Abstract
The capacity of coral-dinoflagellate mutualisms to adapt to a changing climate relies in part on standing variation in host and symbiont populations, but rarely have the interactions between symbiotic partners been considered at the level of individuals. Here, we tested the importance of inter-individual variation with respect to the physiology of coral holobionts. We identified six genetically distinct Acropora palmata coral colonies that all shared the same isoclonal Symbiodinium ‘fitti’ dinoflagellate strain. No other Symbiodinium could be detected in host tissues. We exposed fragments of each colony to extreme cold and found that the stress-induced change in symbiont photochemical efficiency varied up to 3.6-fold depending on host genetic background. The S. ‘fitti’ strain was least stressed when associating with hosts that significantly altered the expression of 184 genes under cold shock; it was most stressed in hosts that only adjusted 14 genes. Key expression differences among hosts were related to redox signaling and iron availability pathways. Fine-scale interactions among unique host colonies and symbiont strains provide an underappreciated source of raw material for natural selection in coral symbioses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Reef ecosystems thrive thanks to a mutualism between scleractinian corals and photosynthetic dinoflagellates in the genus Symbiodinium1. These endosymbiotic algae are sheltered within host cells, so biochemical changes in one partner directly impact the other's cellular environment2. Sustained hot or cold stress can cause symbiont loss known as coral bleaching3,4, driving fitness consequences ranging from reduced host reproductive output to colony death5. These selective pressures act on physiological variation among coral-dinoflagellate symbioses, potentially leading to local adaptation of each partner6,7. However, the contribution of physiological variation among individuals to functional variation among combined holobionts is poorly understood.
Phenotypic differences among individuals engaged in symbiosis act synergistically to expand the range of holobiont functional diversity subject to selective pressures8. Such interactive genetic effects are observed in diverse systems including insect-bacteria, plant-bacteria and plant-fungus associations9. Climate change intensifies selection among coral holobionts, but uncertainty surrounds the rate at which corals and their symbionts may acclimate or adapt to a changing environment10. Adjacent colonies with identical host and symbiont compositions at the species level show different bleaching susceptibilities11,12, indicating that intraspecific variation exists. Despite renewed emphasis on the fundamental concept that natural selection acts on variation among individuals within species13, our understanding of the adaptive significance of fine-scale genetic effects in coral holobionts is still in its infancy9.
To date, most studies have focused on stress performance among corals associating with unique Symbiodinium taxa (ranging from species to higher order clades). For a given coral species, colonies paired with stress-resistant symbiont taxa often perform differently than colonies paired with stress-sensitive taxa. Such colonies might be more tolerant to increased temperatures14, grow more slowly15, exhibit altered transcription16 and possess distinct heritabilities for holobiont traits17. Interactions below the species level have received less attention, though they may produce similar effects18. For example, at the population level, holobiont thermotolerance and host gene expression vary between two genetically-differentiated populations of a coral species despite sharing one symbiont species across sites19,20. Conversely, thermotolerance varies among groups of coral juveniles reared with different populations of a particular symbiont species despite belonging to a single host population7.
Differences have also been observed among individuals within coral populations. Experimental crosses between genotyped colonies reveal incompatibilities among parents in terms of fertilization rates and larval survival21. Moreover, batches of symbiont-free, half-sibling larvae exhibit different physiological and molecular responses to temperature stress depending on the identity of the sperm donor21,22. However, host genotype effects on symbiont performance have not been documented in adult colonies because the symbiont community has not been measured at the same fine-scale resolution. Although manipulation of the symbiont community is possible in coral juveniles, a major drawback of this approach is that during early development most corals lack the Symbiodinium specificity characteristic of adults23. Thus, juvenile symbiosis dynamics are not necessarily representative of mature associations.
Here, we investigated functional diversity among coral holobionts at the finest scale possible, using neutral markers to resolve both partners to the level of individuals within species. We took advantage of the Acropora palmata—Symbiodinium ‘fitti’ system, where the mature coral usually associates with just one symbiont species and each host colony harbors only one asexually-derived symbiont strain24. This allowed us to identify genetically distinct host colonies sharing the same S. ‘fitti’ strain. We exposed these colonies to cold temperature shock to test the hypothesis that host genotype influences the photochemical stress response of a resident clonal symbiont in hospite. We also tracked host gene expression to identify molecular pathways involved in the interaction.
Results
Host diversity and symbiont uniformity
Based on microsatellite alleles, there were at least 15 Acropora palmata genotypes and nine Symbiodinium ‘fitti’ strains present on the reef sampled in Puerto Morelos, Mexico (Supplementary Table S1). In the experimental colonies (highlighted in Supplementary Table S1 and referred to as host multilocus genotypes A, B, D, X, Y and Z), only one Symbiodinium ITS2 type was present in each colony as indicated by the ITS2 DGGE profile and sequence characteristic of S. ‘fitti’ (sensu Symbiodinium type A3 from the Caribbean, Genbank Accession: AF333507)25. More sensitive qPCR assays failed to detect any background symbionts from the other clades known to associate with Caribbean corals (Clades B, C and D; Supplementary Fig. S1). Furthermore, each colony contained only a single strain (clone) of S. ‘fitti’ based on allele homogeneity at all loci. Thus, each holobiont represented a unique pairing of a single host and a single symbiont genotype, where all hosts were distinct and all resident symbiont populations were essentially identical. All six colonies were located in close proximity to each other. Fragments of each colony were exposed to cold shock in aquaria.
