Abstract
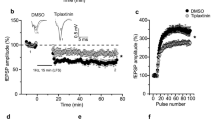
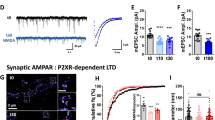
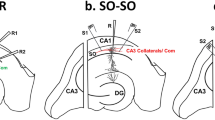
Pro- and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) activate two distinct receptors: p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) and TrkB. Mature BDNF facilitates hippocampal synaptic potentiation through TrkB. Here we report that proBDNF, by activating p75NTR, facilitates hippocampal long-term depression (LTD). Electron microscopy showed that p75NTR localized in dendritic spines, in addition to afferent terminals, of CA1 neurons. Deletion of p75NTR in mice selectively impaired the NMDA receptor–dependent LTD, without affecting other forms of synaptic plasticity. p75NTR−/− mice also showed a decrease in the expression of NR2B, an NMDA receptor subunit uniquely involved in LTD. Activation of p75NTR by proBDNF enhanced NR2B-dependent LTD and NR2B-mediated synaptic currents. These results show a crucial role for proBDNF-p75NTR signaling in LTD and its potential mechanism, and together with the finding that mature BDNF promotes synaptic potentiation, suggest a bidirectional regulation of synaptic plasticity by proBDNF and mature BDNF.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, B. BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation. Learn. Mem. 10, 86–98 (2003).
Poo, M.M. Neurotrophins as synaptic modulators. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 24–32 (2001).
Korte, M. et al. Hippocampal long-term potentiation is impaired in mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 8856–8860 (1995).
Figurov, A., Pozzo-Miller, L., Olafsson, P., Wang, T. & Lu, B. Regulation of synaptic responses to high-frequency stimulation and LTP by neurotrophins in the hippocampus. Nature 381, 706–709 (1996).
Patterson, S.L. et al. Recombinant BDNF rescues deficits in basal synaptic transmission and hippocampal LTP in BDNF knockout mice. Neuron 16, 1137–1145 (1996).
Lessmann, V., Gottmann, K. & Malcangio, M. Neurotrophin secretion: current facts and future prospects. Prog. Neurobiol. 69, 341–374 (2003).
Lu, B. Pro-region of neurotrophins: role in synaptic modulation. Neuron 39, 735–738 (2003).
Mowla, S.J. et al. Biosynthesis and post-translational processing of the precursor to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 12660–12666 (2001).
Seidah, N.G., Benjannet, S., Pareek, S., Chretien, M. & Murphy, R.A. Cellular processing of the neurotrophin precursors of NT3 and BDNF by the mammalian proprotein convertases. FEBS Lett. 379, 247–250 (1996).
Kaplan, D.R. & Miller, F.D. Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 10, 381–391 (2000).
Huang, E.J. & Reichardt, L.F. Trk receptors: roles in neuronal signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 609–642 (2003).
Lee, R., Kermani, P., Teng, K.K. & Hempstead, B.L. Regulation of cell survival by secreted proneurotrophins. Science 294, 1945–1948 (2001).
Chao, M.V. & Bothwell, M. Neurotrophins: to cleave or not to cleave. Neuron 33, 9–12 (2002).
Ibanez, C.F. Jekyll-Hyde neurotrophins: the story of proNGF. Trends Neurosci. 25, 284–286 (2002).
Nykjaer, A. et al. Sortilin is essential for proNGF-induced neuronal cell death. Nature 427, 843–848 (2004).
Beattie, M.S. et al. ProNGF induces p75-mediated death of oligodendrocytes following spinal cord injury. Neuron 36, 375–386 (2002).
Harrington, A.W. et al. Secreted proNGF is a pathophysiological death-inducing ligand after adult CNS injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 6226–6230 (2004).
Teng, H.K. et al. ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin. J. Neurosci. 25, 5455–5463 (2005).
Dechant, G. & Barde, Y.A. The neurotrophin receptor p75(NTR): novel functions and implications for diseases of the nervous system. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 1131–1136 (2002).
Barker, P.A. p75NTR is positively promiscuous: novel partners and new insights. Neuron 42, 529–533 (2004).
Lou, H. et al. Sorting and activity-dependent secretion of BDNF require interaction of a specific motif with the sorting receptor carboxypeptidase e. Neuron 45, 245–255 (2005).
Mowla, S.J. et al. Differential sorting of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 19, 2069–2080 (1999).
Chen, Z.-Y. et al. Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Met66) alters the intracellular trafficking and activity-dependent secretion of wild-type bdnf in neurosecretory cells and cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 24, 4401–4411 (2004).
Lee, K.F. et al. Targeted mutation of the gene encoding the low affinity NGF repector p75 leads to deficits in the peripheral sensory nervous system. Cell 69, 737–749 (1992).
Pang, P.T. et al. Cleavage of proBDNF by tPA/plasmin is essential for long-term hippocampal plasticity. Science 306, 487–491 (2004).
Liu, L. et al. Role of NMDA receptor subtypes in governing the direction of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Science 304, 1021–1024 (2004).
Massey, P.V. et al. Differential roles of NR2A and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in cortical long-term potentiation and long-term depression. J. Neurosci. 24, 7821–7828 (2004).
Cabin, D.E. et al. Synaptic vesicle depletion correlates with attenuated synaptic responses to prolonged repetitive stimulation in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. J. Neurosci. 22, 8797–8807 (2002).
Mischel, P.S. et al. The extracellular domain of p75NTR is necessary to inhibit neurotrophin-3 signaling through TrkA. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 11294–11301 (2001).
