Abstract
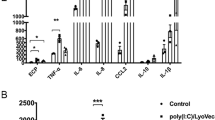
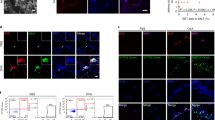
Key intracytosolic pattern recognition receptors of innate immunity against bacterial infections are nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors (NLRs). We elucidated the NOD1 and NOD2-mediated activation of human eosinophils, the principal effector cells for allergic inflammation, upon interacting with human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells in allergic asthma. Eosinophils constitutively expressed NOD1,2 but exhibited nonsignificant responses to release chemokines upon the stimulation by NOD1 ligand γ-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelic acid (iE-DAP) and NOD2 ligand muramyl dipeptide (MDP). However, iE-DAP and MDP could significantly upregulate cell surface expression of CD18 and intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 on eosinophils and ICAM-1 on BEAS-2B cells, as well as induce chemokines CCL2 and CXCL8 release in the coculture system (all P<0.05). Both eosinophils and BEAS-2B cells were the main source for CXCL8 and CCL2 release in the coculture system upon iE-DAP or MDP stimulation. Direct interaction between eosinophils and BEAS-2B cells is responsible for CCL2 release, and soluble mediators are implicated in CXCL8 release. ERK and NF-κB play regulatory roles for the expression of adhesion molecules and chemokines in coculture. Treatment with NOD1,2 ligand could induce the subepithelial fibrosis and significantly enhance the serum concentration of total IgE, chemokine CCL5 for eosinophils and T helper type 2 (Th2) cells and asthma Th2 cytokine IL-13 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of ovalbumin-sensitized allergic asthmatic mice (all P<0.05). This study provides further evidence of bacterial infection-mediated activation of NOD1,2 in triggering allergic asthma via the activation of eosinophils interacting with bronchial epithelial cells at inflammatory airway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hogan SP, Rosenberg HF, Moqbel R, Phipps S, Foster PS, Lacy P et al. Eosinophils: biological properties and role in health and disease. Clin Exp Allergy 2008; 38: 709–750.
Lemière C, Ernst P, Olivenstein R, Yamauchi Y, Govindaraju K, Ludwig MS et al. Airway inflammation assessed by invasive and noninvasive means in severe asthma: eosinophilic and noneosinophilic phenotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 118: 1033–1039.
Takafuji S, Ohtoshi T, Takizawa H, Tadokoro K, Ito K . Eosinophil degranulation in the presence of bronchial epithelial cells. Effect of cytokines and role of adhesion. J Immunol 1996; 156: 3980–3985.
Wong CK, Wang CB, Ip WK, Tian YP, Lam CW . Role of p38 MAPK and NF-κB for chemokine release in co-culture of human eosinophils and bronchial epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol 2005; 139: 90–100.
Wang CB, Wong CK, Ip WK, Tian YP, Lam CW . Induction of IL-6 in co-culture of bronchial epithelial cells and eosinophils is regulated by p38 MAPK and NF-κB. Allergy 2005; 60: 1378–1385.
Cheung PF, Wong CK, Ho AW, Hu S, Chen DP, Lam CW . Activation of human eosinophils and epidermal keratinocytes by Th2 cytokine IL-31: implication for the immunopathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Int Immunol 2010; 22: 453–467.
Schröder NW, Crother TR, Naiki Y, Chen S, Wong MH, Yilmaz A . Innate immune responses during respiratory tract infection with a bacterial pathogen induce allergic airway sensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 122: 595–602.
Crother TR, Schröder NW, Karlin J, Chen S, Shimada K, Slepenkin A et al. Chlamydia pneumoniae infection induced allergic airway sensitization is controlled by regulatory T-cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e20784.
Papadopoulos NG, Christodoulou I, Rohde G, Agache I, Almqvist C, Bruno A et al. Viruses and bacteria in acute asthma exacerbations—a GA2 LEN-DARE systematic review. Allergy 2011; 66: 458–468.
Takeuchi O, Akira S . Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010; 140: 805–820.
Carneiro LA, Magalhaes JG, Tattoli I, Philpott DJ, Travassos LH . NOD-like proteins in inflammation and disease. J Pathol 2008; 214: 136–148.
Schroder K, Tschopp J . The inflammasomes. Cell 2010; 140: 821–832.
Tsuji Y, Watanabe T, Kudo M, Arai H, Strober W, Chiba T . Sensing of commensal organisms by the intracellular sensor NOD1 mediates experimental pancreatitis. Immunity 2012; 37: 326–338.
Sabbah A, Chang TH, Harnack R, Frohlich V, Tominaga K, Dube PH et al. Activation of innate immune antiviral responses by Nod2. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 1073–1080.
Pedra JH, Cassel SL, Sutterwala FS . Sensing pathogens and danger signals by the inflammasome. Curr Opin Immunol 2009; 21: 10–16.
