Abstract
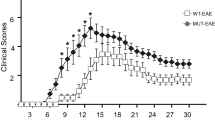
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurological disorder that causes paralysis in young adults and affects women more frequently than men. The etiology of MS is not known, but it is generally viewed as an autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS), influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Recent studies have identified interleukin-7 receptor α (IL-7Rα) as a risk factor for MS. But the role of IL-7Rα in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS is not known. In this study we demonstrate that IL-7Rα-deficient (IL-7Rα−/−) mice remain resistant to MOGp35-55-induced EAE. When compared with C57BL/6 wild-type mice, IL-7Rα−/− mice showed less severe inflammation and demyelination in the CNS. The attenuation of EAE in IL-7Rα−/− mice was associated with a decrease in T-helper (Th) 1 and Th17 responses in the CNS and lymphoid organs. IL-7Rα−/− mice also showed an increase in Th2 response and CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. These findings highlight that IL-7Rα confers susceptibility by influencing autoimmune Th1/Th17 responses in EAE model of MS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whitacre CC, Reingold SC, O’Looney PA . A gender gap in autoimmunity. Science 1999; 283: 1277–1278.
Noseworthy JH, Lucchinetti C, Rodriguez M, Weinshenker BG . Multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 938–952.
Hemmer B, Cepok S, Nessler S, Sommer N . Pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: an update on immunology. Curr Opin Neurol 2002; 15: 227–231.
Steinman L, Martin R, Bernard C, Conlon P, Oksenberg JR . Multiple sclerosis: deeper understanding of its pathogenesis reveals new targets for therapy. Annu Rev Neurosci 2002; 25: 491–505.
Hafler DA, Compston A, Sawcer S, Lander ES, Daly MJ, De Jager PL et al. Risk alleles for multiple sclerosis identified by a genomewide study. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 851–862.
Gregory SG, Schmidt S, Seth P, Oksenberg JR, Hart J, Prokop A et al. Interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) shows allelic and functional association with multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1083–1091.
Lundmark F, Duvefelt K, Iacobaeus E, Kockum I, Wallstrom E, Khademi M et al. Variation in interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) influences risk of multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1108–1113.
Svejgaard A . The immunogenetics of multiple sclerosis. Immunogenetics 2008; 60: 275–286.
Akkad DA, Hoffjan S, Petrasch-Parwez E, Beygo J, Gold R, Epplen JT . Variation in the IL7RA and IL2RA genes in German multiple sclerosis patients. J Autoimmun 2009; 32: 110–115.
D’Netto MJ, Ward H, Morrison KM, Ramagopalan SV, Dyment DA, DeLuca GC et al. Risk alleles for multiple sclerosis in multiplex families. Neurology 2009; 72: 1984–1988.
Zuvich RL, McCauley JL, Oksenberg JR, Sawcer SJ, De Jager PL, Aubin C et al. Genetic variation in the IL7RA/IL7 pathway increases multiple sclerosis susceptibility. Hum Genet 2010; 127: 525–535.
Liu W, Putnam AL, Xu-Yu Z, Szot GL, Lee MR, Zhu S et al. CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4+T reg cells. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1701–1711.
Sojka DK, Huang YH, Fowell DJ . Mechanisms of regulatory T-cell suppression—a diverse arsenal for a moving target. Immunology 2008; 124: 13–22.
Peschon JJ, Morrissey PJ, Grabstein KH, Ramsdell FJ, Maraskovsky E, Gliniak BC et al. Early lymphocyte expansion is severely impaired in interleukin 7 receptor-deficient mice. J Exp Med 1994; 180: 1955–1960.
Kim K, Lee CK, Sayers TJ, Muegge K, Durum SK . The trophic action of IL-7 on pro-T cells: inhibition of apoptosis of pro-T1, -T2, and -T3 cells correlates with Bcl-2 and Bax levels and is independent of Fas and p53 pathways. J Immunol 1998; 160: 5735–5741.
Leonard WJ, Noguchi M, Russell SM . Sharing of a common gamma chain, gamma c, by the IL-2, IL-4, and IL-7 receptors: implications for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (XSCID). Adv Exp Med Biol 1994; 365: 225–232.
