Abstract
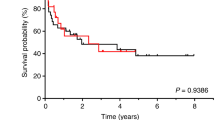
High-dose chemotherapy with autologous SCT has become standard of care for patients with relapsed aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). To improve safety and efficacy of this treatment, new conditioning regimens are being developed. We retrospectively reviewed clinical data of patients with relapsed NHL treated at our institution with i.v. BU and CY (BU/CY) as conditioning regimen for autologous SCT between January 2000 and April 2005. We identified 43 patients (24 men, 19 women, median age 50) with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (n=28), follicular lymphoma (n=8), mantle cell lymphoma (n=4) and peripheral T-cell lymphoma (n=3). Following salvage chemotherapy, there were 26 complete responses, 13 partial responses and 4 stable diseases. Median time to neutrophil and platelet recovery was 11 and 13.5 days, respectively. Treatment-related toxicities included nausea/vomiting, diarrhea and mucositis. The 100-day mortality was 9%: sepsis (n=1), pneumonia (n=1) and hepatic veno-occlusive disease (n=2). Twenty-one patients were followed until death and twenty-one surviving patients were followed for a median of 29 months (range 0.4–76). Three-year estimates of event-free survival, progression-free survival and overall survival were 35, 39 and 43%, respectively. We conclude that i.v. BU/CY is a safe and effective conditioning regimen for autologous SCT in relapsed NHL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, Somers R, Van der Lelie H, Bron D et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1540–1545.
Shipp MA, Abeloff MD, Antman KH, Carroll G, Hagenbeek A, Loeffler M et al. International consensus conference on high-dose therapy with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: report of the jury. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 423–429.
Mounier N, Gisselbrecht C . Conditioning regimens before transplantation in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol 1998; 9 (Suppl 1): S15–S21.
Sheridan WP, Boyd AW, Green MD, Russell DM, Thomas RJ, McGrath KM et al. High-dose chemotherapy with busulphan and cyclophosphamide and bone-marrow transplantation for drug-sensitive malignancies in adults: a preliminary report. Med J Aust 1989; 151: 379–386.
de Magalhaes-Silverman M, Lister J, Rybka W, Wilson J, Ball E . Busulfan and cyclophosphamide (BU/CY2) as preparative regimen for patients with lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 777–781.
Andersson BS, Kashyap A, Gian V, Wingard JR, Fernandez H, Cagnoni PJ et al. Conditioning therapy with intravenous busulfan and cyclophosphamide (IV BuCy2) for hematologic malignancies prior to allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a phase II study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2002; 8: 145–154.
Russell JA, Savoie ML, Balogh A, Turner AR, Larratt L, Chaudhry MA et al. Allogeneic transplantation for adult acute leukemia in first and second remission with a novel regimen incorporating daily intravenous busulfan, fludarabine, 400 CGY total-body irradiation, and thymoglobulin. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 814–821.
de Lima M, Couriel D, Thall PF, Wang X, Madden T, Jones R et al. Once-daily intravenous busulfan and fludarabine: clinical and pharmacokinetic results of a myeloablative, reduced-toxicity conditioning regimen for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML and MDS. Blood 2004; 104: 857–864.
Fernandez HF, Tran HT, Albrecht F, Lennon S, Caldera H, Goodman MS . Evaluation of safety and pharmacokinetics of administering intravenous busulfan in a twice-daily or daily schedule to patients with advanced hematologic malignant disease undergoing stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2002; 8: 486–492.
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM et al. Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 1244.
Bearman SI, Appelbaum FR, Back A, Petersen FB, Buckner CD, Sullivan KM et al. Regimen-related toxicity and early posttransplant survival in patients undergoing marrow transplantation for lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 1989; 7: 1288–1294.
Mills W, Chopra R, McMillan A, Pearce R, Linch DC, Goldstone AH . BEAM chemotherapy and autologous bone marrow transplantation for patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 1995; 13: 588–595.
van Besien K, Tabocoff J, Rodriguez M, Andersson B, Mehra R, Przepiorka D et al. High-dose chemotherapy with BEAC regimen and autologous bone marrow transplantation for intermediate grade and immunoblastic lymphoma: durable complete remissions, but a high rate of regimen-related toxicity. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 549–555.
Bhatia S, Robison LL, Francisco L, Carter A, Liu Y, Grant M et al. Late mortality in survivors of autologous hematopoietic-cell transplantation: report from the Bone Marrow Transplant Survivor Study. Blood 2005; 105: 4215–4222.
Kroger N, Hoffknecht M, Hanel M, Kruger W, Zeller W, Stockschlader M et al. Busulfan, cyclophosphamide and etoposide as high-dose conditioning therapy in patients with malignant lymphoma and prior dose-limiting radiation therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21: 1171–1175.
Hanel M, Kroger N, Sonnenberg S, Bornhauser M, Kruger W, Kroschinsky F et al. Busulfan, cyclophosphamide, and etoposide as high-dose conditioning regimen in patients with malignant lymphoma. Ann Hematol 2002; 81: 96–102.
Aggarwal C, Gupta S, Vaughan WP, Saylors BG, Salzman DE, Katz RO et al. Improved outcomes in intermediate- and high-risk aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation substituting intravenous for oral busulfan in a busulfan, cyclophosphamide, and etoposide preparative regimen. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 770–777.
Caballero MD, Perez-Simon JA, Iriondo A, Lahuerta J, Sierra J, Marin J et al. High-dose therapy in diffuse large cell lymphoma: results and prognostic factors in 452 patients from the GEL-TAMO Spanish Cooperative Group. Ann Oncol 2003; 14: 140–151.
Philip T, Armitage JO, Spitzer G, Chauvin F, Jagannath S, Cahn JY et al. High-dose therapy and autologous bone marrow transplantation after failure of conventional chemotherapy in adults with intermediate-grade or high-grade non-Hodgkin′s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 1987; 316: 1493–1498.
Freedman AS, Takvorian T, Anderson KC, Mauch P, Rabinowe SN, Blake K et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation in B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: very low treatment-related mortality in 100 patients in sensitive relapse. J Clin Oncol 1990; 8: 784–791.
Stone RM, Neuberg D, Soiffer R, Takvorian T, Whelan M, Rabinowe SN et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome as a late complication following autologous bone marrow transplantation for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 1994; 12: 2535–2542.
Cheng T, Forsyth P, Chaudhry A, Morris D, Gluck S, Russell JA et al. High-dose thiotepa, busulfan, cyclophosphamide and ASCT without whole-brain radiotherapy for poor prognosis primary CNS lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 679–685.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Escalón, M., Stefanovic, A., Venkatraman, A. et al. Autologous transplantation for relapsed non-Hodgkin's lymphoma using intravenous busulfan and cyclophosphamide as conditioning regimen: a single center experience. Bone Marrow Transplant 44, 89–96 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.429
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.429
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Phase II study of safety and efficacy of BEB (bendamustine, etoposide, and busulfan) conditioning regimen for autologous stem cell transplantation in non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Annals of Hematology (2020)
-
Thiotepa-based high-dose therapy for autologous stem cell transplantation in lymphoma: a retrospective study from the EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)
-
In vivo selection of autologous MGMT gene-modified cells following reduced-intensity conditioning with BCNU and temozolomide in the dog model
Cancer Gene Therapy (2012)
-
Intravenous Busulfan: A Guide to Its Use as Conditioning Treatment before Transplantation of Haematopoietic Progenitor Cells
Clinical Drug Investigation (2012)
-
Fotemustine plus etoposide, cytarabine and melphalan (FEAM) as a new conditioning regimen for lymphoma patients undergoing auto-SCT: a multicenter feasibility study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2010)