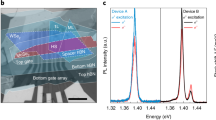
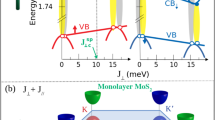
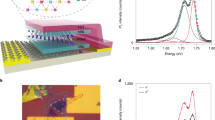
Abstract
The valley degree of freedom in layered transition-metal dichalcogenides provides an opportunity to extend the functionalities of spintronics and valleytronics devices. The achievement of spin-coupled valley polarization induced by the non-equilibrium charge-carrier imbalance between two degenerate and inequivalent valleys has been demonstrated theoretically and by optical experiments. However, the generation of a valley and spin current with the valley polarization in transition-metal dichalcogenides remains elusive. Here we demonstrate a spin-coupled valley photocurrent, within an electric-double-layer transistor based on WSe2, whose direction and magnitude depend on the degree of circular polarization of the incident radiation and can be further modulated with an external electric field. This room-temperature generation and electric control of a valley and spin photocurrent provides a new property of electrons in transition-metal dichalcogenide systems, and thereby enables additional degrees of control for quantum-confined spintronic devices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murakami, S., Nagaosa, N. & Zhang, S. C. Dissipationless quantum spin current at room temperature. Science 301, 1348–1351 (2003).
Awschalom, D. D. & Flatte, M. E. Challenges for semiconductor spintronics. Nature Phys. 3, 153–159 (2007).
Zutic, I., Fabian, J. & Das Sarma, S. Spintronics: fundamentals and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 323–410 (2004).
Ganichev, S. D. et al. Spin-galvanic effect. Nature 417, 153–156 (2002).
Kikkawa, J. M. & Awschalom, D. D. Lateral drag of spin coherence in gallium arsenide. Nature 397, 139–141 (1999).
Ivchenko, E. L. & Ganichev, S. D. in Spin Physics in Semiconductors (ed. Dyakonov, M. I.) 245–277 (Springer Series in Solid Sciences 157, Springer, 2008).
Ganichev, S. D. & Prettl, W. Spin photocurrents in quantum wells. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 15, R935–R983 (2003).
McIver, J. W., Hsieh, D., Steinberg, H., Jarillo-Herrero, P. & Gedik, N. Control over topological insulator photocurrents with light polarization. Nature Nanotech. 7, 96–100 (2012).
Karch, J. et al. Photoexcitation of valley-orbit currents in (111)-oriented silicon metal–oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors. Phys. Rev. B 83, 121312 (2011).
Karch, J. et al. Orbital photogalvanic effects in quantum-confined structures. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22, 355307 (2010).
Bychkov, Y. A. & Rashba, E. I. Properties of a 2d electron-gas with lifted spectral degeneracy. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 39, 78–81 (1984).
Winkler, R. Spin orientation and spin precession in inversion-asymmetric quasi-two-dimensional electron systems. Phys. Rev. B 69, 045317 (2004).
Xiao, D., Liu, G. B., Feng, W. X., Xu, X. D. & Yao, W. Coupled spin and valley physics in monolayers of MoS2 and other group-VI dichalcogenides. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 196802 (2012).
Yao, W., Xiao, D. & Niu, Q. Valley-dependent optoelectronics from inversion symmetry breaking. Phys. Rev. B 77, 235406 (2008).
Rycerz, A., Tworzydlo, J. & Beenakker, C. W. J. Valley filter and valley valve in graphene. Nature Phys. 3, 172–175 (2007).
Xiao, D., Yao, W. & Niu, Q. Valley-contrasting physics in graphene: magnetic moment and topological transport. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 236809 (2007).
Mak, K. F., He, K. L., Shan, J. & Heinz, T. F. Control of valley polarization in monolayer MoS2 by optical helicity. Nature Nanotech. 7, 494–498 (2012).
Zeng, H. L., Dai, J. F., Yao, W., Xiao, D. & Cui, X. D. Valley polarization in MoS2 monolayers by optical pumping. Nature Nanotech. 7, 490–493 (2012).
Cao, T. et al. Valley-selective circular dichroism of monolayer molybdenum disulphide. Nature Commun. 3, 887 (2012).
Jones, A. M. et al. Optical generation of excitonic valley coherence in monolayer WSe2 . Nature Nanotech. 8, 634–638 (2013).
Ross, J. S. et al. Electrical control of neutral and charged excitons in a monolayer semiconductor. Nature Commun. 4, 1474 (2013).
