Abstract
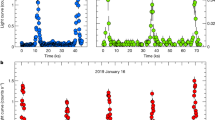
Eta Carinae is one of the most massive, luminous and unstable stars known. The basic nature of this star is poorly understood, despite much study1,2. It is a fluctuating source of hard X-rays3,4,5, indicative of gas at an unusually high temperature (60 million kelvin): the mechanism for producing this gas has yet to be established, but may be related to strong shocks in a dense stellar wind. We have monitored the hard X-ray emission (2–10 keV) from η Car over the past 1.5 years, in order to better understand the nature of these emissions and their variations. We show here that there has been an overall increase in the mean X-ray flux which has accelerated since January 1997, and that there are also small-scale periodic outbursts that occur every 85 days. It has recently been argued6,7 that η Car is in fact a binary stellar system whose components are approaching periastron near 1 January 1998. If this is indeed the case, then it is plausible that the hard X-ray emission is produced by shocks associated with the collision of the winds from the two stars, in which case the X-ray flux should increase through periastron, and rapidly decline thereafter. Continued monitoring will test this prediction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davidson, K. & Humphreys, R. M. Eta Carinae and its environment. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 35, 1–32 (1997).
Davidson, K. in Physics of Luminous Blue Variables (eds Davidson, K., Moffat, A. & Lamers, H.) 101–107 (Kluwer, Dordrecht, (1989)).
Corcoran, M. F., Rawley, G. L., Swank, J. H. & Petre, R. First detection of X-ray variability from Eta Carinae. Astrophys. J. 445, L121–L124 (1995).
Chlebowski, T., Seward, F. D., Swank, J. H. & Szymkowiak, A. E. X-rays from Eta Carinae. Astrophys. J. 281, 665–672 (1984).
Corcoran, M. F. et al. The ASCA X-ray spectrum of η Carinae. Astrophys. J. (in the press).
Damineli, A., Conti, P. S. & Lopes, D. F. Eta Carinae: a long period binary? New Astron. 2, 387–390 (1997).
Davidson, K. Is Eta Carinae a long-period binary? New Astron. 2, 387–390 (1997).
Morse, J. Examining Eta Carinae. Sky Telesc. 92(4), 13 (1996).
Gaviola, E. Eta Carinae. I. The nebulosity. Astrophys. J. 111, 408–413 (1950).
Bradt, H. V., Rothschild, R. E. & Swank, J. H. The X-ray timing explorer mission. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 97, 355–360 (1993).
Ishibashi, K. et al. Eta CARINAE. IAU Circ.No. 6668(1997).
Corcoran, M. F., Swank, J. H., Petre, R., Ishibashi, K. & Davidson, K. Eta CARINAE. IAU Circ.No. 6701(1997).
Koyama, K., Makishima, K., Tanaka, Y. & Tsunemi, H. Thermal X-ray emission with intense 6.7 keV iron line from the Galactic Ridge. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jrn 38, 121–131 (1986).
Rauw, G. et al. WR 22: the most massive Wolf-Rayet star ever weighed. Astron. Astrophys. 306, 771–782 (1996).
Tanaka, Y., Inoue, H. & Holt, S. S. The X-ray astronomy satellite ASCA. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn 46, L37–L41 (1994).
Hillier, J. D. & Allen, D. A. Aspectroscopic investigation of Eta Carinae and the Homunculus Nebula. I — Overview of the spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 262, 153–170 (1992).
Prilutskii, O. F. & Usov, V. V. X-rays from Wolf-Rayet binaries. Sov. Astron. 20, 2–3 (1976).
Mullan, D. Displaced narrow absorption components in the spectra of mass-losing OB stars — Indications of corotating interaction regions? Astron. Astrophys. 165, 157–162 (1986).
Sterken, C., de Groot, M. J. H. & van Genderen, A. M. Apulsating star inside eta Carinae. II. The variability of the pulsation period. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 116, 9–14 (1996).
Stevens, I. R., Blondin, J. M. & Pollock, A. M. T. Colliding winds from early-type stars in binary systems. Astrophys. J. 386, 265–287 (1992).
Willis, a. J., Schild, H. & Stevens, I. R. ROSAT observations of γ Velorum (WC8+O9I). I. The discovery of colliding-wind X-ray emission. Astron. Astrophys. 298, 549–566 (1995).
Corcoran, M. F. X-ray emission from colliding wind binaries. Rev. Mex. Astron. Astrophys. Conf. Ser. 5, 54–60 (1996).
Trümper, J. The ROSAT mission. Adv. Space Res. 2, 241–249 (1982).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Jahoda, M. Stark, J. Lochner, C. Heikkila, B. Patterer and the staff of the RXTE Guest Observer Facility at GSFC for their help in reducing the RXTE data. This research has made use of the Simbad database, operated at CDS, Strasbourg, France, and NASA's Astrophysics Data System Abstract Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corcoran, M., Ishibashi, K., Swank, J. et al. Increasing X-ray emissions and periodic outbursts from the massive star η Carinae. Nature 390, 587–589 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/37558
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/37558
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.