Abstract
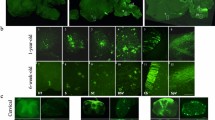
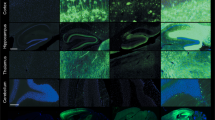
Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) is caused by an inherited deficiency of α-L-iduronidase (IDUA). The result is a progressive, lysosomal storage disease with central nervous system (CNS) as well as systemic involvement. To target gene therapy to the CNS, recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors carrying IDUA sequence were administered to MPS I mice via injection into cerebrospinal fluid. In contrast to intravenous administration, this intrathecal administration was effective in generating widespread IDUA activity in the brain, with the cerebellum and olfactory bulbs having highest activities. In general, IDUA levels correlated with vector dose, although this correlation was obscured in cerebellum by particularly high variability. High doses of vector (4 × 1010 particles) provided IDUA levels approaching or exceeding normal levels in the brain. Histopathology indicated that the number of cells with storage vacuoles was reduced extensively or was eliminated entirely. Elimination of storage material in Purkinje cells was particularly dramatic. A lower vector dose (2 × 109 particles) reduced both the number of storage cells and the extent of storage per cell, but the effect was not complete. Some perivascular cells with storage persisted, and this cell type appeared to be more resistant to treatment than neurons or glial cells. We conclude that intrathecal administration of AAV-IDUA delivers vector to brain cells, and that this route of administration is both minimally invasive and effective.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neufeld EF, Muenzer J . The Mucopolysaccharidoses. McGraw-Hill: New York, 2001 pp 3421–3452.
Peters C, Shapiro EG, Anderson J, Henslee-Downey PJ, Klemperer MR, Cowan MJ et al. Hurler syndrome: II. Outcome of HLA-genotypically identical sibling and HLA-haploidentical related donor bone marrow transplantation in fifty-four children. The Storage Disease Collaborative Study Group. Blood 1998; 91: 2601–2608.
Peters C, Balthazor M, Shapiro EG, King RJ, Kollman C, Hegland JD et al. Outcome of unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation in 40 children with Hurler syndrome. Blood 1996; 87: 4894–4902.
Staba SL, Escolar ML, Poe M, Kim Y, Martin PL, Szabolcs P et al. Cord-blood transplants from unrelated donors in patients with Hurler's syndrome. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 1960–1969.
Kakkis ED, Muenzer J, Tiller GE, Waber L, Belmont J, Passage M et al. Enzyme-replacement therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis I. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 182–188.
Wraith JE, Clarke LA, Beck M, Kolodny EH, Pastores GM, Muenzer J et al. Enzyme replacement therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis I: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, multinational study of recombinant human alpha-L-iduronidase (laronidase). J Pediatr 2004; 144: 581–588.
Hartung SD, Frandsen JL, Pan D, Koniar BL, Graupman P, Gunther R et al. Correction of metabolic, craniofacial, and neurologic abnormalities in MPS I mice treated at birth with adeno-associated virus vector transducing the human alpha-L-iduronidase gene. Mol Ther 2004; 9: 866–875.
Desmaris N, Verot L, Puech JP, Caillaud C, Vanier MT, Heard JM . Prevention of neuropathology in the mouse model of Hurler syndrome. Ann Neurol 2004; 56: 68–76.
Di Domenico C, Villani GR, Di Napoli D, Reyero EG, Lombardo A, Naldini L et al. Gene therapy for a mucopolysaccharidosis type I murine model with lentiviral-IDUA vector. Hum Gene Ther 2005; 16: 81–90.
Kobayashi H, Carbonaro D, Pepper K, Petersen D, Ge S, Jackson H et al. Neonatal gene therapy of MPS I mice by intravenous injection of a lentiviral vector. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 776–789.
Grewal SS, Wynn R, Abdenur JE, Burton BK, Gharib M, Haase C et al. Safety and efficacy of enzyme replacement therapy in combination with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in Hurler syndrome. Genet Med 2005; 7: 143–146.
Zheng Y, Rozengurt N, Ryazantsev S, Kohn DB, Satake N, Neufeld EF . Treatment of the mouse model of mucopolysaccharidosis I with retrovirally transduced bone marrow. Mol Genet Metab 2003; 79: 233–244.
