Abstract
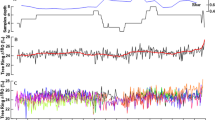
The D/H ratio of non-exchangeable hydrogen atoms in tree rings is a reliable record of the stable isotope ratio of source water used by a given tree during its growth1–6. Depending on the site of growth, this source water has been shown to be the summer rains or groundwater or both7–9. Because the isotope ratio of any of these source waters is influenced by climate, tree ring isotope data provide a fine climatic signature in most cases. However, isotope dendroclimate studies so far have been focused mainly in North America2,4,7,9,10 and to a lesser degree in Europe. We report here analysis of a record spanning 145 yr from a tree, Juniperus procera, from Kenya in East Africa. The D/H ratio correlates reasonably well with the recorded levels of the adjacent Lake Victoria and brings out interesting palaeoclimatic inferences from a region for which very little such data are available. Significantly, the relatively severe arid conditions around 1920s and the record rainfall around 1961 are reflected in the tree ring isotope ratio. This suggests that such tree ring isotope records could be used in the palaeoclimatic reconstruction of this area and could be applied to tropical environments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein, S., Thompson, P. & Yapp, C. J. Science 198, 1209–1215 (1977).
Epstein, S. & Yapp, C. J. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 30, 252–261 (1977).
Epstein, S., Yapp, C. J. & Hall, J. H. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 30, 241–251 (1976).
Yapp, C. J. & Epstein, S. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 34, 333–350 (1977).
Epstein, S. & Yapp, C. J. Nature 266, 477–478 (1977).
Yapp, C. J. & Epstein, S. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 46, 955–965 (1982).
Yapp, C. J. & Epstein, S. Nature 297, 636–639 (1982).
White, J. C., Cook, E. R., Lawrence, R. J. & Broecker, W. S. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 49, 237–246 (1985).
Yapp, C. J. & Epstein, S. J. geophys. Res. 90, No. D2 3747–3752 (1985).
Gray, J. & Song, J. S. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 70, 129–138 (1984).
Deniro, M. J. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 54, 177–185 (1981).
Dansgaard, W. Tellus 16, 436–468 (1964).
Cerling, T. E., Hay, R. L. & O'Neil, J. R. Nature 267, 137–138 (1977).
Craig, H. Science 133, 1702–1703 (1961).
Lamb, H. H. Climate, History and the Modern World (Methuen, London, 1982).
Lamb, H. H. Geogr. J. 132, 183–212 (1966).
Butzer, K. W. Recent history of an Ethiopian Delta (University of Chicago Press, 1971).
Thompson, B. W. & Morth, H. T. Weather 20, 226–227 (1965).
Champion, A. J. Geogr. J. 89, 97–118 (1937).
Environmental change in the West African Sahel (National Academy Press, Washington, 1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnamurthy, R., Epstein, S. Tree ring D/H ratio from Kenya, East Africa and its palaeoclimatic significance. Nature 317, 160–162 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/317160a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/317160a0
This article is cited by
-
Crossdating Juniperus procera from North Gondar, Ethiopia
Trees (2011)
-
Dendrochronology in the dry tropics: the Ethiopian case
Trees (2011)
-
Climatic significance ofδD time series in tree rings from Tianmu Mountain
Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences (2001)
-
Is there a stable isotope evidence for the CO2 fertilization effect?
Journal of Earth System Science (2000)
-
Climatic trends from isotopic records of tree rings: The past 100?200 years
Climatic Change (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.