Abstract
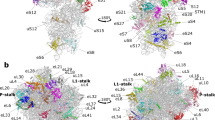
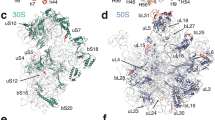
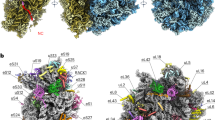
The 30S ribosomal subunit binds messenger RNA and the anticodon stem-loop of transfer RNA during protein synthesis. A crystallographic analysis of the structure of the subunit from the bacterium Thermus thermophilus is presented. At a resolution of 5.5 Å, the phosphate backbone of the ribosomal RNA is visible, as are the α-helices of the ribosomal proteins, enabling double-helical regions of RNA to be identified throughout the subunit, all seven of the small-subunit proteins of known crystal structure to be positioned in the electron density map, and the fold of the entire central domain of the small-subunit ribosomal RNA to be determined.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts, B. et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell (Garland, New York, 1995).
von Böhlen, K. et al. Characterization and preliminary attempts for derivatization of crystals of large ribosomal subunits from Haloarcula marismortui diffracting to 3 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 222, 11–15 (1991).
Trakhanov, S. D. et al. Crystallization of 70 S ribosomes and 30 S ribosomal subunits from Thermus thermophilus. FEBS Lett. 220, 319–322 (1987).
Yusupov, M. M., Tischenko, S. V., Trakhanov, S. D., Ryazantsev, S. N. & Garber, M. B. Anew crystalline form of 30 S ribosomal subunits from Thermus thermophilus. FEBS Lett. 238, 113–115 (1988).
Yonath, A. et al. Characterization of crystals of small ribosomal subunits. J. Mol. Biol. 203, 831–834 (1988).
Yonath, A. et al. Crystallographic studies on the ribosome, a large macromolecular assembly exhibiting severe nonisomorphism, extreme beam sensitivity and no internal symmetry. Acta Crystallogr. A 54, 945–955 (1998).
Lata, K. R. et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunit in ice. J. Mol. Biol. 262, 43–52 (1996).
McCutcheon, J. P. et al. Location of translational initiation factor IF3 on the small ribosomal subunit. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 4301–4306 (1999).
Mueller, F. & Brimacombe, R. Anew model for the three-dimensional folding of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA. I. Fitting the RNA to a 3D electron microscopic map at 20 Å. J. Mol. Biol. 271, 524–544 (1997).
Allain, F. H. & Varani, G. Structure of the P1 helix from group I self-splicing introns. J. Mol. Biol. 250, 333–353 (1995).
Ramakrishnan, V. & White, S. W. Structure of ribosomal protein S5 reveals sites of interaction with 16S RNA. Nature 358, 768–771 (1992).
Lindahl, M. et al. Crystal structure of the ribosomal protein S6 from Thermus thermophilus. EMBO J. 13, 1249–1254 (1994).
Jaishree, T. N., Ramakrishnan, V. & White, S. W. Solution structure of prokaryotic ribosomal protein S17 by high-resolution NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 35, 2845–2853 (1996).
Davies, C., Ramakrishnan, V. & White, S. W. Structural evidence for specific S8–RNA and S8–protein interactions within the 30S ribosomal subunit; ribosomal protein S8 from Bacillus stearothermophilus at 1.9 Å resolution. Structure 4, 1093–1104 (1996).
Berglund, H. Rak, A. Serganov, A., Garber, M. & Härd, T. Solution structure of the ribosomal RNA binding protein S15 from Thermus thermophilus. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 20–23 (1997).
Winberly, B. T., White, S. W. & Ramakrishnan, V. The structure of ribosomal protein S7 at 1.9 Å resolution reveals a β-hairpin motif that binds double-stranded nucleic acids. Structure 5, 1187–1198 (1997).
Hosaka, H. et al. Ribosomal protein S7: a new RNA-binding motif with structural similarities to a DNA architectural factor. Structure 5, 1199–1208 (1997).
