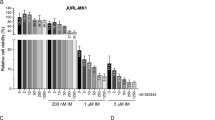
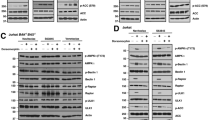
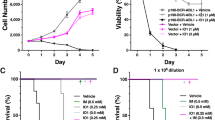
Abstract
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is driven by Bcr-Abl, a constitutively active protein-tyrosine kinase that stimulates proliferation and survival of myeloid progenitors. Global inhibition of myeloid Src family kinase (SFK) activity with the broad-spectrum pyrrolo-pyrimidine inhibitor, A-419259, blocks proliferation and induces apoptosis in CML cell lines, suggesting that transformation by Bcr-Abl requires SFK activity. However, the contribution of Hck and other individual SFKs to Bcr-Abl signaling is less clear. Here, we developed an A-419259-resistant mutant of Hck by replacing the gatekeeper residue (Thr-338; c-Src numbering) in the inhibitor-binding site with a bulkier methionine residue (Hck-T338M). This substitution reduced Hck sensitivity to A-419259 by more than 30-fold without significantly affecting kinase activity in vitro. Expression of Hck-T338M protected K-562 CML cells and Bcr-Abl-transformed TF-1 myeloid cells from the apoptotic and antiproliferative effects of A-419259. These effects correlated with persistence of Hck-T338M kinase activity in the presence of the compound, and were accompanied by sustained Erk and Stat5 activation. In contrast, control cells expressing equivalent levels of wild-type Hck retained sensitivity to the inhibitor. We also show for the first time that A-419259 induces cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in primary CD34+ CML cells with equal potency to imatinib. These data suggest that Hck has a nonredundant function as a key downstream signaling partner for Bcr-Abl and may represent a potential drug target in CML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram CL, Courtneidge SA . (2000). Src family tyrosine kinases and growth factor signaling. Exp Cell Res 254: 1–13.
Ben-Neriah Y, Daley GQ, Mes-Masson AM, Witte ON, Baltimore D . (1986). The chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific p210 protein is the product of the bcr/abl hybrid gene. Science 233: 212–214.
Bhatia R, Holtz M, Niu N, Gray R, Snyder DS, Sawyers CL et al. (2003). Persistence of malignant hematopoietic progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients in complete cytogenetic remission following imatinib mesylate treatment. Blood 101: 4701–4707.
Bishop AC, Ubersax JA, Petsch DT, Matheos DP, Gray NS, Blethrow J et al. (2000). A chemical switch for inhibitor-sensitive alleles of any protein kinase. Nature 407: 395–401.
Blencke S, Ullrich A, Daub H . (2003). Mutation of threonine 766 in the epidermal growth factor receptor reveals a hotspot for resistance formation against selective tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 278: 15435–15440.
Blencke S, Zech B, Engkvist O, Greff Z, Orfi L, Horvath Z et al. (2004). Characterization of a conserved structural determinant controlling protein kinase sensitivity to selective inhibitors. Chem Biol 11: 691–701.
Boggon TJ, Eck MJ . (2004). Structure and regulation of Src family kinases. Oncogene 23: 7918–7927.
Briggs SD, Sharkey M, Stevenson M, Smithgall TE . (1997). SH3-mediated Hck tyrosine kinase activation and fibroblast transformation by the Nef protein of HIV-1. J Biol Chem 272: 17899–17902.
Briggs SD, Smithgall TE . (1999). SH2-kinase linker mutations release Hck tyrosine kinase and transforming activities in rat-2 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 274: 26579–26583.
Carlesso N, Frank DA, Griffin JD . (1996). Tyrosyl phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins in hematopoietic cell lines transformed by Bcr/Abl. J Exp Med 183: 811–820.
Cools J, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, Stover EH, Legare RD, Cortes J et al. (2003). A tyrosine kinase created by fusion of the PDGFRA and FIP1L1 genes as a therapeutic target of imatinib in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. N Engl J Med 348: 1201–1214.
Copland M, Hamilton A, Elrick LJ, Baird JW, Allan EK, Jordanides N et al. (2006). Dasatinib (BMS-354825) targets an earlier progenitor population than imatinib in primary CML but does not eliminate the quiescent fraction. Blood 107: 4532–4539.
Cortes J, O’Brien S, Kantarjian H . (2004). Discontinuation of imatinib therapy after achieving a molecular response. Blood 104: 2204–2205.
