Abstract
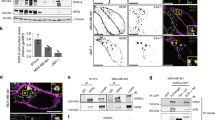
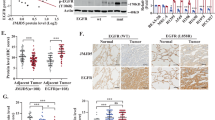
Several distinct mutations within the kinase domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are associated with non-small cell lung cancer, but mechanisms underlying their oncogenic potential are incompletely understood. Although normally ligand-induced kinase activation targets EGFR to Cbl-mediated receptor ubiquitinylation and subsequent degradation in lysosomes, we report that certain EGFR mutants escape this regulation. Defective endocytosis characterizes a deletion mutant of EGFR, as well as a point mutant (L858R-EGFR), whose association with c-Cbl and ubiquitinylation are impaired. Our data raise the possibility that refractoriness of L858R-EGFR to downregulation is due to enhanced heterodimerization with the oncogene product HER2, which leads to persistent stimulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann J, Kalyankrishna S, Massion PP, Ohm JE, Girard L, Shigematsu H et al. (2005). Aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and enhanced sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Res 65: 226–235.
Baulida J, Kraus MH, Alimandi M, Di Fiore PP, Carpenter G . (1996). All ErbB receptors other than the epidermal growth factor receptor are endocytosis impaired. J Biol Chem 271: 5251–5257.
Dikic I, Giordano S . (2003). Negative receptor signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15: 128–135.
Engelman JA, Janne PA, Mermel C, Pearlberg J, Mukohara T, Fleet C et al. (2005). ErbB-3 mediates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in gefitinib-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 3788–3793.
Friedman LM, Rinon A, Schechter B, Lyass L, Lavi S, Bacus SS et al. (2005). Synergistic down-regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases by combinations of mAbs: Implications for cancer immunotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 1915–1920.
Graus Porta D, Beerli RR, Daly JM, Hynes NE . (1997). ErbB-2, the preferred heterodimerization partner of all ErbB receptors, is a mediator of lateral signaling. EMBO J 16: 1647–1655.
Hynes NE, Horsch K, Olayioye MA, Badache A . (2001). The ErbB receptor tyrosine family as signal integrators. Endocr Relat Cancer 8: 151–159.
Karunagaran D, Tzahar E, Beerli RR, Chen X, Graus Porta D, Ratzkin BJ et al. (1996). ErbB-2 is a common auxiliary subunit of NDF and EGF receptors: implications for breast cancer. EMBO J 15: 254–264.
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M et al. (2005). EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. New Engl J Med 352: 786–792.
Kokai Y, Myers JN, Wada T, Brown VI, LeVea CM, Davis JG et al. (1989). Synergistic interaction of p185c-neu and the EGF receptor leads to transformation of rodent fibroblasts. Cell 58: 287–292.
Levkowitz G, Klapper LN, Tzahar E, Freywald A, Sela M, Yarden Y . (1996). Coupling of the c-Cbl protooncogene product to ErbB-1/EGF-receptor but not to other ErbB proteins. Oncogene 12: 1117–1125.
Levkowitz G, Waterman H, Ettenberg SA, Katz M, Tsygankov AY, Alroy I et al. (1999). Ubiquitin ligase activity and tyrosine phosphorylation underlie suppression of growth factor signaling by c-Cbl/Sli-1. Mol Cell 4: 1029–1040.
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW et al. (2004). Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350: 2129–2139.
Marmor MD, Yarden Y . (2004). Role of protein ubiquitylation in regulating endocytosis of receptor tyrosine kinases. Oncogene 23: 2057–2070.
Muthuswamy SK, Gilman M, Brugge JS . (1999). Controlled dimerization of ErbB receptors provides evidence for differential signaling by homo- and heterodimers. Mol Cell Biol 19: 6845–6857.
Ouyang X, Gulliford T, Zhang H, Smith G, Huang G, Epstein RJ . (2001). Association of ErbB2 Ser1113 phosphorylation with epidermal growth factor receptor co-expression and poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 218: 47–54.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S et al. (2004). EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304: 1497–1500.
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I et al. (2004). EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from ‘never smokers’ and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 13306–13311.
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, Rieli GJ, Somwar R, Zakowski MF et al. (2005). Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to Gefitinib or Erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Medicine 2: e73.
Polo S, Sigismund S, Faretta M, Guidi M, Capua MR, Bossi G et al. (2002). A single motif responsible for ubiquitin recognition and monoubiquitination in endocytic proteins. Nature 416: 451–455.
Sigismund S, Woelk T, Puri C, Maspero E, Tacchetti C, Transidico P et al. (2005). Clathrin-independent endocytosis of ubiquitinated cargos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 2760–2765.
Sliwkowski MX, Schaefer G, Akita RW, Lofgren JA, Fitzpatrick VD, Nuijens A et al. (1994). Coexpression of erbB2 and erbB3 proteins reconstitutes a high affinity receptor for heregulin. J Biol Chem 269: 14661–14665.
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J . (2004). Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science 305: 1163–1167.
Tracy S, Mukohara T, Hansen M, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Janne PA . (2004). Gefitinib induces apoptosis in the EGFRL858R non-small-cell lung cancer cell line H3255. Cancer Res 64: 7241–7244.
Waterman H, Alroy I, Strano S, Seger R, Yarden Y . (1999). The C-terminus of the kinase-defective neuregulin receptor ErbB-3 confers mitogenic superiority and dictates endocytic routing. EMBO J 18: 3348–3358.
Waterman H, Katz M, Rubin C, Shtiegman K, Lavi S, Elson A et al. (2002). A mutant EGF-receptor defective in ubiquitylation and endocytosis unveils a role for Grb2 in negative signaling. EMBO J 21: 303–313.
Wells A, Welsh JB, Lazar CS, Wiley HS, Gill GN, Rosenfeld MG . (1990). Ligand-induced transformation by a non-internalizing epidermal growth factor receptor. Science 247: 962–964.
Wiley HS, Burke PM . (2001). Regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling by endocytic trafficking. Traffic 2: 12–18.
Worthylake R, Opresko LK, Wiley HS . (1999). ErbB-2 amplification inhibits down-regulation and induces constitutive activation of both ErbB-2 and epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem 274: 8865–8874.
Yang S, Qu S, Perez-Tores M, Sawai A, Rosen N, Solit DB et al. (2006). Association with HSP90 inhibits Cbl-mediated down-regulation of mutant epidermal growth factor receptors. Cancer Res 66: 6990–6997.
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX . (2001). Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 127–137.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Wallace Langdon and Dirk Bohmann for plasmids. Our laboratory is supported by research grants from the National Cancer Institute (grant CA72981, to YY), the Israel Cancer Research Fund and the German-Israel Foundation. YY is the incumbent of the Harold and Zelda Goldenberg Professorial Chair.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shtiegman, K., Kochupurakkal, B., Zwang, Y. et al. Defective ubiquitinylation of EGFR mutants of lung cancer confers prolonged signaling. Oncogene 26, 6968–6978 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210503
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210503
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Kremen2 drives the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by preventing SOCS3-mediated degradation of EGFR
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases and cancer: oncogenic mechanisms and therapeutic approaches
Oncogene (2021)
-
Drug resistance of targeted therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer harbored EGFR mutation: from mechanism analysis to clinical strategy
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2021)
-
The ubiquitin system: orchestrating cellular signals in non-small-cell lung cancer
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2020)
-
DRAM1 plays a tumor suppressor role in NSCLC cells by promoting lysosomal degradation of EGFR
Cell Death & Disease (2020)