Symbiont photochemistry
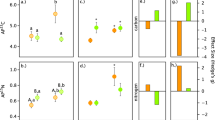
The photochemistry of the S. ‘fitti’ strain as measured by the quantum yield of charge separation of photosystem II (ΔF/Fm?; Fig. 1A,B) and the maximum excitation pressure over photosystem II (Qm; Fig. 1C) varied under ambient (27 °C) and cold (20 °C) conditions. Although solar radiation and Qm fluctuated from day to day, the cold treatment effect (ΔQm) remained remarkably stable (Fig. 1A,B). A repeated measures analysis revealed that the day of observation was not a significant factor (ANOVA, F2,10 = 0.738, α = 0.05, p = 0.502); we therefore treated values from different days as technical replicates to obtain measures of error for each host background. All data sets were normally distributed.
Physiology of an isoclonal Symbiodinium ‘fitti’ strain found in six genetically distinct Acropora palmata colonies.
Shown are diurnal oscillations in the quantum yield of charge separation for photosystem II over the course of the experiment for (A) ‘small ΔQm’ colonies (hosts B and Z; later referred to as ‘Dynamic’) and (B) ‘large ΔQm’ colonies (hosts A, D, X, and Y; later referred to as ‘Static’). The vertical line indicates when cold shock treatment began. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals for either two or four holobiont measurements, respectively. (C) Reaction norm of pressure over photosystem II (Qm) for ambient and cold exposure. (D) The difference in pressure over photosystem II between cold and ambient exposure (ΔQm). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals for three measurements per fragment (one per day of exposure).
Holobionts with clonal symbionts differed in ΔQm (ANOVA, F5,12 = 7.582, α = 0.05, p = 0.002; Fig. 1D), with the average change under cold stress ranging from +0.12 ± 0.08 (s.d.) in the host B background to +0.43 ± 0.03 (s.d.) in the host D background. Positive values indicate a decrease in photochemical efficiency, so while all holobionts were negatively impacted by cold shock, the effect on the S. ‘fitti’ strain was less pronounced in certain host backgrounds (those with ‘small ΔQm’) than in others (those with ‘large ΔQm’). A post-hoc test confirmed the existence of two homogenous subgroups: the ‘small ΔQm’ group containing colonies B and Z and the ‘large ΔQm’ group containing colonies Z, A, D, X and Y (Tukey's HSD, α = 0.05). Although colony Z was statistically intermediate, we elected to classify it in the ‘small ΔQm’ group on the basis that all of its ΔQm values (3/3) fell below the mean for all ΔQm observations. This made it more similar to colony B (3/3 below the mean) than to colonies A (1/3 below the mean), D (0/3 below the mean), X (1/3 below the mean) and Y (0/3 below the mean).
When testing for other differences among holobionts prior to the experimental treatment, we observed deviations in symbiont density (ANOVA, F5,24 = 76.34, α = 0.05, p < 0.001; Supplementary Fig. S2A) but not cell ellipsoid volume (ANOVA, F5,234 = 1.78, α = 0.05, p = 0.119; Supplementary Fig. S2C). ΔQm did not correlate with either metric in simple linear regressions (density: R2 = 7.4%, n = 6, α = 0.05, p = 0.603; volume: R2 = 8.1%, n = 6, α = 0.05, p = 0.536; Supplementary Fig. S2B,D).
Host gene expression
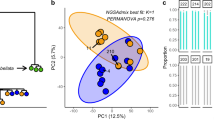
Using a host-specific microarray to contrast the most extreme colonies (B and Z vs. D and Y), the combination of two photochemical phenotypes and two temperature treatments yielded four gene expression profiles. Hierarchical clustering and principle component analysis (PCA) on expression profiles supported similar groupings (Fig. 2A,B). The first PCA axis explained a majority of the total variation (41.35%) and corresponded to a split between ‘small ΔQm’ (a.k.a. Dynamic) colonies and ‘large ΔQm’ (a.k.a. Static) colonies (see below). The second PCA axis explained 34.63% of the total variation and corresponded to a split between cold and ambient temperature treatments.
Acropora palmata microarray clustering.
(A) Unrooted hierarchical clustering of samples based on expression profiles as calculated in R using the hclust function and complete linkage agglomeration method. (B) Principle components 1 and 2 (x- and y-axis, respectively) of sample gene expression as calculated in R using the prcomp function and a covariance matrix. PC1 is associated with colony phenotype (Static or Dynamic), while PC2 is associated with temperature treatment (cold or ambient).
Under cold shock, hosts with symbionts showing a ‘small ΔQm’ photochemical response significantly altered expression of 184 probes (FDR q < 0.05; Fig. 3A,B). These differentially expressed probes (DEPs) comprised 54 unique genes with annotation information (Supplementary Table S2). Given the relatively large transcriptional response, we refer to these holobionts as ‘Dynamic.’ In contrast, hosts with symbionts showing a ‘large ΔQm’ response altered only 14 DEPs comprising 2 unique, annotated genes (Fig. 3A,B; Supplementary Table S2). We refer to these holobionts as ‘Static.’ Within temperature treatments, there was a total of 103 DEPs in the Dynamic vs. Static holobiont contrast—16 unique, annotated genes—indicating fixed expression differences (Fig. 3C,D; Supplementary Table S3). No transcripts showed a photochemical phenotype by temperature treatment interaction. ΔQm and total number of cold shock DEPs were marginally correlated at a relaxed α = 0.1 (R2 = 87.1%, p = 0.067; Fig. 4), but note the small sample size (n = 4) and the dependence among DEP counts within photochemistry categories due to combining replicates for the differential expression analysis.
Differential expression quantification.
