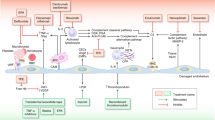
Abstract
Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TA-TMA) is an early complication of hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). A high mortality rate is documented in patients who are refractory to calcineurin inhibitor cessation. Estimates of TA-TMA prevalence vary significantly and are higher in allogeneic compared with autologous HCT. Furthermore, our understanding of the pathophysiology that is strongly related to diagnosis and treatment options is limited. Recent evidence has linked TA-TMA with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, a disease of excessive activation of the alternative pathway of complement, opening the Pandora’s box in treatment options. As conventional treatment management is highly inefficient, detection of complement activation may allow for early recognition of patients who will benefit from complement inhibition. Preliminary clinical results showing successful eculizumab administration in children and adults with TA-TMA need to be carefully evaluated. Therefore, realizing the unmet needs of better understanding TA-TMA in this complex setting, we aimed to summarize current knowledge focusing on (1) critical evaluation of diagnostic criteria, (2) epidemiology and prognosis, (3) recent evidence of complement activation and endothelial damage and (4) treatment options.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ye Y, Zheng W, Wang J, Hu Y, Luo Y, Tan Y et al. Risk and prognostic factors of transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a nested case control study. Hematol Oncol (e-pub ahead of print 1 June 2016; doi:10.1002/hon.2310).
Sakellari I, Gavriilaki E, Boussiou Z, Batsis I, Mallouri D, Constantinou V et al. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: an unresolved complication of unrelated allogeneic transplant for hematologic diseases. Hematol Oncol (e-pub ahead of print 19 September 2016; doi:10.1002/hon.2346).
Changsirikulchai S, Myerson D, Guthrie KA, McDonald GB, Alpers CE, Hingorani SR . Renal thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic cell transplant: role of GVHD in pathogenesis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2009; 4: 345–353.
Nakamae H, Yamane T, Hasegawa T, Nakamae M, Terada Y, Hagihara K et al. Risk factor analysis for thrombotic microangiopathy after reduced-intensity or myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am J Hematol 2006; 81: 525–531.
Willems E, Baron F, Seidel L, Frere P, Fillet G, Beguin Y . Comparison of thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with high-dose or nonmyeloablative conditioning. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 689–693.
Uderzo C, Bonanomi S, Busca A, Renoldi M, Ferrari P, Iacobelli M et al. Risk factors and severe outcome in thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transplantation 2006; 82: 638–644.
Ho VT, Cutler C, Carter S, Martin P, Adams R, Horowitz M et al. Blood and marrow transplant clinical trials network toxicity committee consensus summary: thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 571–575.
Jodele S, Davies SM, Lane A, Khoury J, Dandoy C, Goebel J et al. Diagnostic and risk criteria for HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study in children and young adults. Blood 2014; 124: 645–653.
Fuge R, Bird JM, Fraser A, Hart D, Hunt L, Cornish JM et al. The clinical features, risk factors and outcome of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura occurring after bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 58–64.
Jodele S, Zhang K, Zou F, Laskin B, Dandoy CE, Myers KC et al. The genetic fingerprint of susceptibility for transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood 2016; 127: 989–996.
Laskin BL, Goebel J, Davies SM, Jodele S . Small vessels, big trouble in the kidneys and beyond: hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood 2011; 118: 1452–1462.
Legendre CM, Licht C, Muus P, Greenbaum LA, Babu S, Bedrosian C et al. Terminal complement inhibitor eculizumab in atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med 2013; 368: 2169–2181.
Rathbone J, Kaltenthaler E, Richards A, Tappenden P, Bessey A, Cantrell A . A systematic review of eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome (aHUS). BMJ Open 2013; 3: e003573.
Jodele S, Dandoy CE, Danziger-Isakov L, Myers KC, El-Bietar J, Nelson A et al. Terminal complement blockade after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is safe without meningococcal vaccination. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2016; 22: 1337–1340.
Vasu S, Wu H, Satoskar A, Puto M, Roddy J, Blum W et al. Eculizumab therapy in adults with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Bone Marrow Transplant 2016; 51: 1241–1244.
