Abstract
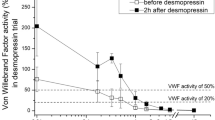
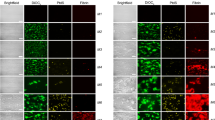
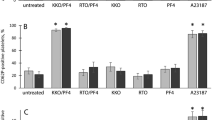
Blood platelets seal off leaks in the vessel wall to prevent haemorrhage by a mechanism involving their activation, adhesion to the zone of vessel injury and aggregation1. This physiologically important haemostatic process requires Factor VIII/von Willebrand factor (vWF), a plasma glycoprotein missing in the genetic, haemorrhagic disorder called von Willebrand disease, in which platelets cannot adhere to the subendothelial layer of the vessel wall2. Thus vWF is necessary for anchoring platelets to the vessel wall, and it mediates platelet–platelet interaction. This interaction requires an appropriate receptor on the platelet surface. Until recently, the antibiotic ristocetin was used to induce in vitro receptor-mediated binding of vWF to platelets and to cause their aggregation or agglutination3–7. But although a useful laboratory tool8, ristocetin is clearly non-physiological, so we turned our attention to thrombin, which appears in venous blood within 45 s of venipuncture and is a very potent physiological inducer of platelet aggregation. Thrombin causes platelets to change shape from discoid to spiny spheres, and alters the platelet membrane resulting in release of ADP, serotonin and other constituents of platelet storage granules9. We recently showed that low concentrations (0.1–0.5 nM) of thrombin, attainable in blood, induce binding of vWF to a specific platelet receptor10. We now report that the binding of vWF to platelet receptors is also induced by ADP on its addition to platelets. Moreover, ADP released from platelet storage granules by thrombin is, at least in part, responsible for subsequent binding of 125I-labelled vWF.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Born, G. V. R. in Platelets and Thrombosis (eds Sherry, S. & Scriabine, A.) 113–126 (University Park Press, Baltimore, 1974).
Tschopp, T. B., Weiss, H. J. & Baumgartner, H. R. J. lab. clin. Med. 83, 296–300 (1974).
Zucker, M. B., Kim, S. J., McPherson, J. & Grant, R. A. Br. J. Haemat. 35, 535–549 (1977).
Schneider-Trip, M. D., Jenkins, C. S. P., Kahle, L. H., Sturk, A. & ten Gate, J. W. Br. J. Haemat. 43, 99–112 (1979).
Jenkins, C. S. P., Clemetson, K. J. & Luscher, E. F. J. lab. clin. Med. 93, 220–231 (1979).
Morisato, D. K. & Gralnick, H. R. Blood 55, 9–15 (1980).
Kao, K. J., Pizzo, S. V. & McKee, P. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 5317–5320 (1979).
Howard, M. A. & Firkin, B. G. Thromb. Diath. haemorrh. 26, 362–369 (1971).
White, J. G. in Hematology (eds Williams, W. J., Bentler, E., Erslev, A. J. & Rundles, R. W.) 1023–1039 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1980).
Fujimoto, T., Ohara, S. & Hawiger, J. J. clin. Invest. 69 (in the press).
Timmons, S. & Hawiger, J. Thromb. Res. 12, 297–306 (1978).
Hawiger, J., Niewiarowski, S., Gurewich, V. & Thomas, D. P. J. lab. clin. Med. 75, 93–108 (1970).
Miletich, J. P., Jackson, C. M. & Majerus, P. W. J. biol. Chem. 253, 6908–6916 (1965).
Born, G. V. R. Nature 194, 927–929 (1962).
Grant, R. A., Zucker, M. B. & McPherson, J. Am. J. Physiol. 230, 1406–1410 (1976).
Begent, N. A. & Born, G. V. R. Nature 227, 926–930 (1970).
Born, G. V. R. Ciba Fdn Symp. 71, 61–78 (1980).
Mustard, J. F., Packham, M. A., Kinlough-Rathbone, R. L., Perry, D. W. & Rogoeczi, E. Blood 52, 453–466, 1978.
Marguerie, G. A., Plow, E. F. & Edgington, T. S. J. biol. Chem. 254, 5357–5363 (1979).
Bennet, J. S. & Vilaire, G. J. clin. Invest. 64, 1393–1401, (1979).
Hawiger, J., Parkinson, S. & Timmons, S. Nature 283, 195–197 (1980).
Niewiarowski, S., Brudzynski, A. Z., Morinelli, T. A., Brudzynski, T. M. & Stewart, G. J. J. biol. Chem. 256, 917–925 (1981).
Peerschke, E. I., Zucker, M. B., Grant, R. A., Egan, J. J. & Johnson, M. M. Blood 55, 841–847 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujimoto, T., Hawiger, J. Adenosine diphosphate induces binding of von Willebrand factor to human platelets. Nature 297, 154–156 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/297154a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/297154a0
This article is cited by
-
Blood cells: an historical account of the roles of purinergic signalling
Purinergic Signalling (2015)
-
Factor VIII/von willebrand factor: A multivalent ligand binding to platelets and collagen
Blut (1986)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.