(A) The total number of differentially expressed probes (DEPs) in response to temperature (‘cold’ or ‘ambient’) that were unique or shared among Static or Dynamic hosts and (B) overlap in the number of annotated, nonredundant, differentially expressed genes (top number) and probes (bottom number in parentheses) that were significant (FDR q < 0.05) for cold vs. ambient contrasts. (C) The total number of probes differentially expressed in response to colony phenotype (‘large’ or ‘small’ ΔQm; aka ‘Static’ or ‘Dynamic’) that were unique or shared among cold- or ambient-treated hosts and (D) overlap in the number of annotated, nonredundant, differentially expressed genes (top number) and probes (bottom number in parentheses) that were significant (FDR q < 0.05) for Static vs. Dynamic colony phenotype contrasts.
Correlation between the photochemistry (ΔQm) of an isoclonal Symbiodinium ‘fitti’ strain and gene expression of four Acropora palmata genotypes (number of differentially expressed probes, or DEPs).
White fills indicate Dynamic host gene expression phenotypes, while gray fills represent Static host gene expression phenotypes. Note that combining replicates for the differential expression analysis led to dependence among DEP counts within photochemistry categories.
When comparing cold stress responses in each group side-by-side (Fig. 5), many of the significantly upregulated genes in Dynamic hosts were also upregulated in Static hosts, but the magnitude of the change was small, rendering them statistically insignificant. Genes differentially expressed between cold and ambient temperatures in Dynamic holobionts were involved in redox maintenance, transmembrane transport and calcium and redox signaling. The gene list was functionally enriched for the GO terms signal transduction, response to stimulus, (ribo)nucleotide metabolic processes and biological regulation. Static hosts were fixed for greater expression of genes involved in oxidative stress response (specifically iron availability) and redox signaling regardless of temperature treatment. This gene list was functionally enriched for ion binding.
Expression heatmaps.
The transcription profile for all 54 annotated genes with significant differential expression in Dynamic hosts responding to cold stress (FDR q < 0.05) is shown as a heatmap of scaled expression coefficients (standard scores above or below the gene mean), along with a heatmap for the same genes in Static hosts. Asterisks precede genes that also showed significant expression differences in Static hosts (FDR q < 0.05).
Discussion
We found that a single, isoclonal Symbiodinium ‘fitti’ strain’s photochemical response to cold shock varied when engaged in symbiosis with six genetically distinct Acropora palmata colonies (Fig. 1). These responses correlated with detectable host transcription changes (Figs 2, 3, 4, 5). Differences among colonies could not be attributed to background symbiont strains (Supplementary Fig. S1), symbiont cell density (Supplementary Fig. S2A,B), symbiont size (Supplementary Fig. S2C,D), or environmental heterogeneity. Because the dominant symbiont cells were genetically uniform at ten microsatellite markers and no other Symbiodinium were detected, host genotype emerged as the likely factor determining symbiont stress response phenotype in our experiment.
Genetic variation among S. ‘fitti’ strains as identified with 10 microsatellite loci is far greater than variation within strains24. However, even small somatic differences can result in phenotypic differences between ‘clonal populations’ in some systems (e.g. Cryptococcus neoformans)26. Assessing intracolony heterogeneity in the performance of the dominant symbiont strain was outside the scope of this work, but such diversity, if present, might have also contributed to the observed variation in ΔQm along with host genotype. Additional factors that may have been important but could not be accounted for in this experiment included the impact of other organisms associated with the coral microbiota (e.g. archae, viruses and bacteria), environmental microvariation at scales <0.5 m and epigenetic factors. However, epigenetic factors would be confounded with host genotype and environmental microvariation was at least absent in the aquaria. If members of the microbial community other than Symbiodinium played a role, they would have had to differ consistently among host genotype groups. Hence, while these factors represent interesting targets for future studies, the observed differences in symbiont stress response are difficult to explain without considering the host genotype as important.
Cold temperatures slow the rates of electron transport and carbon fixation, decreasing photosystem II yield (ΔF/Fm?) and increasing maximal excitation pressure (Qm). As expected, we observed elevated Qm in all six holobiont fragments exposed to cold shock. However, the magnitude of change in pressure (ΔQm) varied up to 3.6-fold among holobionts despite the clonality of the S. ‘fitti’ strain shared by all colonies. Multiple host expression changes took place in colonies where the S. ‘fitti’ photoresponse was minimal (‘Dynamic’ hosts), whereas in the remaining colonies, host transcription changes were muted (‘Static’ hosts) and symbionts experienced greater fluctuation and diminishment in photochemical efficiency (Fig. 4). These responses may indicate a phenotypic buffering effect27, where symbiont performance is maintained within a narrow physiological range when occurring within Dynamic hosts.
Based on gene identities and expression patterns, we propose that the capacity of the host to manage its cellular environment, specifically redox state and iron availability, affects the resident symbiont’s cold stress response. We observed three types of gene expression responses: (1) cold shock genes that changed in Dynamic hosts but not Static hosts, (2) cold shock genes that changed in both types of host (but to a more extreme degree in Dynamic hosts) and (3) fixed differences in gene expression between Static and Dynamic hosts. We discuss examples of each expression pattern below.
The first category of genes includes those that changed only in Dynamic hosts under thermal stress. For example, Dynamic corals increased glutaredoxin expression 5.6-fold in response to cold shock, while expression remained constant in Static corals. Glutaredoxins facilitate electron transfer in the glutathione cycle, which helps to maintain cellular redox homeostasis (Fig. 6A)28. Cold shock inhibits photochemistry and induces Symbiodinium to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which can diffuse into host cells29. Because H2O2 can serve as an electron carrier in the glutathione cycle30, stressed symbionts may directly disrupt host redox homeostasis, signaling the host nucleus much like a plant chloroplast signals the plant nucleus during stress31. In turn, the host may modify its cellular environment through glutaredoxin-mediated thiol signaling, which can induce downstream transcriptional adjustments that include antioxidant activity28. Such adjustments may reduce the stress experienced by the symbiont, perhaps explaining why Symbiodinium in Dynamic hosts appeared to be less compromised during cold shock.
