Abstract
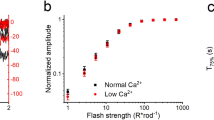
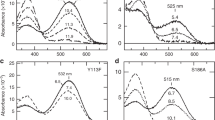
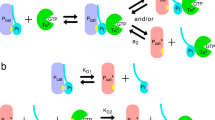
DURING light-adaptation by the vertebrate eye, the rods are desensitized and the light response is accelerated1,2. When light is absorbed by the rods, a phosphodiesterase is activated that hydrolyses cyclic GMP3,4. A light-induced decrease in cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration5–7 is part of this light-adaptation process8,9. The protein S-modulin (Mr 26,000) is known to increase the fraction of light-activated cyclic GMP-phosphodiesterase (PDE) at high Ca2+ concentrations in frog rod photoreceptors10. Here I present evidence that S-modulin lengthens the lifetime of active PDE (PDE*) at high Ca2+ concentrations. These S-modulin effects are observed in the physiological range of Ca2+ concentration (30 nM to 1 µM; half-maximum effects at 200–400 nM). At the high Ca2+ concentrations at which S-modulin prolongs the lifetime of PDE*, S-modulin inhibits rhodopsin phosphorylation (half-maximum effect at ˜100 nM Ca2+). ATP is necessary for the S-modulin effects on PDE activation. I therefore conclude that the Ca2+-dependent regulation of PDE by S-modulin is mediated by rhodopsin phosphorylation. This regulation seems to be the principal mechanism of light adaptation in vertebrate photoreceptors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baylor, D. A. & Hodgkin, A. L. J. Physiol. 242, 729–758 (1974).
Baylor, D. A., Lamb, T. D. & Yau, K.-W. J. Physiol. 288, 589–611 (1979).
Stryer, L. A. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 87–119 (1986).
Kaupp, U. B. & Koch, K.-W. A. Rev. Physiol. 54, 153–175 (1992).
Yau, K.-W. & Nakatani, K. Nature 313, 579–582 (1985).
McNaughton, P. A., Cervetto, L. & Nunn, B. J. Nature 322, 261–263 (1986).
Ratto, G. M., Payne, R., Owen, W. G. & Tsien, R. Y. J. Neurosci. 8, 3240–3246 (1988).
Matthews, H. R., Murphy, R. L. W., Fain, G. & Lam, T. D. Nature 334, 67–69 (1988).
Nakatani, K. & Yau, K.-W. Nature 334, 69–71 (1988).
Kawamura, S. & Murakami, M. Nature 349, 420–423 (1991).
Kawamura, S., Takamatsu, K. & Kitamura, K. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 186, 411–417 (1992).
Kawamura, S. & Bownds, M. D. J. gen. Physiol. 77, 571–591 (1981).
Barkdoll, A. E. III, Pugh, E. N. Jr & Sitaramayya, A. J. gen. Physiol. 93, 1091–1108 (1989).
Torre, V., Matthews, H. R. & Lamb, T. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 7109–7113 (1986).
Liebman, P. A. & Pugh, E. N. Jr Nature 287, 734–736 (1980).
Kawamura, S. Biochim. biophys. Acta 732, 276–281 (1983).
Dizhoor, A. M. et al. Science 251, 915–918 (1991).
Lambrecht, H.-G. & Koch, K.-W. EMBO J. 10, 793–798 (1991).
Benovic, J. L., Bouvier, M., Caron, M. G. & Lefkowitz, R. J. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 4, 405–428 (1988).
Kawamura, S. & Murakami, M. Biochim. biophys. Acta 870, 256–266 (1986).
Yee, R. & Liebman, P. A. J. biol. Chem. 253, 8902–8909 (1978).
Kawamura, S. & Murakami, M. J. gen. Physiol. 94, 649–668 (1989).
Laemmli, U. K. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawamura, S. Rhodopsin phosphorylation as a mechanism of cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase regulation by S-modulin. Nature 362, 855–857 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/362855a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/362855a0
This article is cited by
-
Functional compartmentalization of photoreceptor neurons
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2021)
-
Biochemistry and physiology of zebrafish photoreceptors
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2021)
-
Regulation of retinal membrane guanylyl cyclase (RetGC) by negative calcium feedback and RD3 protein
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2021)
-
Versatile functional roles of horizontal cells in the retinal circuit
Scientific Reports (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.