DiSanto JP, Muller W, Guy-Grand D, Fischer A, Rajewsky K . Lymphoid development in mice with a targeted deletion of the interleukin 2 receptor gamma chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 377–381.
Mazel S, Burtrum D, Petrie HT . Regulation of cell division cycle progression by bcl-2 expression: a potential mechanism for inhibition of programmed cell death. J Exp Med 1996; 183: 2219–2226.
Watanabe N, Hanabuchi S, Marloie-Provost MA, Antonenko S, Liu YJ, Soumelis V . Human TSLP promotes CD40 ligand-induced IL-12 production by myeloid dendritic cells but maintains their Th2 priming potential. Blood 2005; 105: 4749–4751.
Ziegler SF, Liu YJ . Thymic stromal lymphopoietin in normal and pathogenic T cell development and function. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 709–714.
Al-Shami A, Spolski R, Kelly J, Fry T, Schwartzberg PL, Pandey A et al. A role for thymic stromal lymphopoietin in CD4(+) T cell development. J Exp Med 2004; 200: 159–168.
Bayer AL, Lee JY, de la Barrera A, Surh CD, Malek TR . A function for IL-7R for CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. J Immunol 2008; 181: 225–234.
Bright JJ, Du C, Sriram S . Tyrphostin B42 inhibits IL-12-induced tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of Janus kinase-2 and prevents experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 1999; 162: 6255–6262.
Natarajan C, Bright JJ . Curcumin inhibits experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by blocking IL-12 signaling through Janus kinase-STAT pathway in T lymphocytes. J Immunol 2002; 168: 6506–6513.
Natarajan C, Bright JJ . Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists inhibit experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by blocking IL-12 production, IL-12 signaling and Th1 differentiation. Genes Immun 2002; 3: 59–70.
Mo C, Chearwae W, O’Malley JT, Adams SM, Kanakasabai S, Walline CC et al. Stat 4 isoforms differentially regulate inflammation and demyelination in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 2008; 181: 5681–5690.
Bergamaschi R . Prognosis of multiple sclerosis: clinical factors predicting the late evolution for an early treatment decision. Expert Rev Neurother 2006; 6: 357–364.
Pokryszko-Dragan A, Gruszka E, Bilinska M, Dubik-Jezierzanska M . Secondary progressive multiple sclerosis- clinical course and potential predictive factors. Neurol Neurochir Pol 2008; 42: 6–11.
Komiyama Y, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A, Ishigame H, Kakuta S et al. IL-17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 2006; 177: 566–573.
Bebo Jr BF, Schuster JC, Adlard K, Vandenbark AA, Offner H . Interleukin 7 is a potent co-stimulator of myelin specific T cells that enhances the adoptive transfer of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Cytokine 2000; 12: 324–331.
van Roon JA, Glaudemans KA, Bijlsma JW, Lafeber FP . Interleukin 7 stimulates tumour necrosis factor alpha and Th1 cytokine production in joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2003; 62: 113–119.
van Roon JA, Verweij MC, Wijk MW, Jacobs KM, Bijlsma JW, Lafeber FP . Increased intraarticular interleukin-7 in rheumatoid arthritis patients stimulates cell contact-dependent activation of CD4(+) T cells and macrophages. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 1700–1710.
Gran B, Zhang GX, Yu S, Li J, Chen XH, Ventura ES et al. IL-12p35-deficient mice are susceptible to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: evidence for redundancy in the IL-12 system in the induction of central nervous system autoimmune demyelination. J Immunol 2002; 169: 7104–7110.
Cua DJ, Sherlock J, Chen Y, Murphy CA, Joyce B, Seymour B et al. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature 2003; 421: 744–748.
Pflanz S, Timans JC, Cheung J, Rosales R, Kanzler H, Gilbert J et al. IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4(+) T cells. Immunity 2002; 16: 779–790.
Li J, Gran B, Zhang GX, Rostami A, Kamoun M . IL-27 subunits and its receptor (WSX-1) mRNAs are markedly up-regulated in inflammatory cells in the CNS during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurol Sci 2005; 232: 3–9.
Anderson AC, Reddy J, Nazareno R, Sobel RA, Nicholson LB, Kuchroo VK . IL-10 plays an important role in the homeostatic regulation of the autoreactive repertoire in naive mice. J Immunol 2004; 173: 828–834.
