Abstract
Objective:
The role of the central melanocortin system in the development of obesity has been extensively studied. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within several candidate genes have been associated with food intake and obesity-related phenotypes; however, few of these associations have been replicated. SNPs in the agouti-related protein (AGRP) gene coding (Ala67Thr, 199G/A) and promoter (−38C/T) have been reported to be associated with body mass index (BMI), fat mass (FM) and percent body fat, in populations of European and African descent. In this study, we evaluated the association between the functional AGRP −38C/T promoter SNP and weight-related traits, namely BMI, FM and fat-free mass (FFM), as well as diabetes status.
Design:
An association study of the AGRP −38C/T SNP and indices of obesity and diabetes status.
Subjects:
A well-characterized population of 538 West Africans from Ghana and Nigeria recruited in the AADM (Africa America Diabetes Mellitus) study (mean age 52 years, 41.3% males, 71% diabetic).
Measurements:
Genotyping of the AGRP −38C/T SNP, BMI, FM, FFM and fasting plasma glucose.
Results:
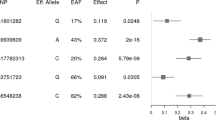
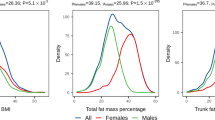
Women carrying two copies of the variant T allele had significantly lower BMI (OR=0.47; 95% CI, 0.25–0.87). Also, men with at least one copy of the variant T allele were over two times less likely to be diabetic than other men (OR=0.44; 95% CI, 0.22–0.89).
Conclusion:
Our results replicate previous findings and implicate the AGRP −38C/T SNP in the regulation of body weight in West Africans.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Clement K, Ferre P . Genetics and the pathophysiology of obesity. Pediatr Res 2003; 53: 721–725.
Comuzzie A, Allison D . The search for human obesity genes. Science 1998; 280: 1374–1377.
Comuzzie A . The emerging pattern of the genetic contribution to human obesity. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 16: 611–621.
Geller F, Reichwald K, Dempfle A, Illig T, Vollmert C, Herpertz S et al. Melanocortin-4 receptor gene variant I103 is negatively associated with obesity. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 74: 572–581.
Hinney A, Hohmann S, Geller F, Vogel C, Hess C, Wermter A et al. Melanocortin-4 receptor gene: case–control study and transmission disequilibrium test confirm that functionally relevant mutations are compatible with a major gene effect for extreme obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 4258–4267.
Vaisse C, Clement K, Guy-Grand B, Froguel P . A frameshift mutation in human MC4R is associated with a dominant form of obesity. Nat Genet 1998; 20: 113–114.
Li W, Reed D, Lee J, Xu W, Kilker R, Sodam B et al. Sequence variants in the 5′ flanking region of the leptin gene are associated with obesity in women. Ann Hum Genet 1999; 63: 227–234.
Liu Y, Rocha-Sanchez S, Liu P, Long J, Lu Y, Elze L et al. Tests of linkage and/or association of the LEPR gene polymorphisms with obesity phenotypes in Caucasian nuclear families. Physiol Genomics 2004; 17: 101–106.
Krude H, Biebermann H, Gruters A . Mutations in the human proopiomelanocortin gene. Ann NY Acad Sci 2003; 994: 233–239.
Jackson R, Creemers J, Ohagi S, Raffin-Sanson M, Sanders L, Montague C et al. Obesity and impaired prohormone processing associated with mutations in the human prohormone convertase 1 gene. Nat Genet 1997; 16: 303–306.
Ellacott K, Cone R . The central melanocortin system and the integration of short and long-term regulators of energy homeostasis. Recent Prog Horm Res 2004; 59: 395–408.
Mayfield D, Brown A, Page G, Garvey W, Shriver M, Argyropoulos G . A role for the agouti-related protein promoter in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 287: 568–573.
Mountjoy K, Wong J . Obesity, diabetes and functions for proopiomelanocortin-derived peptides. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1997; 128: 171–177.
Marks D, Boucher N, Lanouette C, Perusse L, Brookhart G, Comuzzie A et al. Ala67Thr polymorphism in the agouti-related peptide gene is associated with inherited leanness in humans. Am J Med Genet 2004; 126A: 267–271.
Ollmann M, Wilson B, Yang Y, Kerns J, Chen Y, Gantz I et al. Antagonism of central melanocortin receptors in vitro and in vivo by agouti-related protein. Science 1997; 278: 135–138.
Qu S, Yang Y, Li J, Zeng Q, Gantz I . Agouti-related protein is a mediator of diabetic hyperphagia. Regul Pept 2001; 98: 69–75.
Mizuno T, Makimura H, Silverstein J, Roberts J, Lopingco T, Mobbs C . Fasting regulates hypothalamic neuropeptide Y, agouti-related peptide, and proopiomelanocortin in diabetic mice independent of changes in leptin or insulin. Endocrinology 1999; 140: 4551–4557.
Graham M, Shutter J, Sarmiento U, Sarosi I, Stark K . Overexpression of Agrt leads to obesity in transgenic mice. Nat Genet 1997; 17: 273–274.
Michaud E, Mynatt R, Miltenberger R, Klebig M, Wilkinson J, Zemel M et al. Role of the agouti gene in obesity. J Endocrinol 1997; 155: 207–209.