Mechanistic models for molecular interactions between partners related to (A) glutaredoxin and redox signaling and (B) ferritin and iron availability.
Lines connect interacting molecules or processes. Terminal arrows indicate activation or enhancement, terminal straight lines indicate inhibition. Terms in dashed squares represent targets of positive or negative regulation.
The second category includes a set of cold shock genes that were upregulated in all corals, but the magnitude of the change was smaller in Static hosts relative to Dynamic hosts. As a result, only the changes in Dynamic hosts were statistically significant. This pattern suggests that different coral genotypes fundamentally respond to cold stress in similar ways. Rather than using a separate set of genes that may have buffered symbiont performance, Dynamic hosts accentuated an existing response. The mechanism may relate once again to glutaredoxin. For example, eight ‘accentuated’ genes encoded proteins with disulfide bonds (Supplementary Table S3), which can be targeted by glutaredoxin-mediated thiol signaling32. Because Static hosts did not adjust glutaredoxin levels, they may not have been able to mount a strong transcriptional response (Fig. 5). Regardless of the mechanisms involved, stress-related expression polymorphisms that vary by degree rather than identity are evident within coral populations33 and here we show that at least some of them correspond to variation in the performance of a Symbiodinium clone.
The third and final category includes genes that showed fixed differences in expression among coral genotypes regardless of the treatment temperature. For hosts with Static gene expression patterns, both control and experimental colonies appeared to exhibit greater levels of sustained expression in certain genes relative to that found in hosts with Dynamic expression patterns. For example, three ferritin-related genes were expressed 5- to 22-fold higher in Static hosts under both ambient and cold conditions (Supplementary Table S3). Ferritin acts as an iron-sequestration molecule, importantly reducing the availability of free iron for spontaneous ROS generation via the Fenton pathway (Fig. 6B)34. Symbiodinium appear to be iron-limited in hospite35 and likely rely on the host as an iron source. Because ferritin expression levels generally reflect the size of the free iron pool in the cell36, host ferritin levels may dictate symbiont iron limitation, affecting both symbiont and host performance. This may explain why at least one ferritin gene in A. palmata appears to be under intense positive selection37.
The maintenance of phenotypic polymorphisms may be favored in the presence of spatial and temporal environmental variability38. We observed distinct stress responses among the six holobionts in our study; had more genotypes been included in the experiment, more extreme and intermediate phenotypes might have been recovered. While each phenotype is apparently functional, relative success may depend on whether the environment is stable or fluctuating. For example, Static hosts with elevated ferritin (and therefore high levels of free iron available to their symbionts) may benefit from enhanced Symbiodinium performance provided conditions remain stress-free. Indeed, we found improved photochemical efficiency (i.e. lower ambient Qm) among Static colonies at ambient temperature relative to Dynamic colonies (Fig. 1C; t-test, p = 0.049). During temperature anomalies, however, excess iron ions may become a liability as they promote ROS production and tissue damage39,40. In contrast, the symbionts in Dynamic hosts are not as photochemically efficient at ambient temperature, but their efficiency does not decline as severely during stress. Such a trade-off may support polymorphism within the mutualism. Further experiments encompassing more genotypes, more natural temperature conditions and longer acclimation periods will enable a better understanding of the ecological relevance of these findings.
Hot and cold temperature anomalies can lead to widespread coral mortality12,41, guiding the outcomes of natural selection42. Given that physiological variation exists within species of coral hosts and dinoflagellate symbionts, it is important to recognize that the holobiont is a unit of selection in these symbioses12,43,44,45. The variation resulting from interactions between particular host and symbiont genotypes may play a role in the evolutionary response to climate change, an important consideration when predicting the status of coral mutualisms in the future46. Selection may be particularly strong for alleles affecting the molecular pathways linked to symbiosis maintenance and photochemistry during temperature stress, such as those outlined here. Intriguingly, only Dynamic hosts appeared to participate in the annual synchronized spawning event in Puerto Morelos, whereas none of the Static hosts spawned (Parkinson et al., personal observation). Though anecdotal, this pattern is compelling because it suggests holobionts composed of different host-symbiont genotype pairings may also have different fitness outcomes, providing raw material for natural selection.
This study provides new evidence of functional diversity among individual coral colonies. Our finding that genotype interactions among host and symbiont individuals can influence population-level dynamics emphasizes the need to preserve existing genotypic richness in coral populations18. While not investigated here, the maintenance of symbiont genotypic diversity may also be important when managing reefs or designing coral restoration nurseries. Though it is rare to find adult A. palmata coral clone mates with different S. ‘fitti’ strains24, such cases will be necessary to test how holobiont physiology varies with symbiont genotype, to provide a more concrete link between genotype interactions and fitness effects and to draw accurate conclusions about micro-coevolution. Coral-dinoflagellate interactions have rarely been studied at this level of genetic resolution in the past, but given their potential ecological and evolutionary significance, they merit further investigation.
Materials and Methods
Study system
The Caribbean Elkhorn coral, Acropora palmata, primarily associates with one phylogenetic lineage of Symbiodinium (ITS2 type A3)47. Based on hierarchical molecular markers (LaJeunesse et al. unpublished data), the Caribbean A3 lineage represents a cohesive species and is provisionally termed Symbiodinium ‘fitti’ nomen nudum48. The host spawns symbiont-free gametes, so S. ‘fitti’ cells must be acquired from the environment by each generation. Within host tissues, the haploid symbiont mostly propagates asexually via cell division24,49, meaning each coral can be viewed as a culture vessel for a single symbiont strain.