Bettelli E, Das MP, Howard ED, Weiner HL, Sobel RA, Kuchroo VK . IL-10 is critical in the regulation of autoimmune encephalomyelitis as demonstrated by studies of IL-10- and IL-4-deficient and transgenic mice. J Immunol 1998; 161: 3299–3306.
Begolka WS, Vanderlugt CL, Rahbe SM, Miller SD . Differential expression of inflammatory cytokines parallels progression of central nervous system pathology in two clinically distinct models of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 1998; 161: 4437–4446.
Brocke S, Gijbels K, Allegretta M, Ferber I, Piercy C, Blankenstein T et al. Treatment of experimental encephalomyelitis with a peptide analogue of myelin basic protein. Nature 1996; 379: 343–346.
Mann-Chandler MN, Kashyap M, Wright HV, Norozian F, Barnstein BO, Gingras S et al. IFN-gamma induces apoptosis in developing mast cells. J Immunol 2005; 175: 3000–3005.
Dieckmann D, Bruett CH, Ploettner H, Lutz MB, Schuler G . Human CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory, contact-dependent T cells induce interleukin 10-producing, contact-independent type 1-like regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 2002; 196: 247–253.
Jonuleit H, Schmitt E, Kakirman H, Stassen M, Knop J, Enk AH . Infectious tolerance: human CD25(+) regulatory T cells convey suppressor activity to conventional CD4(+) T helper cells. J Exp Med 2002; 196: 255–260.
Zheng SG, Wang JH, Gray JD, Soucier H, Horwitz DA . Natural and induced CD4+CD25+ cells educate CD4+CD25- cells to develop suppressive activity: the role of IL-2, TGF-beta, and IL-10. J Immunol 2004; 172: 5213–5221.
Murai M, Turovskaya O, Kim G, Madan R, Karp CL, Cheroutre H et al. Interleukin 10 acts on regulatory T cells to maintain expression of the transcription factor Foxp3 and suppressive function in mice with colitis. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 1178–1184.
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY . Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 2003; 4: 330–336.
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S . Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 2003; 299: 1057–1061.
Gambineri E, Torgerson TR, Ochs HD . Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, and X-linked inheritance (IPEX), a syndrome of systemic autoimmunity caused by mutations of FOXP3, a critical regulator of T-cell homeostasis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003; 15: 430–435.
Khattri R, Cox T, Yasayko SA, Ramsdell F . An essential role for Scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nat Immunol 2003; 4: 337–342.
Brunkow ME, Jeffery EW, Hjerrild KA, Paeper B, Clark LB, Yasayko SA et al. Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 68–73.
Mazzucchelli R, Hixon JA, Spolski R, Chen X, Li WQ, Hall VL et al. Development of regulatory T cells requires IL-7Rαstimulation by IL-7 or TSLP. Blood 2008; 112: 3283–3292.
Huber S, Schrader J, Fritz G, Presser K, Schmitt S, Waisman A et al. P38 MAP kinase signaling is required for the conversion of CD4+CD25- T cells into iTreg. PLoS ONE 2008; 3: e3302.
Stephens LA, Malpass KH, Anderton SM . Curing CNS autoimmune disease with myelin-reactive Foxp3+ Treg. Eur J Immunol 2009; 39: 1108–1117.
Raikwar HP, Muthian G, Rajasingh J, Johnson C, Bright JJ . PPARgamma antagonists exacerbate neural antigen-specific Th1 response and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 2005; 167: 99–107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walline, C., Kanakasabai, S. & Bright, J. IL-7Rα confers susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Genes Immun 12, 1–14 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2010.49
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2010.49
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of effector function of CNS autoreactive CD4 T cells through inhibitory receptors and IL-7Rα
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2016)
-
Blockade of CD127 Exerts a Dichotomous Clinical Effect in Marmoset Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2016)
-
Perspectives of the relationship between IL-7 and autoimmune diseases
Clinical Rheumatology (2013)
-
Type I Interferons: Beneficial in Th1 and Detrimental in Th17 Autoimmunity
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2013)
-
Induction and molecular signature of pathogenic TH17 cells
Nature Immunology (2012)