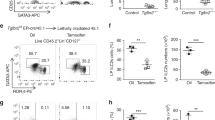
Abstract
The primary role of cytokines in haemato-lymphopoiesis is thought to be the regulation of cell growth and survival1,2,3. But the instructive action of cytokines in haematopoiesis has not been well addressed4. Here we show that a clonogenic common lymphoid progenitor5, a bone marrow-resident cell that gives rise exclusively to lymphocytes (T, B and natural killer cells), can be redirected to the myeloid lineage by stimulation through exogenously expressed interleukin (IL)-2 and GM-CSF (granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor) receptors. Analysis of mutants of the β-chain of the IL-2 receptor revealed that the granulocyte- and monocyte-differentiation signals are triggered by different cytoplasmic domains, showing that the signalling pathway(s) responsible for these unique developmental outcomes are separable. Finally, we show that the endogenous myelo-monocytic cytokine receptors for GM-CSF and macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) are expressed at low to moderate levels on the more primitive haematopoietic stem cells, are absent on common lymphoid progenitors, and are upregulated after myeloid lineage induction by IL-2. We conclude that cytokine signalling can regulate cell-fate decisions and propose that a critical step in lymphoid commitment is downregulation of cytokine receptors that drive myeloid cell development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fairbairn, L. J., Cowling, G. J., Reipert, B. M. & Dexter, T. M. Suppression of apoptosis allows differentiation and development of a multipotent hemopoietic cell line in the absence of added growth factors. Cell 74, 823–832 ( 1993).
Ogawa, M. Differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 81, 2844–2853 ( 1993).
Watowich, S. S. et al. Cytokine receptor signal transduction and the control of hematopoietic cell development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 12, 91–128 (1996).
Metcalf, D. Stem cells, pre-progenitor cells and lineage-committed cells: are our dogmas correct? Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 872, 289– 303 (1999); discussion 872, 303–304 (1999).
Kondo, M., Weissman, I. L. & Akashi, K. Identification of clonogenic common lymphoid progenitors in mouse bone marrow. Cell 91, 661– 672 (1997).
Ogasawara, K. et al. Requirement for IRF-1 in the microenvironment supporting development of natural killer cells. Nature 391, 700 –703 (1998); erratum 392, 843 (1998).
Lodolce, J. P. et al. IL-15 receptor maintains lymphoid homeostasis by supporting lymphocyte homing and proliferation. Immunity 9, 669–676 (1998).
Kennedy, M. K. et al. Reversible defects in natural killer and memory CD8 T cell lineages in interleukin 15-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 191, 771–780 (2000).
Giri, J. G. et al. Utilization of the beta and gamma chains of the IL-2 receptor by the novel cytokine IL-15. EMBO J. 13, 2822–2830 (1994).
Sugamura, K. et al. The interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain: its role in the multiple cytokine receptor complexes and T cell development in XSCID. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 179–205 (1996).
Kondo, M. et al. Sharing of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor gamma chain between receptors for IL-2 and IL-4. Science 262, 1874–1877 (1993).
Nemoto, T. et al. Differences in the interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor system in human and mouse: alpha chain is required for formation of the functional mouse IL-2 receptor. Eur. J. Immunol. 25, 3001 –3005 (1995).
Asano, M. et al. IL-2 can support growth of CD8+ T cells but not CD4+ T cells of human IL-2 receptor beta-chain transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 153, 5373–5381 ( 1994).
Nakano, T., Kodama, H. & Honjo, T. Generation of lymphohematopoietic cells from embryonic stem cells in culture. Science 265, 1098 –1101 (1994).
Domen, J., Gandy, K. L. & Weissman, I. L. Systemic overexpression of BCL-2 in the hematopoietic system protects transgenic mice from the consequences of lethal irradiation. Blood 91, 2272–2282 (1998).
Henry, C., Marbrook, J., Vann, D. C., Kodlin, D. & Wofsy, C. in Selected Methods in Cellular Immunology (eds Mishell, B. B. & Shiigi, S. M.) 138– 152 (WH Freeman, San Francisco, 1981).
Schlissel, M. S. & Stanhope-Baker, P. Accessibility and the developmental regulation of V(D)J recombination. Semin. Immunol. 9, 161–170 ( 1997).
Hatakeyama, M., Mori, H., Doi, T. & Taniguchi, T. A restricted cytoplasmic region of IL-2 receptor beta chain is essential for growth signal transduction but not for ligand binding and internalization. Cell 59, 837–845 ( 1989).
Nelson, B. H. & Willerford, D. M. Biology of the interleukin-2 receptor. Adv. Immunol. 70, 1– 81 (1998).
Constantinescu, S. N., Ghaffari, S. & Lodish, H. F. The erythropoietin receptor: structure, activation and intracellular signal transduction. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 10, 18–23 ( 1999).
Watanabe, S. et al. Reconstituted human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor transduces growth-promoting signals in mouse NIH 3T3 cells: comparison with signalling in BA/F3 pro-B cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 1440–1448 ( 1993).
Ha, K., Minden, M., Hozumi, N. & Gelfand, E. W. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 44, 4658–4660 (1984).
Palumbo, A., Minowada, J., Erikson, J., Croce, C. M. & Rovera, G. Lineage infidelity of a human myelogenous leukemia cell line. Blood 64, 1059– 1063 (1984).
Cheng, G. Y., Minden, M. D., Toyonaga, B., Mak, T. W. & McCulloch, E. A. T cell receptor and immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in acute myeloblastic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 163, 414–424 ( 1986).
Godfrey, D. I., Kennedy, J., Mombaerts, P., Tonegawa, S. & Zlotnik, A. Onset of TCR-beta gene rearrangement and role of TCR-beta expression during CD3-CD4-CD8- thymocyte differentiation. J. Immunol. 152 , 4783–4792 (1994).
Hardy, R. R., Carmack, C. E., Shinton, S. A., Kemp, J. D. & Hayakawa, K. Resolution and characterization of pro-B and pre-pro-B cell stages in normal mouse bone marrow. J. Exp. Med. 173, 1213–1225 (1991).
Rolink, A. et al. A subpopulation of B220+ cells in murine bone marrow does not express CD19 and contains natural killer cell progenitors. J. Exp. Med. 183, 187–194 (1996).
Ghaffari, S. et al. BCR-ABL and v-SRC tyrosine kinase oncoproteins support normal erythroid development in erythropoietin receptor-deficient progenitor cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13186– 13190 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Honjo for IL-2Rβ transgenic mice; G. Nolan for the retroviral system; S. Watanabe for cDNAs for human GM-CSFRα and βc; G. Q. Daley for a retroviral expression vector for EpoR; S.-I. Nishikawa for OP9 cells and anti-IL-7Rα antibody; and L. Jerabek for laboratory management. This work was supported by USPHS grant to I.L.W, and a Jose Carreras International Leukemia Foundation Grant to K.A. M.K., D.C.S. and A.G.K. are supported by fellowships from the Irvington Institute for Immunology, American Cancer Society California Division, and USPHS Training Grant, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondo, M., Scherer, D., Miyamoto, T. et al. Cell-fate conversion of lymphoid-committed progenitors by instructive actions of cytokines. Nature 407, 383–386 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35030112
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35030112
This article is cited by
-
Vitamin D and Haematopoiesis
Current Tissue Microenvironment Reports (2020)
-
Genomic regions and pathways associated with gastrointestinal parasites resistance in Santa Inês breed adapted to tropical climate
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2017)
-
MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in immune system logic
Nature Reviews Immunology (2016)
-
Emergency granulopoiesis
Nature Reviews Immunology (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.