Abstract
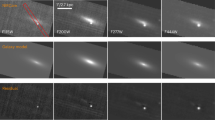
MICROSCOPIC examination of highly radioactive fall-out particles, produced by the series of large-scale nuclear test explosions carried out during September and October 1961, revealed that although they were quite or nearly spherical, their surface states were different from particle to particle and some of them were much creased or had small spherical particles attached to their surface1. Electron microscopic examination followed by electron photomicrography has been carried out to examine their surface state in detail. A vacuum-evaporated silica film backed with evaporated carbon film was used for holding a sample particle. A small drop of benzene was put on the silica film which was supported on a 150 sheet mesh, then a sample particle which had been picked up by the tip of a fine needle was transferred into the drop seen under a microscope. The sample particle was left on the film after the drop evaporated out. Electron photomicrographs of four particles, A, B, C and Z, were taken. In Table 1 are given their diameters, radioactivities and fractionation factors for 141Ce + 144Ce (ref. 2). Fig. 1 (1,2,3) gives electron photomicrographs of particles A, B and C, respectively. Small particles adhered to the surface are thought to be fine fall-out particles which are micron size or smaller3. Fig. 1 (5) is a close-up of a part of particle C. The diameter of this small particle is about l.4µ.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mamuro, T., Fujita, A., Matsunami, T., and Yoshikawa, K., Nature, 196, 529 (1962).
Mamuro, T., Yoshikawa, K., Matsunami, T., Fujita, A., and Azuma, T., Nature (in the press).
Schell, W. R., USNRDL-TR 364 (1959).
Mamuro, T., Fujita, A., Matsunami, T., Yoshikawa, K., and Azuma, T., Nature, 194, 643 (1962).
Mamuro, T., Ann. Rep. Rad. Centre Osaka Prefecture, 2, 10 (1961).
Mamuro, T., J. Atomic Energy Soc., Japan, 4, 299 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MAMURO, T., SEIYAMA, T., MATSUNAMI, T. et al. Electron Microscopic Examination of Highly Radioactive Fail-Out Particles. Nature 197, 478–479 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/197478a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/197478a0
This article is cited by
-
Plutonium-244 fission xenon and primordial xenon in the Allende meteorite
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry (1998)
-
Some of the physical characteristics of hot ?-active aerosol particles
Soviet Atomic Energy (1964)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.