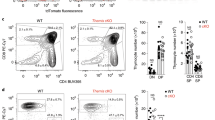
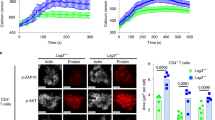
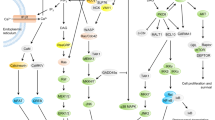
Abstract
A NUMBER of murine T-cell hybridomas undergo apoptosis within a few hours of activation by specific antigens, mitogens, antibodies against the T-cell antigen receptor, or a combination of phorbol ester and calcium ionophore1–3. This phenomenon has been extensively studied as a model for clonal deletion in the immune system, in which potentially autoreactive T cells eliminate themselves by apoptosis after activation, either in the thymus4 or in the periphery5. Here we show that the Fas/CD95 receptor, which can transduce a potent apoptotic signal when ligated6,7, is rapidly expressed following activation of T-cell hybridomas, as is its functional, membrane-bound ligand8. Interference with the ensuing Fas/Fas-ligand interaction inhibits activation-induced apoptosis. Because T-cell receptor ligation can induce apoptosis in a single T hybridoma cell, we suggest that the Fas/Fas-ligand interaction can induce cell death in a cell-autonomous manner.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi, Y., Sahai, B. M. & Green, D. R. Nature 339, 625–626 (1989).
Ucker, D. S., Ashwell, J. D. & Nickas, G. J. Immun. 143, 3461–3469 (1989).
Shi, Y. et al. J. Immun. 144, 3326–3333 (1990).
Smith, C. A., Williams, G. T., Kingston, R., Jenkinson, E. J. & Owen, J. J. T. Nature 337, 181–184 (1989).
Kawabe, Y. & Ochi, A. Nature 349, 245–248 (1991).
Yonehara, S., Ashii, A. & Yonehara, M. J. exp. Med. 169, 1747–1756 (1989).
Trauth, B. C. et al. Science 245, 301–305 (1989).
Suda, T., Takahashi, T., Golstein, P. & Nagata, S. Cell 75, 1169–1178 (1993).
Rouvier, E., Luciani, M. F. & Golstein, P. J. exp. Med. 177, 195–200 (1993).
Ramsdell, F. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 24, 928–933 (1994).
Crowe, P. D., VanArsdale, T. L., Walter, B. N., Dahms, K. M. & Ware, C. F. J. Immun. Meth. 168, 79–89 (1994).
Ramsdell, F. et al. Int. Immun. 6, 1545–1553 (1994).
Ashwell, J. D., Cunningham, R. E., Noguchi, P. D. & Hernandez, D. J. exp. Med. 165, 173–194 (1987).
Green, D. R., Bissonnette, R. P., Glynn, J. M. & Shi, Y. Sem. Immun. 4, 379–388 (1992).
Mercep, M., Noguchi, P. D. & Ashwell, J. D. J. Immun. 142, 4085–4092 (1989).
Zacharchuk, C. M., Mercep, M., Chakroborti, P. K., Simons, S. S. & Ashwell, J. D. J. Immun. 145, 4037–4045 (1990).
Iwata, M., Hanaoka, S. & Sato, K. Eur. J. Immun. 21, 643–648 (1991).
Iwata, M., Mukai, M., Nakai, Y. & Iseki, R. J. Immun. 149, 3302–3308 (1991).
Yang, Y., Vacchio, M. S. & Ashwell, J. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 6170–6174 (1993).
Shi, Y. et al. Science 257, 212–214 (1992).
Bissonnette, R. P., McGahon, A. & Green, D. R. J. exp. Med. 180, 2413–2418 (1994).
Liu, Z.-G., Smith, S. W., McLaughlin, K. A., Schwartz, L. M. & Osborne, B. A. Nature 367, 281–284 (1994).
Woronicz, J. D., Calnan, B., Ngo, V. & Winoto, A. Nature 367, 277–281 (1994).
Sarin, A., Adams, D. H. & Henkart, P. A. J. exp. Med. 178, 1693–1700 (1993).
Shi, L. et al. Science 263, 1143–1145 (1994).
Fotedar, R. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. (in the press).
Russell, J. H., Rush, B., Weaver, C. & Wang, R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 4409–4413 (1993).
Singer, G. G. & Abbas, A. K. Immunity 1, 365–371 (1994).
Matzinger, P. J. Immun. Meth. 145, 185–192 (1991).
McGahon, A. J. et al. in Cell Death (eds Schwartz, L. M. & Osborne, B. A.) (Academic, Orlando, in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunner, T., Mogil, R., LaFace, D. et al. Cell-autonomous Fas (CD95)/Fas-ligand interaction mediates activation-induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas. Nature 373, 441–444 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/373441a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/373441a0
This article is cited by
-
Advances in translational research of the rare cancer type adrenocortical carcinoma
Nature Reviews Cancer (2023)
-
Low quantity and quality of anti-spike humoral response is linked to CD4 T-cell apoptosis in COVID-19 patients
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
T cell apoptosis characterizes severe Covid-19 disease
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
Targeted transcriptome analysis using synthetic long read sequencing uncovers isoform reprograming in the progression of colon cancer
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Role of phototherapy, BAX gene expression in hyperbilirubinemia development in full-term neonates
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.