Magalhaes JG, Fritz JH, le Bourhis L, Sellge G, Travassos LH, Selvanantham T et al. Nod2-dependent Th2 polarization of antigen-specific immunity. J Immunol 2008; 181: 7925–7935.
Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N, Nicolae DL, Chen FF, Ramos R et al. A frame shift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn's disease. Nature 2001; 411: 603–606.
Hysi P, Kabesch M, Moffatt MF, Schedel M, Carr D, Zhang Y . NOD1 variation, immunoglobulin E and asthma. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: 935–941.
Rosenstiel P, Till A, Schreiber S . NOD-like receptors and human diseases. Microbes Infect 2007; 9: 648–657.
Kvarnhammar AM, Petterson T, Cardell LO . NOD-like receptors and RIG-I-like receptors in human eosinophils: activation by NOD1 and NOD2 agonists. Immunology 2011; 134: 314–325.
Wang L, Cummings R, Usatyuk P, Morris A, Irani K, Natarajan V . Involvement of phospholipases D1 and D2 in sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced ERK (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase) activation and interleukin-8 secretion in human bronchial epithelial cells. Biochem J 2002; 367: 751–760.
McAllister F, Henry A, Kreindler JL, Dubin PJ, Ulrich L, Steele C et al. Role of IL-17A, IL-17F, and the IL-17 receptor in regulating growth-related oncogenealpha and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in bronchial epithelium: implications for airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis. J Immunol 2005; 175: 404–412.
Kawaguchi M, Kokubu F, Kuga H, Matsukura S, Hoshino H, Ieki K et al. Modulation of bronchial epithelial cells by IL-17. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001; 108: 804–809.
Wong CK, Cao J, Yin YB, Lam CW . Interleukin-17A activation on bronchial epithelium and basophils: a novel inflammatory mechanism. Eur Respir J 2010; 35: 883–893.
Beigelman A, Gunsten S, Mikols CL, Vidavsky I, Cannon CL, Brody SL et al. Azithromycin attenuates airway inflammation in a noninfectious mouse model of allergic asthma. Chest 2009; 136: 498–506.
Barton JL, Berg T, Didon L, Nord M . The pattern recognition receptor Nod1 activates CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta signalling in lung epithelial cells. Eur Respir J 2007; 30: 214–222.
Farkas L, Stoelcker B, Jentsch N, Heitzer S, Pfeifer M . Muramyldipeptide modulates CXCL-8 release of BEAS-2B cells via NOD2. Scand J Immunol 2008; 68: 315–322.
Bérubé J, Bourdon C, Yao Y, Rousseau S . Distinct intracellular signaling pathways control the synthesis of IL-8 and RANTES in TLR1/TLR2, TLR3 or NOD1 activated human airway epithelial cells. Cell Signal 2009; 21: 448–456.
Cheung PF, Wong CK, Ip WK, Lam CW . FAK-mediated activation of ERK for eosinophil migration: a novel mechanism for infection-induced allergic inflammation. Int Immunol 2008; 20: 353–363.
Lal RB, Edison LJ, Chused TM . Fixation and long-term storage of human lymphocytes for surface marker analysis by flow cytometry. Cytometry 1988; 9: 213–219.
Holler E, Rogler G, Herfarth H, Brenmoehl J, Wild PJ, Hahn J et al. Both donor and recipient NOD2/CARD15 mutations associate with transplant-related mortality and GvHD following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004; 104: 889–894.
Hugot JP . CARD15/NOD2 mutations in Crohn's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006; 1072: 9–18.
Reijmerink NE, Bottema RW, Kerkhof M, Gerritsen J, Stelma FF, Thijs C et al. TLR-related pathway analysis: novel gene-gene interactions in the development of asthma and atopy. Allergy 2010; 65: 199–207.
Weidinger S, Klopp N, Rümmler L, Wagenpfeil S, Baurecht HJ, Gauger A et al. Association of CARD15 polymorphisms with atopy-related traits in a population-based cohort of Caucasian adults. Clin Exp Allergy 2005; 35: 866–872.
Kawaguchi M, Kokubu F, Kuga H, Tomita T, Matsukura S, Kadokura M et al. Expression of eotaxin by normal airway epithelial cells after influenza virus A infection. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2000; 122 ( Suppl 1): 44–49.
Papadopoulos NG, Papi A, Meyer J, Stanciu LA, Salvi S, Holgate ST et al. Rhinovirus infection up-regulates eotaxin and eotaxin-2 expression in bronchial epithelial cells. Clin Exp Allergy 2001; 31: 1060–1066.
Bloemen PG, van den Tweel MC, Henricks PA, Engels F, Wagenaar SS, Rutten AA et al. Expression and modulation of adhesion molecules on human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1993; 9: 586–593.
Look DC, Rapp SR, Keller BT, Holtzman MJ . Selective induction of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 by interferon- in human airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 1992; 263: L79–87.