Shutter J, Graham M, Kinsey A, Scully S, Luthy R, Stark K . Hypothalamic expression of ART, a novel gene related to agouti, is up-regulated in obese and diabetic mutant mice. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 593–602.
Katsuki A, Sumida Y, Gabazza E, Murashima S, Tanaka T, Furuta M et al. Plasma levels of agouti-related protein are increased in obese men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1921–1924.
Vink T, Hinney A, van Elburg A, van Goozen S, Sandkuijl L, Sinke R et al. Association between an agouti-related protein gene polymorphism and anorexia nervosa. Mol Psychiatry 2001; 6: 325–328.
Brown A, Mayfield D, Volaufova J, Argyropoulos G . The gene structure and minimal promoter of the human agouti related protein. Gene 2001; 277: 231–238.
Argyropoulos G, Rankinen T, Neufeld D, Rice T, Province M, Leon A et al. A polymorphism in the human agouti-related protein is associated with late-onset obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 4198–4202.
Rotimi C, Dunston G, Berg K, Akinsete O, Amoah A, Owusu S et al. In search of susceptibility genes for type 2 diabetes in West Africa: the design and results of the first phase of the AADM study. Ann Epidemiol 2001; 11: 51–58.
Luke A, Durazo-Arvizu R, Rotimi C, Prewitt T, Forrester T, Wilks R et al. Relation between body mass index and body fat in black population samples from Nigeria, Jamaica, and the United States. Am J Epidemiol 1997; 145: 620–628.
Pan W, Flegal K, Chang H, Yeh W, Yeh C, Lee W . Body mass index and obesity-related metabolic disorders in Taiwanese and US whites and blacks: implications for definition of overweight and obesity for Asians. Am J Clin Nutr 2004; 79: 31–39.
Storey J, Tibshirani R . Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2003; 100: 9440–9445.
Argyropoulos G, Rankinen T, Bai F, Rice T, Province M, Leon A et al. The agouti-related protein and body fatness in humans. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27: 276–280.
Morton G, Schwartz M . The NPY/AgRP neuron and energy homeostasis. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: S56–S62.
Boden G . Free fatty acids (FFA), a link between obesity and insulin resistance. Front Biosci 1998; 3: D169–D175.
Fan W, Dinulescu D, Butler A, Zhou J, Marks D, Cone R . The central melanocortin system can directly regulate serum insulin levels. Endocrinology 2000; 141: 3072–3079.
Roemmich J, Clark P, Berr S, Mai V, Mantzoros C, Flier J et al. Gender differences in leptin levels during puberty are related to the subcutaneous fat depot and sex steroids. Am J Physiol 1998; 275: E543–E551.
Charbonneau C, Bai F, Richards B, Argyropoulos G . Central and peripheral interactions between the agouti related protein and leptin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 319: 518–524.
Bai F, Rankinen T, Charbonneau C, Belsham D, Rao D, Bouchard C et al. Functional dimorphism of two hAgRP promoter SNPs in linkage disequilibrium. J Med Genet 2004; 41: 350–353.
Schoeller D, Luke A . Bioelectrical impedance analysis prediction equations differ between African Americans and Caucasians, but it is not clear why. Ann NY Acad Sci 2000; 904: 225–226.
Chumlea W, Siervogel R, Yixun W, Hall G, Guo S . Bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy and body composition. Ann NY Acad Sci 2000; 904: 210–213.
Ward L, Heitmann B, Craig P, Stroud D, Azinge E, Jebb S et al. Association between ethnicity, body mass index, and bioelectrical impedance. Implications for the population specificity of prediction equations. Ann NY Acad Sci 2000; 904: 199–202.
Loos R, Rankinen T, Tremblay A, Perusse L, Chagnon Y, Bouchard C . Melanocortin-4 receptor gene and physical activity in the Quebec Family Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2005; 29: 420–428.
Chen G, Adeyemo A, Johnson T, Zhou J, Amoah A, Owusu S et al. A genome-wide scan for quantitative trait loci linked to obesity phenotypes among West Africans. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2005; 29: 255–259.
Rotimi C, Chen G, Adeyemo A, Furbert-Harris P, Guass D, Zhou J et al. A genome-wide search for type 2 diabetes susceptibility genes in West Africans. Diabetes 2004; 53: 838–841.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all individuals who volunteered for this study. We thank Kofi Bonney for programming assistance. Support for this work was provided by the National Institutes of Health Office of Research on Minority Health (ORMH), the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR) and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonilla, C., Panguluri, R., Taliaferro-Smith, L. et al. Agouti-related protein promoter variant associated with leanness and decreased risk for diabetes in West Africans. Int J Obes 30, 715–721 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803047
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803047
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genetic association analysis of 30 genes related to obesity in a European American population
International Journal of Obesity (2014)
-
Polymorphisms of the pro-opiomelanocortin and agouti-related protein genes and their association with chicken production traits
Molecular Biology Reports (2012)
-
Association between a rare SNP in the second intron of human Agouti related protein gene and increased BMI
BMC Medical Genetics (2009)
-
Potent and Selective Agonism of the Melanocortin Receptor 4 With MK-0493 Does Not Induce Weight Loss in Obese Human Subjects: Energy Intake Predicts Lack of Weight Loss Efficacy
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2009)
-
Targeting melanocortin receptors: an approach to treat weight disorders and sexual dysfunction
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2008)