Abstract
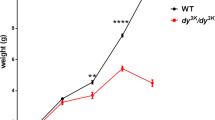
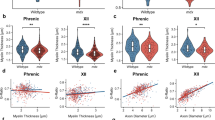
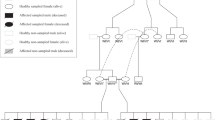
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common and the most severe of the muscular dystrophies in man1. It is inherited as an X-linked recessive trait1 and is characterized by ongoing necrosis of skeletal muscle fibres with regeneration and eventually fibrosis and fatty infiltration2. Although the gene and gene product which are defective in DMD have recently been identified3–5, the pathogenesis of the disease is still poorly understood. A myopathy has been described in the dog6–8 which has been shown to be inherited as an X-linked trait9 and which is therefore a potential model of the human disease. We have studied the phenotypic expression of the disease, canine X-linked muscular dystrophy (CXMD), and have examined the molecular relationship between it and DMD. We report here that dogs with CXMD faithfully mimic the phenotype of Duchenne muscular dystrophy and that they lack the Duchenne gene transcript and its protein product, dystrophin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moser, H. Hum. Genet. 66, 17–40 (1984).
Cullen, M. J. & Mastaglia, F. L. Br. med. Bull. 36, 145–152 (1980).
Monaco, A. P. et al. Nature 323, 646–650 (1986).
Koenig, M. et al. Cell 50, 509–517 (1987).
Hoffman, E. P., Brown, R. H. Jr & Kunkel, L. M. Cell 51, 919–928 (1987).
de Lahunta, A. Veterinary Neuroanatomy and Clinical Neurology (Saunders, Philadelphia, 1977).
Valentine, B. A., Cooper, B. J., Cummings, J. F. & de Lahunta, A. Acta neuropath. 71, 301–310 (1986).
Kornegay, J. N., Tuler, S. M., Miller, D. M. & Levesque, D. C. Muscle Nerve (in the press).
Cooper, B. J., Valentine, B. A., Wilson, S., Patterson, D. F. & Concannon, P. W. J. Hered. (in the press).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. in Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Hoffman, E. P., Monaco, A. P., Feener, C. C. & Kunkel, L. M. Science 238, 347–350 (1987).
Hoffman, E. P. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 318, 1363–1368 (1988).
Bulfield, G., Siller, W. G., Wight, P. A. L. & Moore, K. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 1189–1192 (1984).
Carnwath, J. W. & Shotton, D. M. J. Neural. Sci. 80, 39–54 (1987).
Torres, L. F. B. & Duchen, L. W. Brain 110, 269–300 (1987).
Hyser, C. L. et al. Ann. Neurol. 22, 553–555 (1987).
Fischbeck, K. H. & Schotland, D. L. Ann. Neurol. 13, 217 (1983).
Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz, I. & Borkowska, J. J. Neurol. 218, 48–50 (1978).
Oronzi Scott, M. et al. Science 239, 1418–1420 (1988).
Koenig, M., Monaco, A. P. & Kunkel, L. M. Cell 53, 219–228 (1988).
Kaprielian, Z. & Fambrough, D. M. Devl Biol. 124, 490–503 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, B., Winand, N., Stedman, H. et al. The homologue of the Duchenne locus is defective in X-linked muscular dystrophy of dogs. Nature 334, 154–156 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/334154a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/334154a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.