Abstract
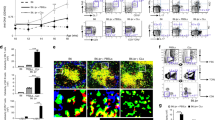
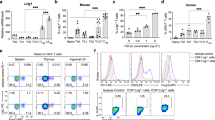
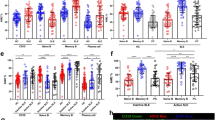
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a complex autoimmune disorder characterized by the production of pathogenic anti-nuclear antibodies. Previous work from our laboratory has shown that the introgression of a New Zealand Black-derived chromosome 4 interval onto a lupus-prone background suppresses the disease. Interestingly, the same genetic interval promoted the expansion of both Natural Killer T- and CD5+ B cells in suppressed mice. In this study, we show that ablation of NKT cells with a CD1d knockout had no impact on either the suppression of lupus or the expansion of CD5+ B cells. On the other hand, suppressed mice had an expanded population of IL-10-producing B cells that predominantly localized to the CD5+CD1dlow compartment. The expansion of CD5+ B cells negatively correlated with the frequency of pro-inflammatory IL-17 A-producing T-cells and kidney damage. Adoptive transfer with a single injection of total B cells with an enriched CD5+ compartment reduced the frequency of memory/activated, IFNγ-producing, and IL-17 A-producing CD4 T-cells but did not significantly reduce autoantibody levels. Taken together, these data suggest that the expansion of CD5+ IL-10-producing B cells and not NKT cells protects against lupus in these mice, by limiting the expansion of pro-inflammatory IL-17 A- and IFNγ-producing CD4 T-cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheung Y, Chang N, Cai Y, Macleod R, Wither JE, Bonventi G . Functional Interplay between Intrinsic B and T Cell Defects. J Immunol 2005; 175: 8154–8164.
Loh C, Pau E, Chang N-H, Wither JE . An intrinsic B-cell defect supports autoimmunity in New Zealand black chromosome 13 congenic mice. Eur J Immunol 2011; 41: 527–536.
Loh C, Pau E, Lajoie G, Li TT, Baglaenko Y, Cheung Y-H et al. Epistatic suppression of fatal autoimmunity in New Zealand black bicongenic mice. J Immunol 2011; 186: 5845–5853.
Zeng D, Liu Y, Sidobre S, Kronenberg M, Strober S . Activation of natural killer T cells in NZB/W mice induces Th1-type immune responses exacerbating lupus. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1211–1222.
Yang J-Q, Wen X, Liu H, Folayan G, Dong X, Zhou M et al. Examining the role of CD1d and natural killer T cells in the development of nephritis in a genetically susceptible lupus model. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56: 1219–1233.
Tang X, Zhang B, Jarrell JA, Price J V, Dai H, Utz PJ et al. Ly108 expression distinguishes subsets of invariant NKT cells that help autoantibody production and secrete IL-21 from those that secrete IL-17 in lupus prone NZB/W mice. J Autoimmun 2014; 50: 87–98.
Wermeling F, Lind SM, Jordö ED, Cardell SL, Karlsson MCI . Invariant NKT cells limit activation of autoreactive CD1d-positive B cells. J Exp Med 2010; 207: 943–952.
Cho Y-N, Kee S-J, Lee S-J, Seo S-R, Kim T-J, Lee S-S et al. Numerical and functional deficiencies of natural killer T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: their deficiency related to disease activity. Rheumatology 2011; 50: 1054–1063.
Bouaziz J-D, Yanaba K, Tedder TF . Regulatory B cells as inhibitors of immune responses and inflammation. Immunol Rev 2008; 224: 201–214.
Mauri C, Gray D, Mushtaq N, Londei M . Prevention of arthritis by interleukin 10-producing B cells. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 489–501.
Carter N a, Vasconcellos R, Rosser EC, Tulone C, Muñoz-Suano A, Kamanaka M et al. Mice lacking endogenous IL-10-producing regulatory B cells develop exacerbated disease and present with an increased frequency of Th1/Th17 but a decrease in regulatory T cells. J Immunol 2011; 186: 5569–5579.
