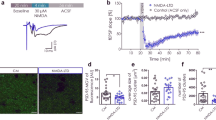
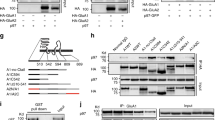
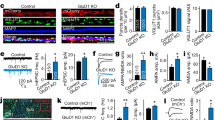
Abstract
Modulation of AMPA–type glutamate channels is important for synaptic plasticity. Here we provide physiological evidence that the activity of AMPA channels is regulated by protein phosphatase 1 (PP–1) in neostriatal neurons and identify two distinct molecular mechanisms of this regulation. One mechanism involves control of PP–1 catalytic activity by DARPP–32, a dopamine– and cAMP–regulated phosphoprotein highly enriched in neostriatum. The other involves binding of PP–1 to spinophilin, a protein that colocalizes PP–1 with AMPA receptors in postsynaptic densities. The results suggest that regulation of anchored PP–1 is important for AMPA–receptor–mediated synaptic transmission and plasticity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albin, R. L., Young, A. B. & Penney, J. B. The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci. 12, 366– 375 (1989).
Beal, M. F. Role of excitotoxicity in human neurological disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2, 657–662 ( 1992).
Davis, K. L., Kahn. R. S., Ko, G. & Davidson, M. Dopamine in schizophrenia: a review and reconceptualization. Am. J. Psychiatry 148, 1474–1486 (1991).
Seeburg, P. H. The TINS/TIPS lecture: the molecular biology of mammalian glutamate recptor channels. Trends Neurosci. 16, 359– 365 (1993).
Hollmann, M. & Heinemann, S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 31–108 (1994).
Gotz, T. et al. Functional properties of AMPA and NMDA receptors expressed in identified types of basal ganglia neurons. J. Neurosci. 17, 204–215 (1997).
Calabresi, P., Maj, R., Pisani, A., Mercuri, N. B. & Bernardi, G. Long–term synaptic depression in the striatum: physiological and pharmacological characterization. J. Neurosci. 12, 4224–4233 ( 1992).
Calabresi, P., Pisani, A., Mercuri, N. B. & Bernardi, G. The corticostriatal projection: from synaptic plasticity to dysfunction of the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci. 19, 19–24 (1996).
Bliss, T. V. P. & Collingridge, G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long–term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361, 31–39 ( 1993).
Manabe, T., Renner, P. & Nicoll, R. A. Postsynaptic contribution to long–term potentiation revealed by the analysis of miniature synaptic currents. Nature 355, 50–55 ( 1992).
Linden, D. J. Long–term synaptic depression in the mammalian brain. Neuron 12, 457–472 ( 1994).
Greengard, P., Jen, J., Nairn, A. C. & Stevens, C. F. Enhancement of the glutamate response by cAMP–dependent protein kinase in hippocampal neurons. Science 253, 1135– 1138 (1991).
Wang, L. Y., Salter M. W. & MacDonald J. F. Regulation of kainate receptors by cAMP–dependent protein kinases and phosphatases. Science 253, 1132–1134 (1991).
McGlade–McCulloh, E., Yamamoto, H., Tan, S. E., Brickey, D. A. & Soderling, T. R. Phosphorylation and regulation of glutamate receptors by calcium/calmodulin–dependent protein kinase II. Nature 362, 640–642 ( 1993).
Gerfen, C. R. The neostriatal mosaic: multiple levels of compartmental organization in the basal ganglia. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 15, 285–320 (1992).
Surmeier, D. J., Song, W. J. & Yan, Z. Coordinated expression of dopamine receptors in neostriatal medium spiny neurons. J. Neurosci. 16, 6579 –6591 (1996).
Surmeier, D. J., Bargas, J., Hemmings, H. C. Jr, Nairn, A. C. & Greengard, P. Modulation of calcium currents by a D1 dopaminergic protein kinase/phosphatase cascade in rat neostriatal neurons. Neuron 14, 385–397 (1995).
Yan, Z. & Surmeier, D. J. D5 dopamine receptors enhance Zn2+–sensitive GABAA currents in striatal cholinergic interneurons through a protein kinase A/protein phosphatase 1 cascade. Neuron 19, 1115– 1126 (1997).
Yan, Z., Song, W. J. & Surmeier, D. J. D2 dopamine receptors reduce N–type Ca2+ currents in rat neostriatal cholinergic interneurons through a membrane–delimited, protein–kinase–C–insensitive pathway. J. Neurophysiol. 77, 1003– 1015 (1997).
Cepeda, C., Buchwald, N. A. & Levine, M. S. Neuromodulatory actions of dopamine in the neostriatum are dependent upon the excitatory amino acid receptor subtypes activated. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 9576 –9580 (1993).
Walaas, S. I., Aswad, D. W. & Greengard, P. A dopamine– and cyclic AMP–regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine–innervated brain regions. Nature 301, 69–71 (1983).