Dai Y, Rahmani M, Corey SJ, Dent P, Grant S . (2004). A Bcr/Abl-independent, Lyn-dependent form of imatinib mesylate (STI-571) resistance is associated with altered expression of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem 279: 34227–34239.
Daley GQ, Van Etten RA, Baltimore D . (1990). Induction of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mice by the p210bcr-abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome. Science 247: 824–830.
Danhauser-Riedl S, Warmuth M, Druker BJ, Emmerich B, Hallek M . (1996). Activation of Src kinases p53/56lyn and p59hck by p210bcr/abl in myeloid cells. Cancer Res 56: 3589–3596.
Das J, Chen P, Norris D, Padmanabha R, Lin J, Moquin RV et al. (2006). 2-aminothiazole as a novel kinase inhibitor template. Structure-activity relationship studies toward the discovery of N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl)]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl] amino)]-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide (dasatinib, BMS-354825) as a potent pan-Src kinase inhibitor. J Med Chem 49: 6819–6832.
de Groot RP, Raaijmakers JA, Lammers JW, Koenderman L . (2000). STAT5-Dependent CyclinD1 and Bcl-xL expression in Bcr-Abl-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun 3: 299–305.
Donato NJ, Wu JY, Stapley J, Lin H, Arlinghaus R, Aggarwal BB et al. (2004). Imatinib mesylate resistance through BCR-ABL independence in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res 64: 672–677.
Eyers PA, Craxton M, Morrice N, Cohen P, Goedert M . (1998). Conversion of SB 203580-insensitive MAP kinase family members to drug-sensitive forms by a single amino-acid substitution. Chem Biol 5: 321–328.
Gesbert F, Griffin JD . (2000). Bcr/Abl activates transcription of the Bcl-X gene through STAT5. Blood 96: 2269–2276.
Goga A, McLaughlin J, Afar DEH, Saffran DC, Witte ON . (1995). Alternative signals to RAS for hematopoietic transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene. Cell 82: 981–988.
Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN et al. (2001). Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 293: 876–880.
Harrison-Findik D, Susa M, Varticovski L . (1995). Association of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase with SHC in chronic myelogeneous leukemia cells. Oncogene 10: 1385–1391.
Holtz MS, Forman SJ, Bhatia R . (2005). Nonproliferating CML CD34+ progenitors are resistant to apoptosis induced by a wide range of proapoptotic stimuli. Leukemia 19: 1034–1041.
Hoover RR, Gerlach MJ, Koh EY, Daley GQ . (2001). Cooperative and redundant effects of STAT5 and Ras signaling in BCR/ABL transformed hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 20: 5826–5835.
Hu Y, Liu Y, Pelletier S, Buchdunger E, Warmuth M, Fabbro D et al. (2004). Requirement of Src kinases Lyn, Hck and Fgr for BCR-ABL1-induced B-lymphoblastic leukemia but not chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 36: 453–461.
Kantarjian H, Sawyers C, Hochhaus A, Guilhot F, Schiffer C, Gambacorti-Passerini C et al. (2002). Hematologic and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med 346: 645–652.
Kantarjian HM, Giles F, Quintas-Cardama A, Cortes J . (2007). Important therapeutic targets in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 13: 1089–1097.
Kelliher MA, McLaughlin J, Witte ON, Rosenberg N . (1990). Induction of a chronic myelogenous leukemia-like syndrome in mice with v-abl and BCR/ABL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 6649–6653.
Kitamura T, Tange T, Terasawa T, Chiba S, Kuwaki T, Miyagawa K et al. (1989). Establishment and characterization of a unique human cell line that proliferates dependently on GM-CSF, IL-3 or erythropoietin. J Cell Physiol 140: 323–334.
Klejman A, Schreiner SJ, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Slupianek A, Wilson MB, Smithgall TE et al. (2002). The Src family kinase Hck couples Bcr-Abl to Stat5 activation in myeloid cells. EMBO J 21: 5766–5774.
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M et al. (2005). EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 352: 786–792.
Lerner EC, Smithgall TE . (2002). SH3-dependent stimulation of Src-family kinase autophosphorylation without tail release from the SH2 domain in vivo. Nat Struct Biol 9: 365–369.
Lerner EC, Trible RP, Schiavone AP, Hochrein JM, Engen JR, Smithgall TE . (2005). Activation of the Src family kinase Hck without SH3-linker release. J Biol Chem 280: 40832–40837.