Yuan, H. T. et al. Zeeman-type spin splitting controlled by an electric field. Nature Phys. 9, 563–569 (2013).
Zhu, Z. Y., Cheng, Y. C. & Schwingenschlogl, U. Giant spin-orbit-induced spin splitting in two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenide semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 84, 153402 (2011).
Yuan, H. T. et al. High-density carrier accumulation in ZnO field-effect transistors gated by electric double layers of ionic liquids. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 1046–1053 (2009).
Efetov, D. K. & Kim, P. Controlling electron–phonon interactions in graphene at ultrahigh carrier densities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 256805 (2010).
Dhoot, A. S., Israel, C., Moya, X., Mathur, N. D. & Friend, R. H. Large electric field effect in electrolyte-gated manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 136402 (2009).
Ueno, K. et al. Discovery of superconductivity in KTaO3 by electrostatic carrier doping. Nature Nanotech. 6, 408–412 (2011).
Bollinger, A. T. et al. Superconductor–insulator transition in La2- xSrxCuO4 at the pair quantum resistance. Nature 472, 458–460 (2011).
Yamada, Y. et al. Electrically induced ferromagnetism at room temperature in cobalt-doped titanium dioxide. Science 332, 1065–1067 (2011).
Jeong, J. et al. Suppression of metal–insulator transition in VO2 by electric field-induced oxygen vacancy formation. Science 339, 1402–1405 (2013).
Yin, C. M. et al. Tunable surface electron spin splitting with electric double-layer transistors based on InN. Nano Lett. 13, 2024–2029 (2013).
Shibata, K., Yuan, H. T., Iwasa, Y. & Hirakawa, K. Large modulation of zero-dimensional electronic states in quantum dots by electric-double-layer gating. Nature Commun. 4, 2664 (2013).
Cho, J. H. et al. Printable ion-gel gate dielectrics for low-voltage polymer thin-film transistors on plastic. Nature Mater. 7, 900–906 (2008).
Olbrich, P. et al. Observation of the orbital circular photogalvanic effect. Phys. Rev. B 79, 121302 (2009).
Ezawa, M. Spin-valley optical selection rule and strong circular dichroism in silicene. Phys. Rev. B 86, 161407 (2012).
Kresse, G. & Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular-dynamics for liquid-metals. Phys. Rev. B 47, 558–561 (1993).
Kresse, G. & Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59, 1758–1775 (1999).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
Hohenberg, P. & Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 136, 864–871 (1964).
Schutte, W. J., Deboer, J. L. & Jellinek, F. Crystal-structures of tungsten disulfide and diselenide. J. Solid State Chem. 70, 207–209 (1987).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering, under contract DE-AC02-76SF00515. B.L., H-J.Z., G.X., H.Y.H. and S-C.Z. also acknowledge FAME, one of six centres of STARnet, a Semiconductor Research Corporation program sponsored by MARCO and DARPA. X-Q.W. and B.S. acknowledge the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB619300 and 2013CB921900) and the NSFC of China (No. 61225019, 11023003 and 61376060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H-T.Y., X-Q.W. and B.L. contributed equally to this work. H-T.Y., H.Y.H. and Y.C. conceived and designed the experiments. H-T.Y. performed the sample fabrication and all optical and transport measurements. H-T.Y., X-F.F., X-Q.W. and B.S. performed the CPGE measurements. B.L., H-J.Z., G.X., Y.X. and S-C.Z. performed all the DFT calculations and theoretical analyses. S-C.Z., H.Y.H. and Y.C. supervised the project. H-T.Y., B.L. and H-J.Z. wrote the manuscript, with input from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1696 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, H., Wang, X., Lian, B. et al. Generation and electric control of spin–valley-coupled circular photogalvanic current in WSe2. Nature Nanotech 9, 851–857 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2014.183
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2014.183
This article is cited by
-
Light control with Weyl semimetals
eLight (2023)
-
Disorder-induced bulk photovoltaic effect in a centrosymmetric van der Waals material
npj 2D Materials and Applications (2023)
-
Berry curvature dipole generation and helicity-to-spin conversion at symmetry-mismatched heterointerfaces
Nature Nanotechnology (2023)
-
Strong bulk photovoltaic effect in engineered edge-embedded van der Waals structures
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Recent developments in CVD growth and applications of 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
Frontiers of Physics (2023)