Mauri C, Ehrenstein MR . The ‘short’ history of regulatory B cells. Trends Immunol 2008; 29: 34–40.
Ouyang W, Rutz S, Crellin NK, Valdez P a, Hymowitz SG . Regulation and functions of the IL-10 family of cytokines in inflammation and disease. Annu Rev Immunol 2011; 29: 71–109.
Maseda D, Candando K . Peritoneal Cavity Regulatory B Cells (B10 Cells) Modulate IFN-γ+ CD4+ T Cell Numbers during Colitis Development in Mice. J Immunol 2013; 191: 2780–2795.
Yang M, Deng J, Liu Y, Ko K-H, Wang X, Jiao Z et al. IL-10-producing regulatory B10 cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis via suppressing Th17 cell generation. Am J Pathol 2012; 180: 2375–2385.
Carter N a, Rosser EC, Mauri C . Interleukin-10 produced by B cells is crucial for the suppression of Th17/Th1 responses, induction of T regulatory type 1 cells and reduction of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2012; 14: R32.
Teichmann LL, Kashgarian M, Weaver CT, Roers A, Müller W, Shlomchik MJ . B cell-derived IL-10 does not regulate spontaneous systemic autoimmunity in MRL.Fas(lpr) mice. J Immunol 2012; 188: 678–685.
Haas KM, Watanabe R, Matsushita T, Nakashima H, Ishiura N, Okochi H et al. Protective and pathogenic roles for B cells during systemic autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice. J Immunol 2010; 184: 4789–4800.
Watanabe R, Ishiura N, Nakashima H, Kuwano Y, Okochi H, Tamaki K et al. Regulatory B cells (B10 cells) have a suppressive role in murine lupus: CD19 and B10 cell deficiency exacerbates systemic autoimmunity. J Immunol 2010; 184: 4801–4809.
Poe JC, Smith SH, Haas KM, Yanaba K, Tsubata T, Matsushita T et al. Amplified B lymphocyte CD40 signaling drives regulatory B10 cell expansion in mice. PLoS One 2011; 6: e22464.
Yang X, Yang J, Chu Y, Wang J, Guan M, Zhu X et al. T follicular helper cells mediate expansion of regulatory B cells via IL-21 in Lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice. PLoS One 2013; 8: e62855.
Gao N, Dresel J, Eckstein V, Gellert R, Störch H, Venigalla RKC et al. Impaired suppressive capacity of activation-induced regulatory B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014; 66: 2849–2861.
Wang L, Zhao P, Ma L, Shan Y, Jiang Z, Wang J et al. Increased interleukin 21 and follicular helper T-like cells and reduced interleukin 10+ B cells in patients with new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 2014; 41: 1781–1792.
Sieber J, Daridon C, Fleischer SJ, Fleischer V, Hiepe F, Alexander T et al. Active systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with a reduced cytokine production by B cells in response to TLR9 stimulation. Arthritis Res Ther 2014; 16: 477.
Jin L, Weiqian C, Lihuan Y . Peripheral CD24hi CD27+ CD19+ B cells subset as a potential biomarker in naïve systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Rheum Dis 2013; 16: 698–708.
Blair PA, Noreña LY, Flores-Borja F, Rawlings DJ, Isenberg DA, Ehrenstein MR et al. CD19(+)CD24(hi)CD38(hi) B cells exhibit regulatory capacity in healthy individuals but are functionally impaired in systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Immunity 2010; 32: 129–140.
Matsushita T, Horikawa M, Iwata Y, Tedder TF . Regulatory B cells (B10 cells) and regulatory T cells have independent roles in controlling experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis initiation and late-phase immunopathogenesis. J Immunol 2010; 185: 2240–2252.