Cheung PF, Wong CK, Ip WK, Lam CW . IL-25 regulates the expression of adhesion molecules on eosinophils: mechanism of eosinophilia in allergic inflammation. Allergy 2006; 61: 878–885.
Proud D, Leigh R . Epithelial cells and airway diseases. Immunol Rev 2011; 242: 186–204.
Kitayama J, Fuhlbrigge RC, Puri KD, Springer TA . P-selectin, L-selectin, and alpha 4 integrin have distinct roles in eosinophil tethering and arrest on vascular endothelial cells under physiological flow conditions. J Immunol 1997; 159: 3929–3939.
Burke-Gaffney A, Hellewell PG . A CD18/ICAM-1-dependent pathway mediates eosinophil adhesion to human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1998; 19: 408–418.
Michail S, Mezoff E, Abernathy F . Role of selectins in the intestinal epithelial migration of eosinophils. Pediatr Res 2005; 58: 644–647.
Spencer LA, Melo RC, Perez SA, Bafford SP, Dvorak AM, Weller PF . Cytokine receptor-mediated trafficking of preformed IL-4 in eosinophils identifies an innate immune mechanism of cytokine secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 3333–3338.
Bandeira-Melo C, Sugiyama K, Woods LJ, Weller PF . Cutting edge: eotaxin elicits rapid vesicular transport-mediated release of preformed IL-4 from human eosinophils. J Immunol 2001; 166: 4813–4817.
Geddes BJ, Wang L, Huang WJ, Lavellee M, Manji GA . Human CARD12 is a novel CED4/Apaf-1 family member that induces apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 284: 77–82.
Inohara M, Chamaillard M, McDonald C, Nuñez G . NOD-LRR proteins: role in host-microbial interactions and inflammatory disease. Annu Rev Biochem 2005; 74: 355–360.
Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos K, Tschopp J . NF-kappaB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 5299–5305.
Pauleau AL, Murray PJ . Role of Nod2 in the response of macrophages to toll-like receptor agonists. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 7531–7539.
Kobayashi KS, Chamaillard M, Ogura Y, Henegariu O, Inohara N, Nuñez G et al. Nod2-dependent regulation of innate and adaptive immunity in the intestinal tract. Science 2005; 307: 731–734.
Park JH, Kim YG, Shaw M, Kanneganti TD, Fujimoto Y, Fukase K et al. Nod1/RICK and TLR signaling regulate chemokine and antimicrobial innate immune responses in mesothelial cells. J Immunol 2007; 179: 514–521.
Cheung PF, Wong CK, Lam CW . Molecular mechanisms of cytokine and chemokine release from eosinophils activated by IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-23: implication for Th17 lymphocytes-mediated allergic inflammation. J Immunol 2008; 180: 5625–5635.
Netea MG, Azam T, Ferwerda G, Girardin SE, Walsh M, Park JS et al. IL-32 synergizes with nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD) 1 and NOD2 ligands for IL-1beta and IL-6 production through a caspase 1-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 16309–16314.
Fritz JH, Girardin SE, Fitting C, Werts C, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Caroff M et al. Synergistic stimulation of human monocytes and dendritic cells by Toll-like receptor 4 and NOD1- and NOD2-activating agonists. Eur J Immunol 2005; 35: 2459–2470.
Weigt SS, Elashoff RM, Keane MP, Strieter RM, Gomperts BN, Xue YY et al. Altered levels of CC chemokines during pulmonary CMV predict BOS and mortality post-lung transplantation. Am J Transplant 2008; 8: 1512–1522.
Gueders MM, Paulissen G, Crahay C, Quesada-Calvo F, Hacha J, van Hove C et al. Mouse models of asthma: a comparison between C57BL/6 and BALB/c strains regarding bronchial responsiveness, inflammation, and cytokine production. Inflamm Res 2009; 58: 845–854.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research Grant Committee General Research Fund, Hong Kong (project reference no.: CUHK 476411, principal investigator: CKW) and direct grant from The Chinese University of Hong Kong (reference no.: 2008.1.018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, C., Hu, S., Leung, KL. et al. NOD-like receptors mediated activation of eosinophils interacting with bronchial epithelial cells: a link between innate immunity and allergic asthma. Cell Mol Immunol 10, 317–329 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2012.77
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2012.77
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Evaluation of serum levels of interferon beta and nucleotide binding and oligomerization domain 2 gene polymorphism in children with cough asthma phenotype: a case–control study
Egyptian Pediatric Association Gazette (2023)
-
Pathogenesis of allergic diseases and implications for therapeutic interventions
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Integrated analysis of mRNA and long noncoding RNA profiles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with bronchial asthma
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2022)
-
Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the novel cytokine interleukin-38 in allergic asthma
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2020)
-
Eosinophils: Nemeses of Pulmonary Pathogens?
Current Allergy and Asthma Reports (2019)