Hemmings, H. C. Jr et al. DARPP–32, a dopamine–regulated neuronal phosphoprotein, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase–1. Nature 310, 503–505 (1984).
Ouimet, C. C., da Cruz e Silva, E. F. & Greengard, P. The alpha and gamma 1 isoforms of protein phosphatase 1 are highly and specifically concentrated in dendritic spines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3396– 3400 (1995).
Allen, P., Ouimet, C. & Greengard, P. Spinophilin, a novel protein phosphatase 1 binding protein localized to dendritic spines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 9956–9961 (1997).
Paternain, A. V., Morales, M. & Lerma, J. Selective antagonism of AMPA receptors unmasks kainate receptor–mediated responses in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 14, 185–189 ( 1995).
Rosenmund, C. & Westbrook, G. L. Calcium–induced actin depolymerization reduces NMDA channel activity. Neuron 10, 805–814 (1993).
Kwon, Y. G. et al. Characterization of the interaction between DARPP–32 and protein phosphatase 1 (PP–1): DARPP–32 peptides antagonize the interaction of PP–1 with binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 3536–3541 (1997).
Fienberg, A. A. et al. DARPP–32: regulator of the efficacy of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Science 281, 838– 842 (1998).
Roche, K. W., O'Brien, R. J., Mammen, A. L., Bernhardt, J. & Huganir, R. L. Characterization of multiple phosphorylation sites on the AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit. Neuron 16, 1179–1188 ( 1996).
Hubbard, M. J. & Cohen, P. On target with a new mechanism for the regulation of protein phosphorylation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 18, 172–176 (1993).
Egloff, M. P. et al. Structural basis for the recognition of regulatory subunits by the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1. EMBO J. 16, 1876–1887 (1997).
Pawson, T. & Scott, J. D. Signaling through scaffold, anchoring, and adaptor proteins. Science 278, 2075– 2080 (1997).
Rosenmund, C. et al. Anchoring of protein kinase A is required for modulation of AMPA/kainate receptors on hippocampal neurons. Nature 368, 853–856 (1994).
Gao, T. et al. cAMP–dependent regulation of cardiac L–type Ca2+ channels requires membrane targeting of PKA and phosphorylation of channel subunits. Neuron 19, 185– 196 (1997).
Petralia, R. S. & Wenthold, R. J. Light and electron immunocytochemical localization of AMPA–selective glutamate receptors in the rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 318, 329–354 (1992).
Craig, A. M., Blackstone, C. D., Huganir, R. L. & Banker, G. The distribution of glutamate receptors in cultured rat hippocampal neurons: postsynaptic clustering of AMPA–selective subunits. Neuron 10, 1055–1068 ( 1993).
Yan, Z. & Surmeier, D. J. Muscarinic (m2/m4) receptors reduce N– and P–type Ca2+ currents in neostriatal cholinergic interneurons through a fast, membrane–delimited, G protein pathway. J. Neurosci. 16, 2592– 2604 (1996).
Hamill, O. P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B. & Sigworth, F. J. Improved patch–clamp techniques for high resolution current recording from cells and cell–free membrane patches. Pfluegers Arch. 391, 85–100 (1981).
Cohen, P. et al. Protein phosphatase–1 and protein phosphatase–2A from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 159, 390–408 (1988).
Goslin, K. & Banker, G. in Culturing Nerve Cells (eds Banker, G., Goslin, K.) 251–282 (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1991).
Acknowledgements
We thank Takuo Watanabe for providing [32P]phosphorylase a. This work was supported by a National Parkinson Foundation grant (Z.Y.) and U.S. Public Health Service Grants MH 40899 and DA 10044 (P.G.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Z., Hsieh–Wilson, L., Feng, J. et al. Protein phosphatase 1 modulation of neostriatal AMPA channels: regulation by DARPP–32 and spinophilin. Nat Neurosci 2, 13–17 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/4516
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/4516
This article is cited by
-
Noradrenaline depresses facial stimulation-evoked cerebellar MLI-PC synaptic transmission via α2-AR/PKA signaling cascade in vivo in mice
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Prostaglandin E2 Increases Neurite Length and the Formation of Axonal Loops, and Regulates Cone Turning in Differentiating NE4C Cells Via PKA
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
The coming together of allosteric and phosphorylation mechanisms in the molecular integration of A2A heteroreceptor complexes in the dorsal and ventral striatal-pallidal GABA neurons
Pharmacological Reports (2021)
-
D1 receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex modulate basal mechanical sensitivity threshold and glutamatergic synaptic transmission
Molecular Brain (2020)
-
Distinct Roles of Protein Phosphatase 1 Bound on Neurabin and Spinophilin and Its Regulation in AMPA Receptor Trafficking and LTD Induction
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)