Ruutu T, Barosi G, Benjamin RJ, Clark RE, George JN, Gratwohl A et al. Diagnostic criteria for hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated microangiopathy: results of a consensus process by an International Working Group. Haematologica 2007; 92: 95–100.
Kennedy GA, Bleakley S, Butler J, Mudie K, Kearey N, Durrant S . Posttransplant thrombotic microangiopathy: sensitivity of proposed new diagnostic criteria. Transfusion 2009; 49: 1884–1889.
Cho BS, Yahng SA, Lee SE, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ et al. Validation of recently proposed consensus criteria for thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation 2010; 90: 918–926.
Ruutu T, Hermans J, Niederwieser D, Gratwohl A, Kiehl M, Volin L et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a survey of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Br J Haematol 2002; 118: 1112–1119.
Laskin BL, Goebel J, Davies SM, Khoury JC, Bleesing JJ, Mehta PA et al. Early clinical indicators of transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in pediatric neuroblastoma patients undergoing auto-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 682–689.
George JN, Li X, McMinn JR, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, Selby GB . Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome following allogeneic HPC transplantation: a diagnostic dilemma. Transfusion 2004; 44: 294–304.
Daly AS, Hasegawa WS, Lipton JH, Messner HA, Kiss TL . Transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy is associated with transplantation from unrelated donors, acute graft-versus-host disease and venoocclusive disease of the liver. Transfus Apher Sci 2002; 27: 3–12.
Powles RL, Clink HM, Spence D, Morgenstern G, Watson JG, Selby PJ et al. Cyclosporin A to prevent graft-versus-host disease in man after allogeneic bone-marrow transplantation. Lancet 1980; 1: 327–329.
Kaloyannidis P, Mallouri D, Hatziioannou K, Batsis I, Yannaki E, Papavasileiou P et al. Low body mass index is an independent risk factor for transplant-associated microangiopathy following total-body irradiation-based conditioning regimens. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 1076–1078.
Mii A, Shimizu A, Kaneko T, Fujita E, Fukui M, Fujino T et al. Renal thrombotic microangiopathy associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Pathol Int 2011; 61: 518–527.
Cutler C, Henry NL, Magee C, Li S, Kim HT, Alyea E et al. Sirolimus and thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 551–557.
Shayani S, Palmer J, Stiller T, Liu X, Thomas SH, Khuu T et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with sirolimus level after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with tacrolimus/sirolimus-based graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 298–304.
Dezern AE, Brodsky RA . Clinical management of aplastic anemia. Expert Rev Hematol 2011; 4: 221–230.
Jodele S, Fukuda T, Vinks A, Mizuno K, Laskin BL, Goebel J et al. Eculizumab therapy in children with severe hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 518–525.
Kanamori H, Takaishi Y, Takabayashi M, Tanaka M, Yamaji S, Tomita N et al. Clinical significance of fragmented red cells after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Int J Hematol 2003; 77: 180–184.
Martinez MT, Bucher C, Stussi G, Heim D, Buser A, Tsakiris DA et al. Transplant-associated microangiopathy (TAM) in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 993–1000.
Cataland SR, Wu HM . Diagnosis and management of complement mediated thrombotic microangiopathies. Blood Rev 2014; 28: 67–74.
Rock GA, Shumak KH, Buskard NA, Blanchette VS, Kelton JG, Nair RC et al. Comparison of plasma exchange with plasma infusion in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Study Group. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 393–397.
Kentouche K, Zintl F, Angerhaus D, Fuchs D, Hermann J, Schneppenheim R et al. von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) in the course of stem cell transplantation. Semin Thromb Hemost 2006; 32: 98–104.
Peyvandi F, Siboni SM, Lambertenghi Deliliers D, Lavoretano S, De Fazio N, Moroni B et al. Prospective study on the behaviour of the metalloprotease ADAMTS13 and of von Willebrand factor after bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol 2006; 134: 187–195.
Sarkodee-Adoo C, Sotirescu D, Sensenbrenner L, Rapoport AP, Cottler-Fox M, Tricot G et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy in blood and marrow transplant patients receiving tacrolimus or cyclosporine A. Transfusion 2003; 43: 78–84.