Lionberger JM, Wilson MB, Smithgall TE . (2000). Transformation of myeloid leukemia cells to cytokine independence by Bcr-Abl is suppressed by kinase-defective Hck. J Biol Chem 275: 18581–18585.
Liu Y, Bishop A, Witucki L, Kraybill B, Shimizu E, Tsien J et al. (1999). Structural basis for selective inhibition of Src family kinases by PP1. Chem Biol 6: 671–678.
Liu Y, Shah K, Yang F, Witucki L, Shokat KM . (1998). A molecular gate which controls unnatural ATP analogue recognition by the tyrosine kinase v-Src. Bioorg Med Chem 6: 1219–1226.
Lugo TG, Witte ON . (1989). The BCR-ABL oncogene transforms Rat-1 cells and cooperates with v-myc. Mol Cell Biol 9: 1263–1270.
Martinelli G, Soverini S, Rosti G, Baccarani M . (2005). Dual tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 19: 1872–1879.
Mauro MJ, Druker BJ, Maziarz RT . (2004). Divergent clinical outcome in two CML patients who discontinued imatinib therapy after achieving a molecular remission. Leuk Res 28 (Suppl 1): S71–S73.
McLaughlin J, Chianese E, Witte ON . (1987). In vitro transformation of immature hematopoietic cells by the P210 BCR/ABL oncogene product of the Philadelphia chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 6558–6562.
Melnick JS, Janes J, Kim S, Chang JY, Sipes DG, Gunderson D et al. (2006). An efficient rapid system for profiling the cellular activities of molecular libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 3153–3158.
Meyn III MA, Wilson MB, Abdi FA, Fahey N, Schiavone AP, Wu J et al. (2006). Src family kinases phosphorylate the Bcr-Abl SH3-SH2 region and modulate Bcr-Abl transforming activity. J Biol Chem 281: 30907–30916.
Million RP, Van Etten RA . (2000). The Grb2 binding site is required for the induction of chronic myeloid leukemia-like disease in mice by the Bcr/Abl tyrosine kinase. Blood 96: 664–670.
Nakajima A, Tauchi T, Ohyashiki K . (2001). ABL-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor, STI571 in vitro, affects Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia and chronic myelogenous leukemia in blastic crisis. Leukemia 15: 989–990.
Neshat MS, Raitano AB, Wang HG, Reed JC, Sawyers CL . (2000). The survival function of the Bcr-Abl oncogene is mediated by Bad-dependent and -independent pathways: roles for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Raf. Mol Cell Biol 20: 1179–1186.
Olivieri A, Manzione L . (2007). Dasatinib: a new step in molecular target therapy. Ann Oncol 18 (Suppl 6): vi42–vi46.
Pendergast AM, Quilliam LA, Cripe LD, Bassing CH, Dai Z, Li N et al. (1993). BCR-ABL-induced oncogenesis is mediated by direct interaction with the SH2 domain of the GRB-2 adaptor protein. Cell 75: 175–185.
Porter M, Schindler T, Kuriyan J, Miller WT . (2000). Reciprocal regulation of Hck activity by phosphorylation of Tyr(527) and Tyr(416). Effect of introducing a high affinity intramolecular SH2 ligand. J Biol Chem 275: 2721–2726.
Ptasznik A, Nakata Y, Kalota A, Emerson SG, Gewirtz AM . (2004). Short interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting the Lyn kinase induces apoptosis in primary, and drug-resistant, BCR-ABL1(+) leukemia cells. Nat Med 10: 1187–1189.
Raffel GD, Parmar K, Rosenberg N . (1996). In vivo association of v-Abl with Shc mediated by a non-phosphotyrosine-dependent SH2 interaction. J Biol Chem 271: 4640–4645.
Ren R . (2002). The molecular mechanism of chronic myelogenous leukemia and its therapeutic implications: studies in a murine model. Oncogene 21: 8629–8642.
Rowley JD . (1973). A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and G Giemsa staining. Nature 243: 290–293.
Sattler M, Mohi MG, Pride YB, Quinnan LR, Malouf NA, Podar K et al. (2002). Critical role for Gab2 in transformation by BCR/ABL. Cancer Cell 1: 479–492.