Clemons, W. M. J, Davies, C., White, S. W. & Ramakrishnan, V. Conformational variability of the N-terminal helix in the structure of ribosomal protein S15. Structure 6, 429–438 (1998).
Nevskaya, N. et al. Crystal structure of ribosomal protein S8 from Thermus thermophius reveals a high degree of structural conservation of a specific RNA binding site. J. Mol. Biol. 279, 233–244 (1998).
Davies, C., Gerstner, R. B., Draper, D. E., Ramakrishnan, V. & White, S. W. The crystal structure of ribosomal protein S4 reveals a two-domain molecule with an extensive RNA-binding surface: one domain shows structural homology to the ETS DNA-binding motif. EMBO J. 17, 4545–4558 (1998).
Markus, M. A., Gerstner, R. B., Draper, D. E. & Torchia, D. A. The solution structure of ribosomal protein S4 delta41 reveals two subdomains and a positively charged surface that may interact with RNA. EMBO J. 17, 4559–4571 (1998).
Capel, M. S. et al. Acomplete mapping of the proteins in the small ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. Science 238, 1403–1406 (1987).
Powers, T. & Noller, H. F. Hydroxyl radical footprinting of ribosomal proteins on 16S rRNA. RNA 1, 194–209 (1995).
Mueller, F. & Brimacombe, R. Anew model for the three-dimensional folding of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA. II. The RNA–protein interaction data. J. Mol. Biol. 271, 545–565 (1997).
Ramakrishnan, V. et al. Position of proteins S6, S11 and S15 in the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 153, 739–760 (1981).
Ungewickell, E., Garrett, R., Ehresmann, C., Stiegler, P. & Fellner, P. An investigation of the 16-S RNA binding sites of ribosomal proteins S4, S8, S15, and S20 from Escherichia coli. Eur. J. Biochem. 51, 165–180 (1975).
Mueller, F., Stark, H., van Heel, M., Rinke-Appel, J. & Brimacombe, R. Anew model for the three-dimensional folding of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA. III. The topography of the functional centre. J. Mol. Biol. 271, 566–587 (1997).
Moazed, D. & Noller, H. F. Binding of tRNA to the ribosomal A and P sites protects two distinct sets of nucleotides in 16 S rRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 211, 135–145 (1990).
Lee, K., Varma, S., SantaLucia, J. J & Cunningham, P. R. In vivo determination of RNA structure–function relationships: analysis of the 790 loop in ribosomal RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 269, 732–743 (1997).
Merryman, C., Moazed, D., McWhirter, J. & Noller, H. F. Nucleotides in 16S rRNA protected by the association of 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits. J. Mol. Biol. 285, 97–105 (1999).
Lodmell, J. S. & Dahlberg, A. E. Aconformational switch in Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA during decoding of messenger RNA. Science 277, 1262–1267 (1997).
Gregory, R. J. et al. Interaction of ribosomal proteins S6, S8, S15 and S18 with the central domain of 16 S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 178, 287–302 (1984).
Greuer, B., Osswald, M., Brimacombe, R. & Stöffler, G. RNA-protein cross-linking in Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunits; determination of sites on 16S RNA that are cross-linked to proteins S3, S4, S7, S9, S10, S11, S17, S18 and S21 by treatment with bis-(2-chloroethyl)-methylamine. Nucleic Acids Res. 15, 3241–3255 (1987).
Wu, H., Jiang, L. & Zimmermann, R. A. The binding site for ribosomal protein S8 in 16S rRNA and spc mRNA from Escherichia coli: minimum structural requirements and the effects of single bulged bases on S8–RNA interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 1687–1695 (1994).
Moine, H., Cachia, C., Westhof, E., Ehresmann, B. & Ehresmann, C. The RNA binding site of S8 ribosomal protein of Escherichia coli: Selex and hydroxyl radical probing studies. RNA 3, 255–268 (1997).
Batey, R. & Williamson, J. Interaction of the Bacillus stearothermophilus ribosomal protein S15 with 16 S rRNA: I. Defining the minimal RNA site. J. Mol. Biol. 261, 536–549 (1996).