Maga TK, Nishimura CJ, Weaver AE, Frees KL, Smith RJ . Mutations in alternative pathway complement proteins in American patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Hum Mutat 2010; 31: E1445–E1460.
Frimat M, Tabarin F, Dimitrov JD, Poitou C, Halbwachs-Mecarelli L, Fremeaux-Bacchi V et al. Complement activation by heme as a secondary hit for atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2013; 122: 282–292.
Kavanagh D, Goodship T . Genetics and complement in atypical HUS. Pediatr Nephrol 2010; 25: 2431–2442.
Jodele S, Licht C, Goebel J, Dixon BP, Zhang K, Sivakumaran TA et al. Abnormalities in the alternative pathway of complement in children with hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood 2013; 122: 2003–2007.
Cataland SR, Holers VM, Geyer S, Yang S, Wu HM . Biomarkers of terminal complement activation confirm the diagnosis of aHUS and differentiate aHUS from TTP. Blood 2014; 123: 3733–3738.
Ham TH, Dingle JH . Studies on destruction of red blood cells. II. Chronic hemolytic anemia with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: certain immunological aspects of the hemolytic mechanism with special reference to serum complement. J Clin Invest 1939; 18: 657–672.
Gavriilaki E, Yuan X, Ye Z, Ambinder AJ, Shanbhag SP, Streiff MB et al. Modified Ham test for atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2015; 125: 3637–3646.
Brady TM, Pruette C, Loeffler LF, Weidemann D, Strouse JJ, Gavriilaki E et al. Typical hus: evidence of acute phase complement activation from a daycare outbreak. J Clin Exp Nephrol 2016; 1: 1337–1340.
Vaught AJ, Gavriilaki E, Hueppchen N, Blakemore K, Yuan X, Seifert SM et al. Direct evidence of complement activation in HELLP syndrome: A link to atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Exp Hematol 2016; 44: 390–398.
Gavriilaki EI, Imus P, Yuan X, Baines A, Jones R, Brodsky RA . Evidence of complement dysregulation in transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Haematologica 2016; 101 (suppl 1): 107 (P327).
Sahin G, Akay OM, Bal C, Yalcin AU, Gulbas Z . The effect of calcineurin inhibitors on endothelial and platelet function in renal transplant patients. Clin Nephrol 2011; 76: 218–225.
Rodriguez R, Nakamura R, Palmer JM, Parker P, Shayani S, Nademanee A et al. A phase II pilot study of tacrolimus/sirolimus GVHD prophylaxis for sibling donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using 3 conditioning regimens. Blood 2010; 115: 1098–1105.
Brown Z, Neild GH . Cyclosporine inhibits prostacyclin production by cultured human endothelial cells. Transplant Proc 1987; 19 (1 Pt 2): 1178–1180.
Garcia-Maldonado M, Kaufman CE, Comp PC . Decrease in endothelial cell-dependent protein C activation induced by thrombomodulin by treatment with cyclosporine. Transplantation 1991; 51: 701–705.
Burke GW, Ciancio G, Cirocco R, Markou M, Olson L, Contreras N et al. Microangiopathy in kidney and simultaneous pancreas/kidney recipients treated with tacrolimus: evidence of endothelin and cytokine involvement. Transplantation 1999; 68: 1336–1342.
Macunluoglu B, Atakan A, Gokce I, Ari E, Tulunay A, Demiralp E et al. Effects of rapamycin and tacrolimus on mature endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells. J Pak Med Assoc 2012; 62: 822–825.
Hwang EA, Kim HS, Ha E, Mun KC . Apoptosis in endothelial cells by cyclosporine. Transplant Proc 2012; 44: 982–984.
Ha E, Mun KC . Effects of cyclosporine on metalloproteinase in endothelial cells. Transplant Proc 2012; 44: 991–992.
Rafiee P, Johnson CP, Li MS, Ogawa H, Heidemann J, Fisher PJ et al. Cyclosporine A enhances leukocyte binding by human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells through inhibition of p38 MAPK and iNOS. Paradoxical proinflammatory effect on the microvascular endothelium. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 35605–35615.