Host and symbiont genotyping
In Spring 2011, colonies of A. palmata (n = 20) were sampled from La Bocana Chica Reef in the Puerto Morelos Reef National Park, Mexico (N 20°52.461′, W 86°51.073′). For each colony, the host was genotyped at five neutral microsatellite loci50 and the S. ‘fitti’ strains were genotyped at ten microsatellite loci48. These ten markers were sensitive enough to detect multiple strains in a single host colony provided the minor strains each represented ≥5% of the symbiont community24. Tissues of colonies sharing identical alleles at all A. palmata loci (or S. ‘fitti’ loci) were deemed to be clone mates of the same host genotype (or symbiont strain). The chance of misidentifying two colonies (or strains) as clonal when in fact they were distinct (the probability of identity) was on the order of 10−7 for the host (or 10−5 for the symbiont)24.
Six holobionts (the ‘experimental colonies’) were targeted for further study based on three criteria: each colony hosted only one isoclonal S. ‘fitti’ strain; the symbiont strain was identical across colonies; and each host represented a unique genotype (see Results). All colonies were found at the same depth (~3 m) distributed between two clusters ~30 m apart: one with four colonies and one with two colonies. Within each cluster, all colonies were located within 0.5 m of each other and it was later revealed that each cluster included at least one Dynamic coral and one Static coral. Though disturbances can contribute to intraspecific physiological variation51, this 'natural common garden' reduced historical environmental heterogeneity. For microhabitat variation to account for the observed differences among colonies, it would have had to occur over spatial scales <0.5 m. All colonies greatly exceeded minimum reproductive size (55 cm along the longest length of live tissue)52 and were therefore expected to spawn.
Because corals sometimes host more than one species of Symbiodinium from different clades, the experimental colonies were further screened with denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) following PCR of the ITS2 region, which detects sub-cladal types that represent ≥5–10% of the total symbiont community25,47. The region was amplified using the primers ITSintFor2 and ITS2CLAMP and bands were visualized on a denaturing gradient gel53. Representative bands were excised, re-amplified with the same primers less the GC-rich clamp and directly sequenced on an Applied Biosciences sequencer (Applied Biosciences, Foster City, CA, USA) at the Pennsylvania State University Genomics Core Facility. Electropherograms were checked visually using CodonCode Aligner software (CodonCode, Dedham, MD, USA).
Though background Symbiodinium from Clades B, C and D have occasionally been detected in A. palmata at low abundance54, only S. ‘fitti’ strains from Clade A are present at appreciable levels in most colonies throughout the Caribbean24,47. Nevertheless, we used clade-specific qPCR assays to test for the presence of these other coral-associated Caribbean symbionts (for methodology, see Supplementary Fig. S1)55,56. We did not check for the primarily free-living, Pacific, or foram/sponge-associated Clades E-I, as their detection would more likely be explained by environmental contamination rather than true endosymbiosis in this system.
Cold stress experiment
In Summer 2011, single fragments (~30 cm2) from the six experimental colonies were collected with hammer and chisel from the growing tip at the top of each coral and transported to a 45 L polycarbonate bin containing filtered seawater maintained at 29 °C to match that day’s reef conditions. The outdoor bin was covered with a neutral density shade cloth that reduced natural irradiance by ~50% relative to full sunlight. The fragments were subdivided into 2 separate pieces of ~10 cm2 each containing tens of individual polyps. After 2 d of acclimation, the temperature treatments began. One piece of each colony was transferred to a shaded 45 L polycarbonate bin containing filtered seawater precooled to ambient (27 °C) conditions. The other piece of each colony was transferred to a bin precooled to extreme cold conditions (20 °C). Temperatures in the bins were maintained with aquarium chillers (Current-USA, CA, USA). Water was circulated with an aquarium pump and changed daily with additional precooled filtered seawater. The fragments were maintained in the treatments for 3 d (until the evening of the third day of exposure) to ensure that the photochemical response was stable. HOBO data loggers (Onset Co., MA, USA) in each bin confirmed that temperatures stayed within ±0.4 °C of the target for each treatment.
The ambient temperature was decreased slightly relative to reef temperature to reduce the risk of unintended bleaching during the experiment. The cold temperature was extreme compared to what the colonies would naturally experience on the reef. Temperatures were not ramped, such that the corals were exposed to instantaneous temperature shock. Given time restrictions at the field site and the expectation that intraspecific differences might be subtle, the exposure was designed not to mimic natural conditions, but to accentuate differences in acute cold shock responses among holobionts. Despite the extreme conditions, all corals survived the experimental treatment.
Symbiont photochemical efficiency and other phenotypes
The in situ photochemical efficiency of the S. ‘fitti’ strain was estimated using a Diving PAM fluorometer (Walz, Germany) with the following settings: Measuring Intensity 12, Saturation Intensity 8, Saturation Width 0.6 s, Damping 2 and Gain 3. For the cold and ambient treatments, maximum excitation pressure over photosystem II (Qm) was calculated daily for each colony as Qm = 1 - [(ΔF/Fm? at noon)/(Fv/Fm at dusk)]57. Qm is a normalized metric that removes the influence of daily fluctuations in solar radiation between clear and overcast days from the factor of interest (in this case temperature). It ranges from 0, where photochemistry is light-limited, to 1, indicating photoinhibition, though photosynthetic performance and pressure do not follow a linear relationship. Generally, negative effects on photosynthetic output are not observed below pressure values of 0.6 (R. Iglesias-Prieto, personal communication). To isolate the effect of cold shock, the Qm of the fragment of a given colony in the ambient treatment was subtracted from the Qm of the corresponding fragment of the same colony in the cold treatment to calculate ΔQm. Thus, ΔQm was comparable among colonies. This normalized metric reflected the relative degree to which the clonal S. ‘fitti’ strain adjusted photochemically to cold stress in different host genotype backgrounds.