Sattler M, Salgia R, Okuda K, Uemura N, Durstin MA, Pisick E et al. (1996). The proto-oncogene product p120CBL and the adaptor proteins CRKL and c-CRK link c-ABL, p190BCR/ABL and p210BCR/ABL to the phosphatidylinositol-3′ kinase pathway. Oncogene 12: 839–846.
Sawyers CL . (1999). Chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 340: 1330–1340.
Schindler T, Sicheri F, Pico A, Gazit A, Levitzki A, Kuriyan J . (1999). Crystal structure of Hck in complex with a Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Mol Cell 3: 639–648.
Schreiner SJ, Schiavone AP, Smithgall TE . (2002). Activation of Stat3 by the Src family kinase Hck requires a functional SH3 domain. J Biol Chem 277: 45680–45687.
Shuai K, Halpern J, ten Hoeve J, Rao XP, Sawyers CL . (1996). Constitutive activation of STAT5 by the BCR-ABL oncogene in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncogene 13: 247–254.
Skorski T, Bellacosa A, Nieborowska-Skorska MN, Majewski M, Martinez R, Choi JK et al. (1997). Transformation of hematopoietic cells by BCR/ABL requires activation of a PI-3K/Akt-dependent pathway. EMBO J 16: 6151–6161.
Smith KM, Yacobi R, Van Etten RA . (2003). Autoinhibition of Bcr-Abl through its SH3 domain. Mol Cell 12: 27–37.
Songyang Z, Shoelson SE, Chaudhuri M, Gish G, Pawson T, Haser WG et al. (1993). SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell 72: 767–778.
Tamborini E, Bonadiman L, Greco A, Albertini V, Negri T, Gronchi A et al. (2004). A new mutation in the KIT ATP pocket causes acquired resistance to imatinib in a gastrointestinal stromal tumor patient. Gastroenterology 127: 294–299.
Trible RP, Emert-Sedlak L, Smithgall TE . (2006). HIV-1 Nef selectively activates SRC family kinases HCK, LYN, and c-SRC through direct SH3 domain interaction. J Biol Chem 281: 27029–27038.
Warmuth M, Bergmann M, Priess A, Hauslmann K, Emmerich B, Hallek M . (1997). The Src family kinase Hck interacts with Bcr-Abl by a kinase- independent mechanism and phosphorylates the Grb2-binding site of Bcr. J Biol Chem 272: 33260–33270.
Wilson MB, Schreiner SJ, Choi H-J, Kamens JS, Smithgall TE . (2002). Selective pyrrolo-pyrimidine inhibitors reveal a necessary role for Src family kinases in Bcr-Abl signal transduction and oncogenesis. Oncogene 21: 8075–8088.
Wu J, Meng F, Kong LY, Peng Z, Ying Y, Bornmann WG et al. (2008). Association between imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutation-negative leukemia and persistent activation of LYN kinase. J Natl Cancer Inst 100: 926–939.
Xu W, Doshi A, Lei M, Eck MJ, Harrison SC . (1999). Crystal structures of c-Src reveal features of its autoinhibitory mechanism. Mol Cell 3: 629–638.
Zhang X, Subrahmanyam R, Wong R, Gross AW, Ren R . (2001). The NH(2)-terminal coiled-coil domain and tyrosine 177 play important roles in induction of a myeloproliferative disease in mice by Bcr-Abl. Mol Cell Biol 21: 840–853.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (CA101828 and GM077629 to TES). We thank Dr David Calderwood of the Abbott Bioresearch Center for the generous gift of the Src family kinase inhibitor, A-419259 and Dr Elisabeth Buchdunger of Novartis, Inc. for providing imatinib mesylate.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pene-Dumitrescu, T., Peterson, L., Donato, N. et al. An inhibitor-resistant mutant of Hck protects CML cells against the antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of the broad-spectrum Src family kinase inhibitor A-419259. Oncogene 27, 7055–7069 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.330
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.330
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hemopoietic Cell Kinase amplification with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptor T depletion leads to polycythemia, aberrant marrow erythoid maturation, and splenomegaly
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Src family kinases interfere with dimerization of STAT5A through a phosphotyrosine-SH2 domain interaction
Cell Communication and Signaling (2015)
-
HIV-1 Nef interaction influences the ATP-binding site of the Src-family kinase, Hck
BMC Chemical Biology (2012)
-
Expressing murine p56Hckca promotes HeLa cells’ motility and invasion via triggering redistribution of F-actin and microtubules
Molecular Biology Reports (2012)