De Masson A, Bouaziz J-D, Le Buanec H, Robin M, O’Meara A, Parquet N et al. CD24hiCD27+ and plasmablast-like regulatory B cells in human chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2015; 125: 1830–1839.
Matsumoto M, Baba A, Yokota T, Nishikawa H, Ohkawa Y, Kayama H et al. Interleukin-10-Producing Plasmablasts Exert Regulatory Function in Autoimmune Inflammation. Immunity 2014; 41: 1040–1051.
Ray A, Basu S, Williams CB, Salzman NH, Dittel BN . A novel IL-10-independent regulatory role for B cells in suppressing autoimmunity by maintenance of regulatory T cells via GITR ligand. J Immunol 2012; 188: 3188–3198.
Nishioka T, Shimizu J, Iida R, Yamazaki S, Sakaguchi S . CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T Cells and CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T Cells in Aged Mice. J Immunol 2006; 176: 6586–6593.
Zelenay S, Lopes-Carvalho T, Caramalho I, Moraes-Fontes MF, Rebelo M, Demengeot J . Foxp3+ CD25- CD4 T cells constitute a reservoir of committed regulatory cells that regain CD25 expression upon homeostatic expansion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 4091–4096.
Mauri C, Bosma A . Immune regulatory function of B cells. Annu Rev Immunol 2012; 30: 221–241.
Yang X, Yang J, Chu Y, Xue Y, Xuan D, Zheng S et al. T follicular helper cells and regulatory B cells dynamics in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One 2014; 9: e88441.
Xu Z, Potula H-HSK, Vallurupalli A, Perry D, Baker H, Croker BP et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Cdkn2c regulates B cell homeostasis and function in the NZM2410-derived murine lupus susceptibility locus Sle2c1. J Immunol 2011; 186: 6673–6682.
Xu Z, Cuda CM, Croker BP, Morel L . The NZM2410-derived lupus susceptibility locus Sle2c1 increases Th17 polarization and induces nephritis in fas-deficient mice. Arthritis Rheum 2011; 63: 764–774.
Liu Y, Li L, Kumar KR, Xie C, Lightfoot S, Zhou XJ et al. Lupus susceptibility genes may breach tolerance to DNA by impairing receptor editing of nuclear antigen-reactive B cells. J Immunol 2007; 179: 1340–1352.
Miyake K, Akahoshi M, Nakashima H . Th subset balance in lupus nephritis. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011; 2011: 980286.
Shin MS, Lee N, Kang I . Effector T-cell subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus: update focusing on Th17 cells. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011; 23: 444–448.
Hsu H-C, Yang P, Wang J, Wu Q, Myers R, Chen J et al. Interleukin 17-producing T helper cells and interleukin 17 orchestrate autoreactive germinal center development in autoimmune BXD2 mice. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 166–175.
Turner J-E, Paust H-J, Steinmetz OM, Peters A, Riedel J-H, Erhardt A et al. CCR6 recruits regulatory T cells and Th17 cells to the kidney in glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2010; 21: 974–985.
Maseda D, Smith SH, DiLillo DJ, Bryant JM, Candando KM, Weaver CT et al. Regulatory B10 cells differentiate into antibody-secreting cells after transient IL-10 production in vivo. J Immunol 2012; 188: 1036–1048.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a research grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research awarded to JW (FRN 102551). JW receives salary support from The Arthritis Centre of Excellence and the Arthritis Research Foundation of the University Health Network. YB is the recipient of a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Doctoral Research Award. KM is the recipient of an Ontario Graduate Scholarship. Special thanks to Eric Gracey for manuscript proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Genes and Immunity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baglaenko, Y., Manion, K., Chang, NH. et al. Suppression of autoimmunity by CD5+ IL-10-producing B cells in lupus-prone mice. Genes Immun 16, 311–320 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2015.17
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2015.17
This article is cited by
-
What rheumatologists need to know about innate lymphocytes
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2016)