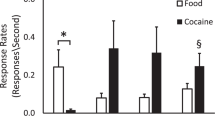
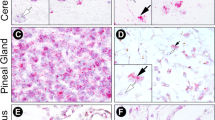
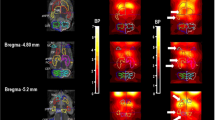
Abstract
The topographic distribution of dopaminergic receptors in the cerebral cortex closely parallels that of the dopaminergic innervation1–6. In the rat, dopaminergic axons which originate in the mesencephalon are confined to a few discrete regions of the neocortex—anterior cingulate cortex, entorhinal cortex, frontal cortex (particularly anteromedial and supragenual areas) and the transitional zone between the neocortex and the pyriform cortex1–4. Moreover, biochemical examinations of processes generally considered to be indicative of dopaminergic neurotransmission—neuronal uptake of labelled dopamine or dopamine-activation of adenylate cyclase activity5,6—have confirmed a highly restricted locus of action of dopaminergic systems in the cerebral cortex. We describe here data obtained using the 2-deoxyglucose technique7 in conjunction with conventional neuropharmacological techniques, suggesting that the influence of dopaminergic systems on cortical function extends beyond the known confines of the mesocortical dopaminergic system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thierry, A. M., Blanc, G., Sobel, A., Stinus, L. & Glowinski, J. Science 182, 499–501 (1973).
Lindvall, O., Björklund, A., Moore, R. Y. & Stenevi, U., Brain Res. 81, 325–331 (1974).
Lindvall, O., Björklund, A. & Divac, I. Adv. biochem. Psychopharmac. 16, 39–46 (1977).
Hökfelt, T., Fuxe, K., Johansson, O. & Ljundahl, A. Eur. J. Pharmac. 25, 108–112 (1974).
Tassin, J. P. et al. Brain Res. 154, 241–251 (1978).
Trabuchi, M., Govoni, S., Tonon, G. C. & Spano, P. F. J. Pharm. Pharmac. 28, 244–245, (1976).
Sokoloff, L. et al. J. Neurochem. 28, 897–916 (1977).
Sokoloff, L. J. Neurochem. 29, 13–26 (1977).
Bunney, B. S. & Aghajanian, J. K. Life Sci. 19, 1383–1392 (1976).
Jacobson, S. & Trojanowski, J. Q. Brain Res. 85, 385–401 (1975).
Krettek, J. E. & Price, J. L. J. comp. Neurol. 171, 157–192 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCulloch, J., Savaki, H., McCulloch, M. et al. Specific distribution of metabolic alterations in cerebral cortex following apomorphine administration. Nature 282, 303–305 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/282303a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/282303a0
This article is cited by
-
Autoradiographic assessment of the effects of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists in vivo
Neurochemical Research (1991)
-
Serotonergic Neuron Stimulation Modulates Thalamocortical Glucose Use in the Conscious Rat
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (1987)
-
Cerebral Circulatory Effects of a Dopaminergic Agonist (Apomorphine) in the Dog
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (1982)
-
Effect of Apomorphine on the Relationship between Local Cerebral Glucose Utilization and Local Cerebral Blood Flow (with an Appendix on its Statistical Analysis)
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (1982)
-
Alterations in Local Cerebral Glucose Utilisation in Specific Thalamic Nuclei following Apomorphine
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (1981)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.