Abstract
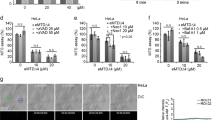
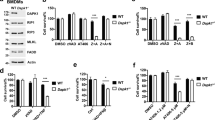
We have identified and characterized a new calcium/calmodulin (Ca2+/CaM) dependent protein kinase termed death-associated protein kinase 2 (DAPK2) that contains an N-terminal protein kinase domain followed by a conserved CaM-binding domain with significant homologies to those of DAP kinase, a protein kinase involved in apoptosis. DAPK2 mRNA is expressed abundantly in heart, lung and skeletal muscle. The mapping results indicated that DAPK2 is located in the central region of mouse chromosome 9. In vitro kinase assay revealed that DAPK2 is autophosphorylated and phosphorylates myosin light chain (MLC) as an exogenous substrate. DAPK2 binds directly to CaM and is activated in a Ca2+/CaM-dependent manner. A constitutively active DAPK2 mutant is generated by removal of the CaM-binding domain (ΔCaM). Treatment of agonists that elevate intracellular Ca2+-concentration led to the activation of DAPK2 and transfection studies revealed that DAPK2 is localized in the cytoplasm. Overexpression of DAPK2, but not the kinase negative mutant, significantly induced the morphological changes characteristic of apoptosis. These results indicate that DAPK2 is an additional member of DAP kinase family involved in apoptotic signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson P. . Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 61: 33–46.
Askew D, Ashmun R, Simmons B and Cleveland J. . 1991 Oncogene 6: 1915–1922.
Bossy-Wetzel E, Bakiri L and Yaniv M. . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 1695–1709.
Cardone M, Salvesen GS, Widmann C, Johnson GL and Frisch SM. . 1997 Cell 90: 315–323.
Cohen O, Feinstein E and Kimchi A. . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 998–1008.
Copeland NG and Jenkins NA. . 1991 Trends Genet. 7: 113–118.
Deiss LP, Feinstein E, Berissi H, Cohen O and Kimchi A. . 1995 Genes Dev. 9: 15–30.
Derijard B, Hibi M, Wu IH, Barrett T, Su B, Deng T, Karin M and Davis RJ. . 1994 Cell 76: 1025–1037.
Evan GI, Wyllie AH, Gilbert CS, Littlewood TD, Land H, Brooks M, Waters CM, Penn LZ and Hancock DC. . 1992 Cell 69: 119–128.
Feinstein E, Wallach D, Boldin M, Varfolomeev E and Kimchi A. . 1996 Trends Biochem. Sci. 20: 342–344.
Giguere V, Beatty B, Squire J, Copeland NG and Jenkins NA. . 1995 Genomics 28: 596–598.
Hakem R, Hakem A, Duncan GS, Henderson JT, Woo M, Soengas MS, Elia A, de la Pompa JL, Kagi D, Khoo W, Potter J, Yoshida R, Kaufman SA, Lowe SW, Penninger JM and Mak TW. . 1998 Cell 94: 339–352.
Hibi M, Lin A, Smeal T, Minden A and Karin M. . 1993 Genes Dev. 7: 2135–2148.
Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, Dijke PT, Saitoh M, Moriguchi T, Takagi M, Matsumoto K, Miyazono K and Gotoh Y. . 1997 Science 275: 90–94.
Inbal B, Cohen O, Polak-Charcon S, Kopolovic J, Vadai E, Eisenbach L and Kimchi A. . 1997 Nature 390: 180–184.
Inohara N, Peso L, Koseki T, Chen S and Nunez G. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 12296–12300.
Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Taylor BA and Lee BK. . 1982 J. Virol. 43: 26–36.
Kawai T, Matsumoto M, Takeda K, Sanjo H and Akira S. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 1642–1651.
Kissil JL, Feinstein E, Cohen O, Jones PA, Tsai YC, Knowles MA, Edymann ME and Kimchi A. . 1997 Oncogene 15: 405–407.
Kuida K, Zheng TS, Na S, Kuan C, Yang D, Karasuyama H, Rakic P and Flavell RA. . 1996 Nature 384: 368–372.
Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan CY, Gu Y, Taya C, Karasuyama H, Su MS, Rakic P and Flavell RA. . 1998 Cell 94: 325–337.
Lahti JM, Xiang J, Heath LS, Campana D and Kidd VJ. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 1–11.
Lassignal Johnson N, Gardner AM, Diener KM, Lange-Cartner CA, Gleavy J, Jarpe MB, Minden A, Karin M, Zon LI and Johnson GL. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 3229–3237.
Lavoie JN, Nguyen M, Marcellus RC, Branton PE and Shore GC. . 1998 J. Cell. Biol. 140: 637–645.
Lowe SW, Schmitt EM, Smith SW, Osborne BA and Jacks T. . 1993 Nature 362: 847–849.
McCarthy JV, Ni J and Dixit VM. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 16968–16975.
Miller TM, Moulder KL, Knudson CM, Creedon DJ, Deshmukh M, Korsmeyer SJ and Johnson Jr EM. . 1997 J. Cell. Biol. 139: 205–217.
Mills JC, Stone NL, Erhardt J and Pittman RN. . 1998 J. Cell. Biol. 140: 627–636.
Nagata S. . 1997 Cell 88: 355–356.
Pecker I, Avraham KB, Gilbert DJ, Savitsky K, Rotman G, Harnik R, Fukao T, Schrok E, Hirotsune S, Tagle DA, Collins FS, Wynshaw-Boris A, Ried T, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Shiloh Y and Ziv Y. . 1996 Genomics 35: 39–45.
Quignon F, De Bels F, Koken K, Feunteun J, Ameisen JC and The H. . 1998 Nature Genet. 20: 259–265.
Roulston D, Espinosa R, Nucifora G, Larson RA, Le-Beau MM and Rowley JD. . 1998 Blood 92: 2879–2885.
Sanjo H, Kawai T and Akira S. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 29066–29071.
Shi L, Nishioka CWK, Th'ng J, Bradbury EM, Litchfield DW and Greenberg AH. . 1994 Science 263: 1143–1145.
Steller H. . 1995 Science 267: 1445–1449.
Thompson JD, Higgins DG and Gibson TJ. . 1994 Nuc. Acid. Res. 22: 2673–4680.
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y. . 1998 Science 281: 1312–1316.
Tian Q, Taupin JL, Elledge S, Robertson M and Anderson P. . 1995 J. Exp. Med. 182: 865–874.
Verheij M, Bose R, Lin XH, Yao B, Jarvis WD, Grant S, Birrer MJ, Szabo E, Zon LI, Kyriakis JM, Haimovitz-Freidman A, Fuks Z and Kolesnick RN. . 1996 Nature 380: 75–79.
White E. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 1–15.
Widman C, Gerwins P, Johnson NL, Japre MB and Johnson GL. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 2416–2429.
Wright SC, Schellenberger U, Ji L, Wang H and Larrick JW. . 1997 FASEB J. 11: 843–849.
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ and Greenberg ME. . 1995 Science 270: 1326–1331.
Xiang J, Chao DT and Korsmeyer SJ. . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 14559–14563.
Yuan J, Shaham L, Ledoux S, Ellis HM and Horvitz HR. . 1993 Cell 75: 641–652.
Acknowledgements
We thank T Aoki and M Hyuga for excellent secretarial assistance, and Deborah B Householder for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education of Japan and in part by the National Cancer Institute, DHHS, under contract with ABL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawai, T., Nomura, F., Hoshino, K. et al. Death-associated protein kinase 2 is a new calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that signals apoptosis through its catalytic activity. Oncogene 18, 3471–3480 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202701
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202701
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A Diagnostic Model for Parkinson’s Disease Based on Anoikis-Related Genes
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
A seven-autophagy-related gene signature for predicting the prognosis of differentiated thyroid carcinoma
World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2022)
-
14-3-3 proteins inactivate DAPK2 by promoting its dimerization and protecting key regulatory phosphosites
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Cell Death Pathways in Ischemic Stroke and Targeted Pharmacotherapy
Translational Stroke Research (2020)
-
DAPK1 Signaling Pathways in Stroke: from Mechanisms to Therapies
Molecular Neurobiology (2017)