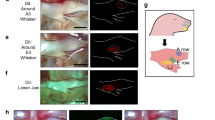
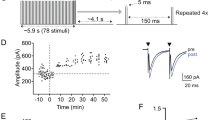
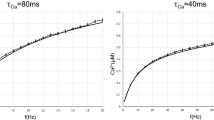
Abstract
We found rat central auditory neurons to fire action potentials in a precise sequence of mini-bursts before the age of hearing onset. This stereotyped pattern was initiated by hair cells in the cochlea, which trigger brief bursts of action potentials in auditory neurons each time they fire a Ca2+ spike. By generating theta-like activity, hair cells may limit the influence of synaptic depression in developing auditory circuits and promote consolidation of synapses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 August 2010
In the version of this article initially published online, the first sentence of the Author Contributions statement was incorrect. The first sentence should read “N.X.T. performed the in vitro IHC and SGN recordings and the in vivo iCIC recordings.” The error has been corrected for the print, PDF and HTML versions of this article.
References
Blankenship, A.G. & Feller, M.B. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 18–29 (2010).
Ben-Ari, Y. Trends Neurosci. 24, 353–360 (2001).
Malenka, R.C. & Bear, M.F. Neuron 44, 5–21 (2004).
Zhang, W. & Linden, D.J. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 885–900 (2003).
Jones, T.A. et al. J. Neurophysiol. 98, 1898–1908 (2007).
Sonntag, M. et al. J. Neurosci. 29, 9510–9520 (2009).
Tritsch, N.X. et al. Nature 450, 50–55 (2007).
Tritsch, N.X. & Bergles, D.E. J. Neurosci. 30, 1539–1550 (2010).
von Gersdorff, H. & Borst, J.G.G. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 53–64 (2002).
Guinan, J.J. Jr. & Li, R.Y. Hear. Res. 49, 321–334 (1990).
Carlier, E., Abonnenc, M. & Pujol, R. J. Physiol. 70, 129–138 (1975).
Walsh, E.J. & Romand, R. in Development of Auditory and Vestibular Systems 2 (ed. R. Romand) 161–210 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1992).
Johnson, S.L., Marcotti, W. & Kros, C.J. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 563, 177–191 (2005).
Brenowitz, S. & Trussell, L.O. J. Neurosci. 21, 9487–9498 (2001).
Larson, J., Wong, D. & Lynch, G. Brain Res. 368, 347–350 (1986).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the US National Center for Research Resources (G12-RR03060) to A.R.-C., the European Union (EUSynapse, LSHM-CT-2005–019055), Heinsius Houbolt fund and SenterNovem (The Netherlands, Neuro-Bsik, BSIK 03053) to J.G.G.B., and the US National Institutes of Health (DC008860 and DC009464) to D.E.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.X.T. performed the in vitro IHC and SGN recordings and the in vivo CIC recordings. A.R.-C. and T.T.H.C. performed the in vivo MNTB recordings. H.C.W. provided technical assistance and performed some in vivo CIC recordings. N.X.T., A.R.-C., J.G.G.B. and D.E.B. designed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Discussion (PDF 2110 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tritsch, N., Rodríguez-Contreras, A., Crins, T. et al. Calcium action potentials in hair cells pattern auditory neuron activity before hearing onset. Nat Neurosci 13, 1050–1052 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2604
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2604
This article is cited by
-
Spontaneous activity in whisker-innervating region of neonatal mouse trigeminal ganglion
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Biophysical mechanism of signal encoding in an auditory neuron
Nonlinear Dynamics (2021)
-
Delayed expression of activity-dependent gating switch in synaptic AMPARs at a central synapse
Molecular Brain (2020)
-
Characterization of HA-tagged α9 and α10 nAChRs in the mouse cochlea
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Long-term potentiation of glycinergic synapses by semi-natural stimulation patterns during tonotopic map refinement
Scientific Reports (2020)