Abstract
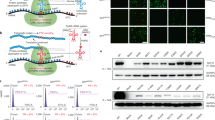
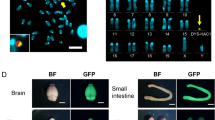
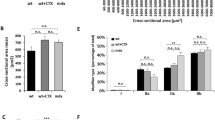
DUCHENNE progressive muscular dystrophy is a lethal and common X-linked genetic disease1 caused by the absence of dystrophin2,3, a 427K protein encoded by a 14 kilobase transcript4. Two approaches have been proposed to correct the dystrophin deficiency in muscle. The first, myoblast transfer therapy, uses cells from normal donors5–7, whereas the second involves direct intramuscular injection of recombinant plasmids expressing dystrophin8. Adenovirus is an efficient vector for in vivo expression of various foreign genes9–13. It has recently been demonstrated that a recombinant adenovirus expressing the lac-Z reporter gene can infect stably many mouse tissues, particularly muscle and heart12,13. We have tested the ability of a recombinant adenovirus, containing a 6.3 kilobase pair Becker-like dystrophin complementary DNA14 driven by the Rous sarcoma virus promoter to direct the expression of a 'minidystrophin' in infected 293 cells and C2 myoblasts, and in the mdx mouse15,16, after intramuscular injection. We report here that in vivo, we have obtained a sarcolemmal immunostaining in up to 50% of fibres of the injected muscle.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emery, A. E. H. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1988).
Zubrzycka-Gaarn, E. E. et al. Nature 333, 466–469 (1988).
Campbell, K. P. & Kahl, S. D. Nature 338, 259–262 (1989).
Koenig, M. et al. Cell 50, 509–517 (1987).
Partridge, T. A., Morgan, J. E., Coulton, G. R., Hoffman, E. P. & Kunkel, L. M. Nature 337, 176–179 (1989).
Huard, J. et al. Muscle Nerve 15, 550–560 (1992).
Gussoni, E. et al. Nature 356, 435–438 (1992).
Acsadi, G. et al. Nature 352, 815–818 (1991).
Stratford-Perricaudet, L. D. et al. Hum. Gene Ther. 1, 241–256 (1990).
Rosenfeld, M. A. et al. Science 252, 431–434 (1991).
Rosenfeld, M. A. et al. Cell 68, 143–155 (1992).
Quantin, B., Perricaudet, L. D., Tajbakhsh, S. & Mandel, J. L. Proc. natn. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 89, 2581–2584 (1992).
Stratford-Perricaudet, L. D., Makeh, I., Perricaudet, M. & Briand, P. J. clin. Invest. 90, 626–630 (1992).
England, S. B. et al. Nature 343, 180–182 (1990).
Bulfield, G., Siller, W. G., Wight, P. A. L. & Moore, K. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 1189–1192 (1984).
Sicinski, P. et al. Science 244, 1578–1580 (1989).
Hoffman, E. P. & Kunkel, L. M. Neuron 2, 1019–1029 (1989).
Shenk, T. & Williams, J. in Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology (ed. Doerfler, W.) 1–39 (Springer, Berlin, 1984).
Gluzman, Y., Reichl, H. & Solnick, D. in Eukaryotic Viral Vectors (ed. Gluzman, Y.) 187–192 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1982).
Ragot, T., Eloit, M. & Perricaudet, M. in Human Gene Transfer (eds Cohen-Haguenauer. O. & Boiron, M.) 249–260 (John Libbey, London, 1991).
Graham, F. L., Smiley, J., Russel, W. C. & Nairn, R. J. gen. Virol. 36, 59–72 (1977).
Levrero, M. et al. Gene 101, 195–201 (1991).
Cartaud, A. et al. Neuroscience 48, 995–1003 (1992).
Hoffman, E. P., Morgan, J., Watkins, S. C. & Partridge, T. A. J. neurol. Sci. 99, 9–25 (1990).
Ginjaar, H. B. et al. FEBS Lett. 308, 293–297 (1992).
Stedman, H. et al. Nature 352, 536–539 (1991).
Jiao, S. et al. Hum. Gene Ther. 3, 21–33 (1992).
Hugnot, J. P. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7506–7510 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ragot, T., Vincent, N., Chafey, P. et al. Efficient adenovirus-mediated transfer of a human minidystrophin gene to skeletal muscle of mdx mice. Nature 361, 647–650 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/361647a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/361647a0
This article is cited by
-
Cell-mediated exon skipping normalizes dystrophin expression and muscle function in a new mouse model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
EMBO Molecular Medicine (2024)
-
Aluminum particles generated during millisecond electric pulse application enhance adenovirus-mediated gene transfer in L929 cells
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Gene therapies in canine models for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Human Genetics (2019)
-
AAV2-mediated follistatin overexpression induces ovine primary myoblasts proliferation
BMC Biotechnology (2014)
-
Electroporation markedly improves Sleeping Beauty transposon-induced tumorigenesis in mice
Cancer Gene Therapy (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.