Neufeld EF . Lysosomal storage diseases. Annu Rev Biochem 1991; 60: 257–280.
Kakkis ED, McEntee MF, Schmidtchen A, Neufeld EF, Ward DA, Gompf RE et al. Long-term and high-dose trials of enzyme replacement therapy in the canine model of mucopolysaccharidosis I. Biochem Mol Med 1996; 58: 156–167.
Shull RM, Kakkis ED, McEntee MF, Kania SA, Jonas AJ, Neufeld EF . Enzyme replacement in a canine model of Hurler syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 12937–12941.
Kakkis ED, Schuchman E, He X, Wan Q, Kania S, Wiemelt S et al. Enzyme replacement therapy in feline mucopolysaccharidosis I. Mol Genet Metab 2001; 72: 199–208.
Wraith EJ, Hopwood JJ, Fuller M, Meikle PJ, Brooks DA . Laronidase treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis I. BioDrugs 2005; 19: 1–7.
Kakkis E, Lester T, Yang R, Tanaka C, Anand V, Lemontt J et al. Successful induction of immune tolerance to enzyme replacement therapy in canine mucopolysaccharidosis I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 829–834.
Kakkis E, McEntee M, Vogler C, Le S, Levy B, Belichenko P et al. Intrathecal enzyme replacement therapy reduces lysosomal storage in the brain and meninges of the canine model of MPS I. Mol Genet Metab 2004; 83: 163–174.
Barranger JA . Marrow transplantation in genetic disease. N Engl J Med 1984; 311: 1629–1631.
Zheng Y, Ryazantsev S, Ohmi K, Zhao HZ, Rozengurt N, Kohn DB et al. Retrovirally transduced bone marrow has a therapeutic effect on brain in the mouse model of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB. Mol Genet Metab 2004; 82: 286–295.
Sakurai K, Iizuka S, Shen JS, Meng XL, Mori T, Umezawa A et al. Brain transplantation of genetically modified bone marrow stromal cells corrects CNS pathology and cognitive function in MPS VII mice. Gene Therapy 2004; 11: 1475–1481.
Cheng SH, Smith AE . Gene therapy progress and prospects: gene therapy of lysosomal storage disorders. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 1275–1281.
Bosch A, Perret E, Desmaris N, Heard JM . Long-term and significant correction of brain lesions in adult mucopolysaccharidosis Type VII mice using recombinant AAV vectors. Mol Ther 2000; 1: 63–70.
Bosch A, Perret E, Desmaris N, Trono D, Heard JM . Reversal of pathology in the entire brain of mucopolysaccharidosis type VII mice after lentivirus-mediated gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther 2000; 11: 1139–1150.
Vite CH, McGowan JC, Niogi SN, Passini MA, Drobatz KJ, Haskins ME et al. Effective gene therapy for an inherited CNS disease in a large animal model. Ann Neurol 2005; 57: 355–364.
Elliger SS, Elliger CA, Aguilar CP, Raju NR, Watson GL . Elimination of lysosomal storage in brains of MPS VII mice treated by intrathecal administration of an adeno-associated virus vector. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 1175–1178.
Elliger SS, Elliger CA, Lang C, Watson GL . Enhanced secretion and uptake of beta-glucuronidase improves adeno-associated viral-mediated gene therapy of mucopolysaccharidosis type VII mice. Mol Ther 2002; 5: 617–626.
Ponder KP, Melniczek JR, Xu L, Weil MA, O'Malley TM, O'Donnell PA et al. Therapeutic neonatal hepatic gene therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis VII dogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 13102–13107.
Daly TM, Ohlemiller KK, Roberts MS, Vogler CA, Sands MS . Prevention of systemic clinical disease in MPS VII mice following AAV-mediated neonatal gene transfer. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 1291–1298.
Sferra TJ, Backstrom K, Wang C, Rennard R, Miller M, Hu Y . Widespread correction of lysosomal storage following intrahepatic injection of a recombinant adeno-associated virus in the adult MPS VII mouse. Mol Ther 2004; 10: 478–491.