Prior to cold exposure, each colony’s average symbiont density and cell volume were determined. Replicate hemocytometer cell counts (n = 5) were taken from a single 1 cm2 tissue plug per colony. Ellipsoid cell volumes were estimated as 4π(abc)•3−1, where a is half the cell’s longest diameter and b and c are taken as half the perpendicular diameter (n = 40 cells per colony). Additionally, all A. palmata colonies at the study site in Puerto Morelos, including those that were not used in this experiment, were observed for signs of annual synchronized spawning between 20:00 h and 23:00 h from Aug. 15–19 by SCUBA divers.
Microarray experiment
The host’s acute response to cold stress was assessed through global gene expression using a microarray designed from the A. palmata transcriptome58. To incorporate biological replication, we included separate RNA extracts from the two host colonies with the smallest symbiont ΔQm (hosts B and Z) and the two host colonies with the largest symbiont ΔQm (hosts D and Y). Total RNA was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, CA, USA) from subsamples of each host colony (n = 4) at each temperature (n = 2) taken 3.5 h after exposure to treatment. Concentration and quality of RNA extracts were quantified on a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, MA, USA) and an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA). High-quality mRNA was hybridized to custom 2-channel microarrays (Nimblegen 6019040401) following published methods22. Associated raw data and a more detailed description of hybridization conditions can be accessed at the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus database through GEO Series accession number GSE50926 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE50926].
Statistical analysis
To analyze photochemistry, ΔQm values for each fragment from all three days were included in repeated measure and one-way ANOVAs in the R statistical environment. Expression data were analyzed in R using the Bioconductor package LIMMA [http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/limma.html] following published methods22. A log base 2 fold change cut-off of 1.5 (=fold change cut-off of 2.8) and false discovery rate (FDR) q-value threshold of 0.05 were used to filter significant results. To visualize transcription profiles, expression values were transformed gene-wise into scaled coefficients (standard scores above or below the probe mean) and plotted as heat maps with MultiExperiment Viewer v4.9 [http://www.tm4.org/mev.html]. An unrooted sample tree was created through hierarchical clustering of expression profiles using the hclust function with the complete linkage agglomeration method in R. Principle component analysis was carried out using the prcomp function and a covariance matrix in R. Lists of differentially expressed genes were analyzed for functional enrichment using default parameters in the online tool GOEAST v1.3 [http://omicslab.genetics.ac.cn/GOEAST/tools.php] based on the original annotation file associated with the microarray. A list of all differentially expressed genes and the R code used in the expression analysis can be accessed in the Pennsylvania State University’s ScholarSphere database [https://scholarsphere.psu.edu/files/8623j6166].
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Parkinson, J. E. et al. Intraspecific diversity among partners drives functional variation in coral symbioses. Sci. Rep. 5, 15667; doi: 10.1038/srep15667 (2015).
References
Baker, A. C. Flexibility and specificity in coral-algal symbiosis: diversity, ecology and biogeography of Symbiodinium. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 34, 661–689 (2003).
Davy, S. K., Allemand, D. & Weis, V. M. Cell biology of cnidarian-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 76, 229–261 (2012).
Jokiel, P. L. & Coles, S. L. Response of Hawaiian and other Indo-Pacific reef corals to elevated temperature. Coral Reefs 8, 155–162 (1990).
Saxby, T., Dennison, W. C. & Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Photosynthetic responses of the coral Montipora digitata to cold temperature stress. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 248, 85–97 (2003).
Szmant, A. M. & Gassman, N. J. The effects of prolonged bleaching on the tissue biomass and reproduction of the reef coral Montastrea annularis. Coral Reefs 8, 217–224 (1990).
Polato, N. R., Concepcion, G. T., Toonen, R. J. & Baums, I. B. Isolation by distance across the Hawaiian Archipelago in the reef-building coral Porites lobata. Mol. Ecol. 19, 4661–4677 (2010).
Howells, E. J. et al. Coral thermal tolerance shaped by local adaptation of photosymbionts. Nat. Clim. Change 2, 116–120 (2012).
Rodriguez, R. J., White, J. F., Arnold, A. E. & Redman, R. S. Fungal endophytes: diversity and functional roles. New Phytol. 182, 314–330 (2009).
Parkinson, J. E. & Baums, I. B. The extended phenotypes of marine symbioses: ecological and evolutionary consequences of intraspecific genetic diversity in coral-algal associations. Front. Microbiol. 5, 445 (2014).
Brown, B. E. & Cossins, A. R. The potential for temperature acclimatisation of reef corals in the face of climate change. In: Coral Reefs: An Ecosystem in Transition (eds. Dubzinsky, Z. & Stambler, N. ). (Springer 2011).
Glynn, P. W., Mate, J. L., Baker, A. C. & Calderon, M. O. Coral bleaching and mortality in Panama and Ecuador during the 1997-1998 El Nino-Southern oscillation event: spatial/temporal patterns and comparisons with the 1982-1983 event. Bull. Mar. Sci. 69, 79–109 (2001).