Serganov, A. A. et al. The 16S rRNA binding site of Thermus thermophilus ribosomal protein S15: comparison with Escherichia coli S15, minimum site and structure. RNA 2, 1124–1138 (1996).
Kalurachchi, K., Uma, K., Zimmermann, R. A. & Nikonowicz, E. P. Structural features of the binding site for ribosomal protein S8 in Escherichia coli 16S rRNA defined using NMR spectroscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 2139–2144 (1997).
Urlaub, H., Thiede, B., Muller, E. C., Brimacombe, R. & Wittmann-Liebold, B. Identification and sequence analysis of contact sites between ribosomal proteins and rRNA in Escherichia coli 30 S subunits by a new approach using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry combined with N-terminal microsequencing. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 14547–14555 (1997).
Atmadja, J. et al. The tertiary folding of Escherichia coli 16S RNA, as studied by in situintra-RNA cross-linking of 30S ribosomal subunits with bis-(2-chloroethyl)-methylamine. Nucleic Acids Res. 14, 659–673 (1986).
Agrawal, R. K., Penczek, P., Grassucci, R. A. & Frank, J. Visualization of elongation factor G on the Escherichia coli 70S ribosome: the mechanism of translocation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6134–6138 (1998).
van Acken, U. Proteinchemical studies on ribosomal proteins S4 and S12 from ram (ribosomal ambiguity) mutants of Escherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 140, 61–68 (1975).
Wittmann-Liebold, B. & Greuer, B. The primary structure of protein S5 from the small subunit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. FEBS Lett. 95, 91–98 (1978).
Allen, G., Capasso, R. & Gualerzi, C. Identification of the amino acid residues of proteins S5 and S8 adjacent to each other in the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 254, 9800–9806 (1979).
Agafonov, D. E., Kolb, V. A. & Spirin, A. S. Proteins on ribosome surface: measurements of protein exposure by hot tritium bombardment technique. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 12892–12897 (1997).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. in Methods in Enzymology (eds Carter, C. W. J. & Sweet, R. M.) 307–325 (Academic, New York, 1997).
Terwilliger, T. & Berendzen, J. Automated MAD and MIR structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 849–861 (1999).
Abrahams, J. P. & Leslie, A. G. W. Methods used in the structure determination of bovine mitochondrial F1 ATPase. Acta Crystallogr. D 52, 30–42 (1996).
Jones, T. A. & Kjeldgaard, M. Electron-density map interpretation. Methods Enzymol. 277B, 173–207 (1997).
Carson, M. Ribbons 2.0. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 958–961 (1991).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the US NIH (to S. W. White & V.R.), the UK MRC and the University of Utah. Beamlines X12B and X25 at the NSLS are supported by the Office of Basic Energy Research of the US Department of Energy and by the NIH. We thank L. Berman and H. Lewis for their help on beamline X25; T. Terwilliger for advice on using SOLVE; P. Reversi and C. Vonrhein for discussions on phasing strategies; M. Pope for gifts of compounds of polytungstate clusters; J. Löwe and G.Schneider for gifts of hexatantalum bromide; B. S. Brunschwig and M. H. Chou for synthesizing osmium hexammine chloride; and S. C. Harrison, K. Nagai and D. Rhodes for critical comments on the manuscript. Coordinates for our partial model fo the 30S have been deposited in the protein data bank, with accession number 1QD7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clemons, W., May, J., Wimberly, B. et al. Structure of a bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit at 5.5 Å resolution. Nature 400, 833–840 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/23631
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/23631
This article is cited by
-
16S rRNA Methyltransferases as Novel Drug Targets Against Tuberculosis
The Protein Journal (2022)
-
Experimental demonstration of the importance of keystone communities for maintaining metacommunity biodiversity and ecosystem functioning
Oecologia (2020)
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and cell sorting of living bacteria
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Cracking pre-40S ribosomal subunit structure by systematic analyses of RNA–protein cross-linking
The EMBO Journal (2010)
-
Enabling technologies in discovery: the 2009 Nobel Prize and its implications in antibiotic design
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.