Stewart PA, Hayakawa EM . Interendothelial junctional changes underlie the developmental ‘tightening’ of the blood–brain barrier. Brain Res 1987; 429: 271–281.
Peel AL, Zolotukhin S, Schrimsher GW, Muzyczka N, Reier PJ . Efficient transduction of green fluorescent protein in spinal cord neurons using adeno-associated virus vectors containing cell type-specific promoters. Gene Therapy 1997; 4: 16–24.
Davidson BL, Stein CS, Heth JA, Martins I, Kotin RM, Derksen TA et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus type 2, 4, and 5 vectors: transduction of variant cell types and regions in the mammalian central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3428–3432.
Rabinowitz JE, Rolling F, Li C, Conrath H, Xiao W, Xiao X et al. Cross-packaging of a single adeno-associated virus (AAV) type 2 vector genome into multiple AAV serotypes enables transduction with broad specificity. J Virol 2002; 76: 791–801.
Thomas CE, Storm TA, Huang Z, Kay MA . Rapid uncoating of vector genomes is the key to efficient liver transduction with pseudotyped adeno-associated virus vectors. J Virol 2004; 78: 3110–3122.
Watson GL, Sayles JN, Chen C, Elliger SS, Elliger CA, Raju NR et al. Treatment of lysosomal storage disease in MPS VII mice using a recombinant adeno-associated virus. Gene Therapy 1998; 5: 1642–1649.
Xu R, Janson CG, Mastakov M, Lawlor P, Young D, Mouravlev A et al. Quantitative comparison of expression with adeno-associated virus (AAV-2) brain-specific gene cassettes. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 1323–1332.
Sands MS, Vogler C, Kyle JW, Grubb JH, Levy B, Galvin N et al. Enzyme replacement therapy for murine mucopolysaccharidosis Type VII. J Clin Invest 1994; 93: 2324–2331.
Ohmi K, Greenberg DS, Rajavel KS, Ryazantsev S, Li HH, Neufeld EF . Activated microglia in cortex of mouse models of mucopolysaccharidoses I and IIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 1902–1907.
Kakkis ED, Matynia A, Jonas AJ, Neufeld EF . Overexpression of the human lysosomal enzyme alpha-L-iduronidase in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Protein Expr Purif 1994; 5: 225–232.
Matsushita T, Elliger S, Elliger C, Podsakoff G, Villarreal L, Kurtzman GJ et al. Adeno-associated virus vectors can be efficiently produced without helper virus. Gene Therapy 1998; 5: 938–945.
Zolotukhin S, Byrne BJ, Mason E, Zolotukhin I, Potter M, Chesnut K et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus purification using novel methods improves infectious titer and yield. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 973–985.
Snyder RO, Xiao X, Samulski RJ . Production of recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors. In: Haines JL, Korf BR, Morton CC, Seidman CE, Seidman JG, Smith DR (eds) Current Protocols in Human Genetics. John Wiley and Sons: New York, 1996, pp 12.11.11–12.11.24.
Acknowledgements
We thank Susan Elliger, Amy Jess, Catherine McDonough and Dorothy Tabron for their technical assistance and expertise, and Dr Berna Atik for statistical analysis. This study was supported in part by a National Institutes of Health grant (R01 DK54285), CHORI and BioMarin Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watson, G., Bastacky, J., Belichenko, P. et al. Intrathecal administration of AAV vectors for the treatment of lysosomal storage in the brains of MPS I mice. Gene Ther 13, 917–925 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302735
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302735
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
CNS-Wide over Expression of Fractalkine Improves Cognitive Functioning in a Tauopathy Model
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2019)
-
Long-term neurologic and cardiac correction by intrathecal gene therapy in Pompe disease
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2017)
-
Normalization and Improvement of CNS Deficits in Mice With Hurler Syndrome After Long-term Peripheral Delivery of BBB-targeted Iduronidase
Molecular Therapy (2014)
-
Retroviral‐vector‐mediated gene therapy to mucopolysaccharidosis I mice improves sensorimotor impairments and other behavioral deficits
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2013)
-
Merits of Combination Cortical, Subcortical, and Cerebellar Injections for the Treatment of Niemann-Pick Disease Type A
Molecular Therapy (2012)