LaJeunesse, T. C. et al. Host-symbiont recombination versus natural selection in the response of coral-dinoflagellate symbioses to environmental disturbance. P. Roy. Soc. Lond. B. Bio. 277, 2925–2934 (2010).
Bolnick, D. I. et al. Why intraspecific trait variation matters in community ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 26, 183–192 (2011).
Abrego, D., Ulstrup, K. E., Willis, B. L. & van Oppen, M. J. H. Species-specific interactions between algal endosymbionts and coral hosts define their bleaching response to heat and light stress. P. Roy. Soc. Lond. B. Bio. 275, 2273–2282 (2008).
Little, A. F., Van Oppen, M. J. & Willis, B. L. Flexibility in algal endosymbioses shapes growth in reef corals. Science 304, 1492–1494 (2004).
DeSalvo, M. K. et al. Coral host transcriptomic states are correlated with Symbiodinium genotypes. Mol. Ecol. 19, 1174–1186 (2010).
Csaszar, N. B. M., Ralph, P. J., Frankham, R., Berkelmans, R. & van Oppen, M. J. H. Estimating the potential for adaptation of corals to climate warming. Plos One 5, e9751 (2010).
Baums, I. B. A restoration genetics guide for coral reef conservation. Mol. Ecol. 17, 2796–2811 (2008).
Kenkel, C. D. et al. Evidence for a host role in thermotolerance divergence between populations of the mustard hill coral (Porites astreoides) from different reef environments. Mol. Ecol. 22, 4335–4348 (2013).
Kenkel, C. D., Meyer, C. & Matz, M. V. Gene expression under chronic heat stress in populations of the mustard hill coral (Porites astreoides) from different thermal environments. Mol. Ecol. 22, 4322–4334 (2013).
Baums, I. B. et al. Genotypic variation influences reproductive success and thermal stress tolerance in the reef building coral, Acropora palmata. Coral Reefs 32, 703–717 (2013).
Polato, N. R., Altman, N. S. & Baums, I. B. Variation in the transcriptional response of threatened coral larvae to elevated temperatures. Mol. Ecol. 22, 1366–1382 (2013).
Coffroth, M. A., Santos, S. R. & Goulet, T. L. Early ontogenetic expression of specificity in a cnidarian-algal symbiosis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 222, 85–96 (2001).
Baums, I. B., Devlin-Durante, M. K. & LaJeunesse, T. C. New insights into the dynamics between reef corals and their associated dinoflagellate endosymbionts from population genetic studies. Mol. Ecol. 23, 4203–4215 (2014).
LaJeunesse, T. C. Diversity and community structure of symbiotic dinoflagellates from Caribbean coral reefs. Mar. Biol. 141, 387–400 (2002).
Ormerod, K. L. et al. Comparative genomics of serial isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans reveals gene associated with carbon utilization and virulence. G3 3, 675–686 (2013).
Reusch, T. B. Climate change in the oceans: evolutionary versus phenotypically plastic responses of marine animals and plants. Evol. Appl. 7, 104–122 (2014).
Holmgren, A. & Fernandes, A. P. Glutaredoxins: glutathione-dependent redox enzymes with functions far beyond a simple thioredoxin backup system. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 6, 63–74 (2004).
Saragosti, E., Tchernov, D., Katsir, A. & Shaked, Y. Extracellular production and degradation of superoxide in the coral Stylophora pistillata and cultured Symbiodinium. Plos One 5, e12508 (2010).
Winterbourn, C. C. & Hampton, M. B. Thiol chemistry and specificity in redox signaling. Free Radical Biol. Med. 45, 549–561 (2008).
Huner, N. P. A., Oquist, G. & Sarhan, F. Energy balance and acclimation to light and cold. Trends Plant Sci. 3, 224–230 (1998).
Buchanan, B. B. & Balmer, Y. Redox regulation: a broadening horizon. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 56, 187–220 (2005).
Barshis, D. J. et al. Genomic basis for coral resilience to climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 1387–1392 (2013).
Torti, F. M. & Torti, S. V. Regulation of ferritin genes and protein. Blood 99, 3505–3516 (2002).
Entsch, B., Sim, R. G. & Hatcher, B. G. Indications from photosynthetic components that iron is a limiting nutrient in primary producers on coral reefs. Mar. Biol. 73, 17–30 (1983).
Kakhlon, O. & Cabantchik, Z. I. The labile iron pool: characterization, measurement and participation in cellular processes. Free Radical Biol. Med. 33, 1037–1046 (2002).
Schwarz, J. A. et al. Coral life history and symbiosis: functional genomic resources for two reef building Caribbean corals, Acropora palmata and Montastraea faveolata. BMC Genomics 9, 435 (2008).
Levins, R. Evolution in Changing Environments. (Princeton University Press, 1968).
Allakhverdiev, S. I. et al. Heat stress: an overview of molecular responses in photosynthesis. Photosynthesis Res. 98, 541–550 (2008).
Allen, D. J. & Ort, D. R. Impacts of chilling temperatures on photosynthesis in warm-climate plants. Trends Plant Sci. 6, 36–42 (2001).
Kemp, D. W. et al. Catastrophic mortality on inshore coral reefs of the Florida Keys due to severe low-temperature stress. Global Change Biol. 17, 3468–3477 (2011).
Guest, J. R. et al. Contrasting patterns of coral bleaching susceptibility in 2010 suggest an adaptive response to thermal stress. Plos One 7, e33353 (2012).
Iglesias-Prieto, R. & Trench, R. K. Photoadaptation, photoacclimation and niche diversification in invertebrate-dinoflagellate symbioses. Proc. 8th Int. Coral Reef Symp. 2, 1319–1324 (1997).