Oliet, S.H., Malenka, R.C. & Nicoll, R.A. Two distinct forms of long-term depression coexist in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells. Neuron 18, 969–982 (1997).
Hempstead, B.L. The many faces of p75NTR. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 12, 260–267 (2002).
Kemp, N. & Bashir, Z.I. Induction of LTD in the adult hippocampus by the synaptic activation of AMPA/kainate and metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuropharmacology 38, 495–504 (1999).
Mulkey, R.M. & Malenka, R.C. Mechanisms underlying induction of homosynaptic long-term depression in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Neuron 9, 967–975 (1992).
Dudek, S.M. & Bear, M.F. Homosynaptic long-term depression in area CA1 of hippocampus and effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 4363–4367 (1992).
Dougherty, K.D. & Milner, T.A. Cholinergic septal afferent terminals preferentially contact neuropeptide Y-containing interneurons compared to parvalbumin-containing interneurons in the rat dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 19, 10140–10152 (1999).
Ikegaya, Y., Ishizaka, Y. & Matsuki, N. BDNF attenuates hippocampal LTD via activation of phospholipase C: implications for a vertical shift in the frequency-response curve of synaptic plasticity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 16, 145–148 (2002).
Kirkwood, A., Rozas, C., Kirkwood, J., Perez, F. & Bear, M.F. Modulation of long-term synaptic depression in visual cortex by acetylcholine and norepinephrine. J. Neurosci. 19, 1599–1609 (1999).
Wright, J.W., Alt, J.A., Turner, G.D. & Krueger, J.M. Differences in spatial learning comparing transgenic p75 knockout, New Zealand Black, C57BL/6, and Swiss Webster mice. Behav. Brain Res. 153, 453–458 (2004).
Peterson, D.A., Dickinson-Anson, H.A., Leppert, J.T., Lee, K.F. & Gage, F.H. Central neuronal loss and behavioral impairment in mice lacking neurotrophin receptor p75. J. Comp. Neurol. 404, 1–20 (1999).
Rosch, H., Schweigreiter, R., Bonhoeffer, T., Barde, Y.A. & Korte, M. The neurotrophin receptor p75NTR modulates long-term depression and regulates the expression of AMPA receptor subunits in the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 7362–7367 (2005).
Bandtlow, C. & Dechant, G. From cell death to neuronal regeneration, effects of the p75 neurotrophin receptor depend on interactions with partner subunits. Sci. STKE 2004, pe24 (2004).
Davis, R.J. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103, 239–252 (2000).
O'Neill, L.A. & Kaltschmidt, C. NF-kappa B: a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends Neurosci. 20, 252–258 (1997).
Yan, Q. & Johnson, E.M., Jr. An immunohistochemical study of the nerve growth factor receptor in developing rats. J. Neurosci. 8, 3481–3498 (1988).
Van der Zee, C.E., Ross, G.M., Riopelle, R.J. & Hagg, T. Survival of cholinergic forebrain neurons in developing p75NGFR-deficient mice. Science 274, 1729–1732 (1996).
Lu, B., Pang, P.T. & Woo, N.H. The yin and yang of neurotrophin action. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. (in the press).
Lee, K.F., Bachman, K., Landis, S. & Jaenisch, R. Dependence of the p75 innervation of some sympathetic targets. Science 263, 1447–1449 (1994).
Dougherty, K.D. & Milner, T.A. p75NTR immunoreactivity in the rat dentate gyrus is mostly within presynaptic profiles but is also found in some astrocytic and postsynaptic profiles. J. Comp. Neurol. 407, 77–91 (1999).
Peters, A., Palay, S.L. & Webster, H.deF. The Fine Structure of the Nervous System (Oxford University Press, New York, 1991).
Ji, Y., Pang, P.T., Feng, L. & Lu, B. Cyclic AMP controls BDNF-induced TrkB phosphorylation and dendritic spine formation in mature hippocampal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 164–172 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by funds from National Institute of Child Health and Human Development intramural program (to B.L.), and US National Institutes of Health grants NS30658 (to B.L.H.) and HL18974 (to T.A.M.). N.H.W. is supported by fellowships from Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research and Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. We would like to thank K. Sakata, J. Chang and K. Pelkey for advice and assistance. We also thank L. Tessarollo for providing p75NTR−/− mice and L. Reichardt for the p75NTR-blocking REX antibody.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Hippocampal LTD induced by LFS is NMDA receptor-dependent. (PDF 177 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Ultrastructural localization of p75NTR immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of p75NTR+/+ (i.e., Ngfr+/+) mice. (PDF 4149 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
proBDNF does not affect hippocampal LTP. (PDF 101 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Attenuated expression of NR2B in area CA1 of p75NTR−/− (i.e., Ngfr−/−) hippocampal slices. (PDF 2513 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, N., Teng, H., Siao, CJ. et al. Activation of p75NTR by proBDNF facilitates hippocampal long-term depression. Nat Neurosci 8, 1069–1077 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1510
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1510
This article is cited by
-
The role of neurotrophic factors in novel, rapid psychiatric treatments
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Assessing the mechanisms of brain plasticity by transcranial magnetic stimulation
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Delayed Outgrowth in Response to the BDNF and Altered Synaptic Proteins in Neurons From SHR Rats
Neurochemical Research (2023)
-
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Novel Dynamically Regulated Therapeutic Modulator in Neurological Disorders
Neurochemical Research (2023)
-
Mitochondria as central hubs in synaptic modulation
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)