green, J., Dinio, T. et al. Gene delivery to human adult and embryonic cell-derived stem cells using biodegradable nanoparticulate polymeric vectors. Gene Ther 16, 533–546 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.182
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.182
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Non-viral gene delivery to human mesenchymal stem cells: a practical guide towards cell engineering
Journal of Biological Engineering (2023)
-
A Combinatorial Library of Biodegradable Polyesters Enables Non-viral Gene Delivery to Post-Mitotic Human Stem Cell-Derived Polarized RPE Monolayers
Regenerative Engineering and Translational Medicine (2020)
-
Highly branched poly(β-amino ester) delivery of minicircle DNA for transfection of neurodegenerative disease related cells
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Co-delivery of doxorubicin and AS1411 aptamer by poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(β-amino esters) polymeric micelles for targeted cancer therapy
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2017)
-
Gene delivery of osteoinductive signals to a human fetal osteoblast cell line induces cell death in a dose-dependent manner
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2015)