Prada, C. et al. Cryptic diversity hides host and habitat specialization in a gorgonian-algal symbiosis. Mol. Ecol. 23, 3330–3340 (2014).
Thornhill, D. J., Lewis, A. M., Wham, D. C. & LaJeunesse, T. C. Host-specialist lineages dominate the adaptive radiation of reef coral endosymbionts. Evolution 68, 352–367 (2014).
Logan, C. A., Dunne, J. P., Eakin, C. M. & Donner, S. D. Incorporating adaptive responses into future projections of coral bleaching. Global Change Biol. 20, 125–139 (2014).
Thornhill, D. J., LaJeunesse, T. C., Kemp, D. W., Fitt, W. K. & Schmidt, G. W. Multi-year, seasonal genotypic surveys of coral-algal symbioses reveal prevalent stability or post-bleaching reversion. Mar. Biol. 148, 711–722 (2006).
Pinzon, J. H., Devlin-Durante, M. K., Weber, M. X., Baums, I. B. & LaJeunesse, T. C. Microsatellite loci for Symbiodinium A3 (S. fitti) a common algal symbiont among Caribbean Acropora (stony corals) and Indo-Pacific giant clams (Tridacna). Conserv. Genet. Resour. 3, 45–47 (2011).
Santos, S. R., Shearer, T. L., Hannes, A. R. & Coffroth, M. A. Fine-scale diversity and specificity in the most prevalent lineage of symbiotic dinoflagellates (Symbiodinium, Dinophyceae) of the Caribbean. Mol. Ecol. 13, 459–469 (2004).
Baums, I. B., Miller, M. W. & Hellberg, M. E. Regionally isolated populations of an imperiled Caribbean coral, Acropora palmata. Mol. Ecol. 14, 1377–1390 (2005).
Pisapia, C., Anderson, K. & Pratchett, M. S. Intraspecific variation in physiological condition of reef-building corals associated with differential levels of chronic disturbance. Plos One 9, e91529 (2014).
Lirman, D. Fragmentation in the branching coral Acropora palmata (Lamarck): growth, survivorship and reproduction of colonies and fragments. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 251, 41–57 (2000).
Sampayo, E. M., Dove, S. & LaJeunesse, T. C. Cohesive molecular genetic data delineate species diversity in the dinoflagellate genus Symbiodinium. Mol. Ecol. 18, 500–519 (2009).
Silverstein, R. N., Correa, A. M. S. & Baker, A. C. Specificity is rarely absolute in coral-algal symbiosis: implications for coral response to climate change. P. Roy. Soc. Lond. B. Bio. 279, 2609–2618 (2012).
Correa, A. M. S., McDonald, M. D. & Baker, A. C. Development of clade-specific Symbiodinium primers for quantitative PCR (qPCR) and their application to detecting clade D symbionts in Caribbean corals. Mar. Biol. 156, 2403–2411 (2009).
McGinley, M. P. et al. Symbiodinium spp. in colonies of eastern Pacific Pocillopora spp. are highly stable despite the prevalence of low-abundance background populations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 462, 1–7 (2012).
Iglesias-Prieto, R., Beltran, V. H., LaJeunesse, T. C., Reyes-Bonilla, H. & Thome, P. E. Different algal symbionts explain the vertical distribution of dominant reef corals in the eastern Pacific. P. Roy. Soc. Lond. B. Bio. 271, 1757–1763 (2004).
Polato, N. R., Vera, J. C. & Baums, I. B. Gene discovery in the threatened Elkhorn coral: 454 sequencing of the Acropora palmata transcriptome. Plos One 6, e28634 (2011).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Sergio Guendulain García and Sandra Mendoza Quiroz as well as the staff of the Parque Nacional Arrecife de Puerto Morelos for support during spawning. Many thanks to Jorge Pinzón, Dan Thornhill, James Marden and Roberto Iglesias-Prieto for discussing earlier drafts of the manuscript. Samples were collected under local permit SGPA/DGVS/04973/09 and exchanged between CITES institutions MX-HR-010-MEX (UNAM) and US107(A) (PSU). This research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF DGE-0750756 to JEP; NSF OCE-0928764 to TCL and IBB), the Instituto de Ciencias del Mar y Limnología (Project Number 608 to ATB) and the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (Project Number 153260 to ATB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.E.P. designed the study, performed field work, analyzed genetic, physiological and microarray data and wrote the manuscript. A.T.B. performed field work and analyzed physiological data. N.S.A. analyzed microarray data. T.C.L. designed the study and analyzed genetic and physiological data. I.B.B. designed the study, performed field work and supervised the writing of the manuscript. All authors contributed editorially to the paper.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Parkinson, J., Banaszak, A., Altman, N. et al. Intraspecific diversity among partners drives functional variation in coral symbioses. Sci Rep 5, 15667 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15667
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15667
This article is cited by
-
Bio-optical signatures of in situ photosymbionts predict bleaching severity prior to thermal stress in the Caribbean coral species Acropora palmata
Coral Reefs (2024)
-
Similarities in biomass and energy reserves among coral colonies from contrasting reef environments
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Coral host physiology and symbiont dynamics associated with differential recovery from mass bleaching in an extreme, macro-tidal reef environment in northwest Australia
Coral Reefs (2021)
-
The enhanced expression of heat stress-related genes in scleractinian coral ‘Porites harrisoni’ during warm episodes as an intrinsic mechanism for adaptation in ‘the Persian Gulf’
Coral Reefs (2021)
-
Uncovering the role of Symbiodiniaceae assemblage composition and abundance in coral bleaching response by minimizing sampling and evolutionary biases
BMC Microbiology (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.