Ikezoe T, Yang J, Nishioka C, Honda G, Furihata M, Yokoyama A . Thrombomodulin protects endothelial cells from a calcineurin inhibitor-induced cytotoxicity by upregulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase/myeloid leukemia cell-1 signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2012; 32: 2259–2270.
Carmona A, Diaz-Ricart M, Palomo M, Molina P, Pino M, Rovira M et al. Distinct deleterious effects of cyclosporine and tacrolimus and combined tacrolimus-sirolimus on endothelial cells: protective effect of defibrotide. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 1439–1445.
Dumler JS, Beschorner WE, Farmer ER, Di Gennaro KA, Saral R, Santos GW . Endothelial-cell injury in cutaneous acute graft-versus-host disease. Am J Pathol 1989; 135: 1097–1103.
Holler E, Kolb HJ, Hiller E, Mraz W, Lehmacher W, Gleixner B et al. Microangiopathy in patients on cyclosporine prophylaxis who developed acute graft-versus-host disease after HLA-identical bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1989; 73: 2018–2024.
Biedermann BC, Sahner S, Gregor M, Tsakiris DA, Jeanneret C, Pober JS et al. Endothelial injury mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and loss of microvessels in chronic graft versus host disease. Lancet 2002; 359: 2078–2083.
Luft T, Dietrich S, Falk C, Conzelmann M, Hess M, Benner A et al. Steroid-refractory GVHD: T-cell attack within a vulnerable endothelial system. Blood 2011; 118: 1685–1692.
Dietrich S, Falk CS, Benner A, Karamustafa S, Hahn E, Andrulis M et al. Endothelial vulnerability and endothelial damage are associated with risk of graft-versus-host disease and response to steroid treatment. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 22–27.
Schmid PM, Bouazzaoui A, Doser K, Schmid K, Hoffmann P, Schroeder JA et al. Endothelial dysfunction and altered mechanical and structural properties of resistance arteries in a murine model of graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 1493–1500.
Schmid PM, Bouazzaoui A, Schmid K, Birner CM, Schach C, Maier LS et al. Vascular alterations in a murine model of acute graft-versus-host disease are associated with decreased serum levels of adiponectin and an increased activity and vascular expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Cell Transplant 2016; 25: 2051–2062.
Ikezoe T, Yang J, Nishioka C, Yokoyama A . Thrombomodulin alleviates murine GVHD in association with an increase in the proportion of regulatory T cells in the spleen. Bone Marrow Transplant 2015; 50: 113–120.
Arai Y, Yamashita K, Mizugishi K, Watanabe T, Sakamoto S, Kitano T et al. Serum neutrophil extracellular trap levels predict thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 1683–1689.
Bell WR, Braine HG, Ness PM, Kickler TS . Improved survival in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clinical experience in 108 patients. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 398–403.
Jodele S, Bleesing JJ, Mehta PA, Filipovich AH, Laskin BL, Goebel J et al. Successful early intervention for hyperacute transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy following pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Pediatr Transplant 2012; 16: E39–E42.
Daly AS, Xenocostas A, Lipton JH . Transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: twenty-two years later. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 709–715.
George JN, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, Kremer Hovinga JA, Lammle B . Thrombotic microangiopathic syndromes associated with drugs, HIV infection, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cancer. Presse Med 2012; 41 (3 Pt 2): e177–e188.
Iacopino P, Pucci G, Arcese W, Bosi A, Falda M, Locatelli F et al. Severe thrombotic microangiopathy: an infrequent complication of bone marrow transplantation. Gruppo Italiano Trapianto Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 47–51.
Jodele S, Laskin BL, Goebel J, Khoury JC, Pinkard SL, Carey PM et al. Does early initiation of therapeutic plasma exchange improve outcome in pediatric stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy? Transfusion 2013; 53: 661–667.
Sarode R, McFarland JG, Flomenberg N, Casper JT, Cohen EP, Drobyski WR et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange does not appear to be effective in the management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome following bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 16: 271–275.
Mulay S, Kreuter JD, Bryant SC, Elliott MA, Hogan WJ, Winters JL et al. Outcomes of plasma exchange in patients with transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy based on time of presentation since transplant. J Clin Apher 2015; 30: 147–153.
