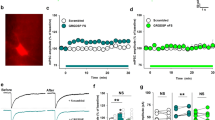
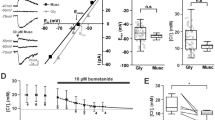
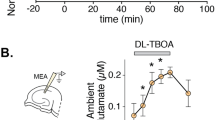
Abstract
The application of tetanic electrical stimuli to the stratum radiatum fibre pathway in the hippocampus in vitro produces an NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor-dependent enhancement of synaptic efficacy1–3. Repeated application of such stimuli produces a progressive enhancement of synaptic efficacy leading to the genesis of spontaneous and stimulation-evoked epileptiform discharges4,5. We have used this in vitro approach to explore the cellular mechanisms which underlie the kindling model of epilepsy. Kindling of the stratum radiatum fibre pathway in vitro induced a progressive, long-lasting reduction of both spontaneous and stimulation-evoked GABAergic (γ-amino butyric acid-mediated) inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (i.p.s.ps). The reduction of i.p.s.ps by kindling was associated with a profound decrease in the sensitivity of CA1 pyramidal neurons to ionophoretically applied GABA and an increase in sensitivity to NMDA. The reduction of i.p.s.ps and GABA sensitivity was prevented by kindling in the presence of the NMDA receptor antagonist D-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (D-APV). These results demonstrate that kindling-like stimulus patterns produce a reduction of GABAergic inhibition in the hippocampus resulting from a stimulus-induced postsynaptic activation of NMDA receptors. The modulation of GABAergic inhibition by NMDA receptors may cause the synaptic plasticity which underlies the kindling model of epilepsy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collingridge, G. L., Kehl, S. J. & McLennan, H. J. Physiol., Lond. 334, 33–46 (1983).
Harris, E. W., Ganong, A. H. & Cotman, C. W. Brain Res. 323, 132–137 (1984).
Wigström, H. & Gustafsson, B. Neurosci. Lett. 44, 327–332 (1984).
Slater, N. T., Stelzer, A. & Galvan, M. Neurosci. Lett. 60, 25–31 (1985).
Stasheff, S. F., Bragdon, A. C. & Wilson, W. A. Brain Res. 344, 296–302 (1985).
Alger, B. E. & Nicoll, R. A. Brain Res. 200, 195–200 (1980).
Wong, R. K. S. & Watkins, D. J. J. Neurophysiol. 48, 938–951 (1982).
Andersen, P., Dingledine, R., Gjerstad, L., Langmoen, I. A. & Mosfeldt Laursen, A. J. Physiol., Lond. 305, 279–296 (1980).
Ben-Ari, Y., Krnjević, K. & Reinhardt, W. C. Can.J. Physiol. Pharmac. 57, 1462–1466 (1979).
McCarren, M. & Alger, B. E. J. Neurophysiol. 53, 557–571 (1985).
Herron, C. E., Williamson, R. & Collingridge, G. L. Neurosci. Lett. 61, 255–260 (1985).
Dingledine, R., Hynes, M. A. & King, G. L. J. Physiol. Lond. 380, 175–189 (1986).
Krnjević, K., Morris, M. E. & Ropert, N. Brain Res. 374, 1–11 (1986).
MacDermott, A. B., Mayer, M. L., Westbrook, G. L., Smith, S. J. & Barker, J. L. Nature 321, 519–522 (1986).
Inoue, M., Oomura, Y., Yakushiji, T. & Akaike, N. Nature 324, 156–158 (1986).
Collingridge, G. L. Trends pharmac. Sci. 6, 407–411 (1985).
Dolphin, A. C., Errington, M. L. & Bliss, T. V. P. Nature 297, 496–498 (1982).
Houser, C. R., Harris, A. B. & Vaughn, J. E. Brain Res. 383, 129–145 (1986).
Roberts, E. Adv. Neurol. 44, 319–341 (1986).
Krnjević, K. Physiol. Rev. 54, 418–540 (1974).
Nicoll, R. A. & Alger, B. E. Science 212, 957–959 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stelzer, A., Slater, N. & ten Bruggencate, G. Activation of NMDA receptors blocks GABAergic inhibition in an in vitro model of epilepsy. Nature 326, 698–701 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/326698a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/326698a0
This article is cited by
-
The 1980s: d-AP5, LTP and a Decade of NMDA Receptor Discoveries
Neurochemical Research (2019)
-
Bidirectional modulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity by Dopaminergic D4-receptors in the CA1 area of hippocampus
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Glycine transporters as novel therapeutic targets in schizophrenia, alcohol dependence and pain
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2013)
-
Functional reactivity of the dopaminergic system following acute and chronic ketamine treatments
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2008)
-
Visual stimuli–induced LTD of GABAergic synapses mediated by presynaptic NMDA receptors
Nature Neuroscience (2006)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.