Abstract
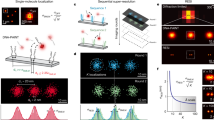
The spatiotemporal resolution of subdiffraction fluorescence imaging has been limited by the difficulty of labeling proteins in cells with suitable fluorophores. Here we report a chemical tag that allows proteins to be labeled with an organic fluorophore with high photon flux and fast photoswitching performance in live cells. This label allowed us to image the dynamics of human histone H2B protein in living cells at ∼20 nm resolution.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hell, S.W. Science 316, 1153–1158 (2007).
Kner, P. et al. Nat. Methods 6, 339–342 (2009).
Betzig, E. et al. Science 313, 1642–1645 (2006).
Hess, S.T., Girirajan, T.P. & Mason, M.D. Biophys. J. 91, 4258–4272 (2006).
Rust, M.J., Bates, M. & Zhuang, X. Nat. Methods 3, 793–796 (2006).
Heilemann, M. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn. 47, 6172–6176 (2008).
Manley, S. et al. Nat. Methods 5, 155–157 (2008).
Hein, B. et al. Biophys. J. 98, 158–163 (2010).
Heilemann, M. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn. 48, 6903–6908 (2009).
Fölling, J. et al. Nat. Methods 5, 943–945 (2008).
Miller, L.W. & Cornish, V.W. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 9, 56–61 (2005).
Gallagher, S.S . et al. ACS Chem. Biol. 7, 547–556 (2009).
Miller, L.W. et al. Nat. Methods 2, 255–257 (2005).
Tokunaga, M., Imamoto, N. & Sogawa, S. Nat. Methods 5, 159–161 (2008).
Thompson, R.E., Larson, D.R. & Webb, W.W. Biophys. J. 82, 2775–2783 (2002).
Woodcock, C.L. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 9021–9025 (1993).
Kimura, H. & Cook, P.R.J. Cell Biol. 153, 1341–1353 (2001).
Heun, P. et al. Science 294, 2181–2186 (2001).
Calloway, N.T. et al. ChemBioChem 8, 767–774 (2007).
van de Linde, S. et al. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 8, 465–469 (2009).
Wolter, S. et al. J. Microsc. 237, 12–22 (2010).
Endesfelder, U. et al. ChemPhysChem 11, 836–840 (2010).
van de Linde, S., Wolter, S., Heilemann, M. & Sauer, M. J. Biotechnol. advance online publication 20 February 2010 (doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.02.010).
Cordes, T. et al. Nano Lett. 10, 645–651 (2010).
Shroff, H., Galbraith, C.G., Galbraith, J.A. & Betzig, E. Nat. Methods 5, 417–423 (2008).
Shannon, C.E. Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers 37, 10–21 (1949).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Biophotonics and the Systems Biology Initiative (Forschungseinheiten der Systembiologie) of the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung and by the US National Institutes of Health (RO1GM54469 and RC1GM091804 to V.W.C. and M.P.S.). R.W. was supported by a Deutscher Akademischer Austausch Dienst fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.W., M.H., S.v.d.L., M.P.S., M.H., V.W.C. and M.S. conceived and designed the experiments. R.W., M.H. and S.v.d.L. performed the experiments. M.H., S.v.d.L. and M.S. analyzed the data. R.W., V.W.C. and M.S. wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
V.W.C. and M.P.S. are inventors of the TMP-tag technology. The TMP-tag technology is licensed and commercialized by Active Motif.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4 and Supplementary Note 1 (PDF 286 kb)
Supplementary Video 1
H2B labeled HeLa cells shown in Figure 1 excited at 647 nm with 5 kW cm−2 at a frame rate of 50 Hz. (MOV 1441 kb)
Supplementary Video 2
H2B labeled HeLa cell excited at 647 nm with 0.5 kW cm−2 at a frame rate of 10 Hz. (MOV 2624 kb)
Supplementary Video 3
H2B labeled HeLa cell shown in Figure 2 excited at 647 nm with 5 kW cm−2 at a frame rate of 50 Hz. (MOV 2826 kb)
Supplementary Video 4
Sequence constructed from Supplementary Video 3 using 500 subsequent frames shifted by 50 frames, respectively. A movie is generated with an apparent time resolution of 1 Hz. However, one should be aware that the experimental time resolution is 10 s corresponding to a frame rate of 50 Hz. (MOV 1311 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wombacher, R., Heidbreder, M., van de Linde, S. et al. Live-cell super-resolution imaging with trimethoprim conjugates. Nat Methods 7, 717–719 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1489
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1489
This article is cited by
-
Enhanced detection of fluorescence fluctuations for high-throughput super-resolution imaging
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
Dynamics and functions of E-cadherin complexes in epithelial cell and tissue morphogenesis
Marine Life Science & Technology (2023)
-
Single-molecule localization microscopy
Nature Reviews Methods Primers (2021)
-
Three-dimensional super-resolution fluorescence imaging of DNA
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Single-molecule localization microscopy and tracking with red-shifted states of conventional BODIPY conjugates in living cells
Nature Communications (2019)