Clark WF, Rock G, Barth D, Arnold DM, Webert KE, Yenson PR et al. A phase-II sequential case-series study of all patients presenting to four plasma exchange centres with presumed relapsed/refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura treated with rituximab. Br J Haematol 2015; 170: 208–217.
Au WY, Ma ES, Lee TL, Ha SY, Fung AT, Lie AK et al. Successful treatment of thrombotic microangiopathy after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation with rituximab. Br J Haematol 2007; 137: 475–478.
Vischini G, Cudillo L, Ferrannini M, Di Daniele N, Cerretti R, Arcese W . Rituximab in post allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation membranous nephropathy: a case report. J Nephrol 2009; 22: 160–163.
Uderzo C, Fumagalli M, De Lorenzo P, Busca A, Vassallo E, Bonanomi S et al. Impact of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura on leukemic children undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 1005–1009.
Yeates L, Slatter MA, Bonanomi S, Lim FL, Ong SY, Dalissier A et al. Use of defibrotide to treat transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a retrospective study of the Paediatric Diseases and Inborn Errors Working Parties of the European Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant (e-pub ahead of print 16 January 2017; doi:10.1038/bmt.2016.351).
Wolff D, Wilhelm S, Hahn J, Gentilini C, Hilgendorf I, Steiner B et al. Replacement of calcineurin inhibitors with daclizumab in patients with transplantation-associated microangiopathy or renal insufficiency associated with graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 38: 445–451.
de Fontbrune FS, Galambrun C, Sirvent A, Huynh A, Faguer S, Nguyen S et al. Use of eculizumab in patients with allogeneic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study from the SFGM-TC. Transplantation 2015; 99: 1953–1959.
Sevindik OG, Alacacioglu I, Katgi A, Solmaz SM, Acar C, Piskin O et al. Renal and neurological response with eculizumab in a patient with transplant associated thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation. Case Rep Hematol 2015; 2015: 425410.
Fernandez C, Lario A, Fores R, Cabrera R . Eculizumab treatment in a patient with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy and steroid-refractory acute graft versus host disease. Hematol Rep 2015; 7: 6107.
Jodele S, Fukuda T, Mizuno K, Vinks AA, Laskin BL, Goebel J et al. Variable eculizumab clearance requires pharmacodynamic monitoring to optimize therapy for thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2016; 22: 307–315.
Risitano AM, Notaro R, Pascariello C, Sica M, del Vecchio L, Horvath CJ et al. The complement receptor 2/factor H fusion protein TT30 protects paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes from complement-mediated hemolysis and C3 fragment. Blood 2012; 119: 6307–6316.
Risitano AM, Ricklin D, Huang Y, Reis ES, Chen H, Ricci P et al. Peptide inhibitors of C3 activation as a novel strategy of complement inhibition for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2014; 123: 2094–2101.
DeZern AE, Uknis M, Yuan X, Mukhina GL, Varela J, Saye J et al. Complement blockade with a C1 esterase inhibitor in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Exp Hematol 2014; 42: 857–61.e1.
Yuan X, Gavriilaki E, Thanassi JA, Yang G, Baines AC, Podos SD et al. Small-molecule Factor D inhibitors selectively block the alternative pathway of complement in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Haematologica (e-pub ahead of print 3 November 2016; doi:10.3324/haematol.2016.153312).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Aplastic Anemia and MDS International Foundation and R01HL133113 (to RAB). EG is supported by the European Hematology Association Clinical Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
RAB is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Alexion Pharmaceuticals and Apellis Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gavriilaki, E., Sakellari, I., Anagnostopoulos, A. et al. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: opening Pandora’s box. Bone Marrow Transplant 52, 1355–1360 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2017.39
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2017.39
This article is cited by
-
Eculizumab treatment in paediatric patients diagnosed with aHUS after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a HSCT-TMA case series from Japanese aHUS post-marketing surveillance
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
Treatment outcome and efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange for transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in a large real-world cohort study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
Early vascular toxicity after pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
Role of the lectin pathway of complement in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated endothelial injury and thrombotic microangiopathy
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
Infectious Challenges with Novel Antibody–Based Therapies
Current Infectious Disease Reports (2021)