Abstract
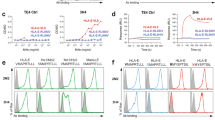
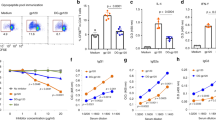
SPECIFIC B lymphocytes can act as very efficient antigen-presenting cells. They bind antigen with high affinity via their immunoglobulin receptors, process it through the class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) pathway, and present its fragments to class II-restricted T lymphocytes1. In general, exogenous antigens and noninfectious viral particles enter the class II pathway and are selectively associated with class II MHC molecules2–4. The presentation of an exogenous antigen in association with class I molecules has been reported for only a few antigens, including the hepatitis B envelope antigen (HBenvAg)5–8. Here we demonstrate that antigen-specific B cells can efficiently deliver HBenvAg to the class I pathway, presenting its fragments to class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) which kill the specific B cells. This could represent a mechanism of suppression of neutralizing anti-hepatitis B virus (HBV) antibody response, a phenomenon that accompanies the development of the chronic HBV-carrier state.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lanzavecchia, A. Nature 314, 537–539 (1985).
Germain, R. N. Nature 322, 687–689 (1986).
Morrison, L. A. et al. J. exp. Med. 163, 903–921 (1986).
Bevan, M. J. Nature 325, 192–194 (1987).
Staerz, U. D., Karasuyama, H. & Garner, A. M. Nature 329, 449–451 (1987).
Yewdell, J. W., Bennink, J. R. & Hosaka, Y. Science 239, 637–640 (1988).
Jin, Y., Sih, J. W. & Berkower, I. J. exp. Med. 168, 293–306 (1988).
Barnaba, V. et al. J. Immun. 143, 2650–2655 (1989).
Ziegler, H. K. & Unanue, E. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 175–178 (1982).
Shimonkevitz, R., Kappler, J., Marrack, P. & Grey, H. J. exp. Med. 158, 303–316 (1983).
Alberti, A. et al. Lancet 1, 1421–1424 (1988).
Moore, M. W., Carbone, F. R. & Bevan, M. J. Cell 54, 777–785 (1988).
Bastin, J. et al. J. exp. Med. 165, 1508–1523 (1987).
Deres, K. et al. Nature 342, 561–564 (1989).
Eble, B. E., Lingappa, V. R. & Ganem, D. Molec. cell. Biol. 6, 1454–1463 (1986).
Standring, D. N., Ou, J. H. & Rutter, W. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 9338–9342 (1986).
Tite, J. P., Powe, M. B. & Ruddle, N. H. J. Immun. 135, 25–33 (1985).
Tite, J. P., Foellmer, H. G., Madri, J. A. & Janeway, C. A. J. Immun. 139, 2892–2898 (1987).
Golding, H. & Singer, A. J. Immun. 135, 1610–1615 (1985).
Shinohara, N. et al. J. Immun. 140, 30–36 (1988).
Shinohara, N., Watanabe, M., Sachs, D. H. & Hozumi, N. Nature 336, 481–484 (1988).
Lanzavecchia, A. Immun. Today 10, 157–159 (1989).
Neurath, A. R. et al. Nature 315, 154–156 (1985).
Quaranta, V. L., Walker, E., Pellegrino, A. & Ferrone, S. J. Immun. 125, 1421–1425 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnaba, V., Franco, A., Alberti, A. et al. Selective killing of hepatitis B envelope antigen-specific B cells by class I-restricted, exogenous antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Nature 345, 258–260 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/345258a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/345258a0
This article is cited by
-
Hepatitis B virus particles activate B cells through the TLR2–MyD88–mTOR axis
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
The immune system view of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
Biology Direct (2020)
-
Restoring, releasing or replacing adaptive immunity in chronic hepatitis B
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2019)
-
Viral subversion of B cell responses within secondary lymphoid organs
Nature Reviews Immunology (2018)
-
Increased CD8+ T cell responses to apoptotic T cell-associated antigens in multiple sclerosis
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2013)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.