Abstract
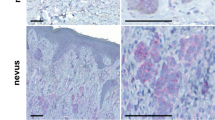
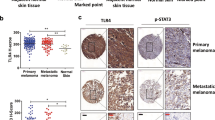
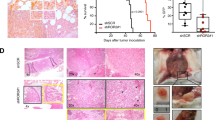
Tyrosine kinase receptors represent targets of great interest for cancer therapy. Here we show, for the first time, the importance of the orphan tyrosine kinase receptor, ROR2, in melanoma progression. Using melanoma tissue microarrays, we show that ROR2 is expressed predominantly in metastatic melanoma. As ROR2 has been shown to specifically interact with the non-canonical Wnt ligand, Wnt5A, this corroborates our earlier data implicating Wnt5A as a mediator of melanoma metastasis. We show here that increases in Wnt5A cause increases in ROR2 expression, as well as the PKC-dependent, clathrin-mediated internalization of ROR2. WNT5A knockdown by siRNA decreases ROR2 expression, but silencing of ROR2 has no effect on WNT5A levels. ROR2 knockdown does, however, result in a decrease in signaling downstream of Wnt5A. Using in vitro and in vivo metastasis assays, we show that ROR2 is necessary for the Wnt5A-mediated metastasis of melanoma cells. These data imply that ROR2 may represent a novel target for melanoma therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzal AR, Rajab A, Fenske CD, Oldridge M, Elanko N, Ternes-Pereira E et al. (2000). Recessive Robinow syndrome, allelic to dominant brachydactyly type B, is caused by mutation of ROR2. Nat Genet 25: 419–422.
Akbarzadeh S, Wheldon LM, Sweet SM, Talma S, Mardakheh FK, Heath JK . (2008). The deleted in brachydactyly B domain of ROR2 is required for receptor activation by recruitment of Src. PLoS ONE 3: e1873.
Bittner M, Meltzer P, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Seftor E, Hendrix M et al. (2000). Molecular classification of cutaneous malignant melanoma by gene expression profiling. Nature 406: 536–540.
Blitzer JT, Nusse R . (2006). A critical role for endocytosis in Wnt signaling. BMC Cell Biol 7: 28.
Da Forno PD, Pringle JH, Hutchinson P, Osborn J, Huang Q, Potter L et al. (2008). WNT5A expression increases during melanoma progression and correlates with outcome. Clin Cancer Res 14: 5825–5832.
Desmet CJ, Peeper DS . (2006). The neurotrophic receptor TrkB: a drug target in anti-cancer therapy? Cell Mol Life Sci 63: 755–759.
Dissanayake SK, Olkhanud PB, O’Connell MP, Carter A, French AD, Camilli TC et al. (2008). Wnt5A regulates expression of tumor associated antigens in melanoma via changes in STAT3 phosphorylation. Cancer Res 68: 10205–10214.
Dissanayake SK, Wade M, Johnson CE, O’Connell MP, Leotlela PD, French AD et al. (2007). The Wnt5A/protein kinase C pathway mediates motility in melanoma cells via the inhibition of metastasis suppressors and initiation of an epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 282: 17259–17271.
He F, Xiong W, Yu X, Espinoza-Lewis R, Liu C, Gu S et al. (2008). Wnt5a regulates directional cell migration and cell proliferation via Ror2-mediated noncanonical pathway in mammalian palate development. Development 135: 3871–3879.
He X, Saint-Jeannet JP, Wang Y, Nathans J, Dawid I, Varmus H . (1997). A member of the Frizzled protein family mediating axis induction by Wnt-5A. Science 275: 1652–1654.
Howe CL, Valletta JS, Rusnak AS, Mobley WC . (2001). NGF signaling from clathrin-coated vesicles: evidence that signaling endosomes serve as a platform for the Ras-MAPK pathway. Neuron 32: 801–814.
Jonsson M, Smith K, Harris AL . (1998). Regulation of Wnt5a expression in human mammary cells by protein kinase C activity and the cytoskeleton. Br J Cancer 78: 430–438.
Katoh M . (2005). WNT/PCP signaling pathway and human cancer (review). Oncol Rep 14: 1583–1588.
Lewis DL, Hagstrom JE, Loomis AG, Wolff JA, Herweijer H . (2002). Efficient delivery of siRNA for inhibition of gene expression in postnatal mice. Nat Genet 32: 107–108.
Liang Z, Yoon Y, Votaw J, Goodman MM, Williams L, Shim H . (2005). Silencing of CXCR4 blocks breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 65: 967–971.
Liu Y, Rubin B, Bodine PV, Billiard J . (2008). Wnt5a induces homodimerization and activation of Ror2 receptor tyrosine kinase. J Cell Biochem 105: 497–502.
Masiakowski P, Carroll RD . (1992). A novel family of cell surface receptors with tyrosine kinase-like domain. J Biol Chem 267: 26181–26190.
National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academy Press: Washington, DC, 1985.
Nishita M, Yoo SK, Nomachi A, Kani S, Sougawa N, Ohta Y et al. (2006). Filopodia formation mediated by receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is required for Wnt5a-induced cell migration. J Cell Biol 175: 555–562.
O’Connell MP, Fiori JL, Baugher KM, Indig FE, French AD, Camilli TC et al. (2009a). Wnt5A activates the calpain-mediated cleavage of filamin A. J Invest Dermatol 129: 1782–1789.
O’Connell MP, Fiori JL, Kershner EK, Frank BP, Indig FE, Taub DD et al. (2009b). HSPG modulation of WNT5A signal transduction in metastatic melanoma cells. J Biol Chem (in press; doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.028498.
O’Connell MP, French AD, Leotlela PD, Weeraratna AT . (2008). Assaying Wnt5A-mediated invasion in melanoma cells. Methods Mol Biol 468: 243–253.
Oishi I, Suzuki H, Onishi N, Takada R, Kani S, Ohkawara B et al. (2003). The receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is involved in non-canonical Wnt5a/JNK signalling pathway. Genes Cells 8: 645–654.
Oldridge M, Fortuna AM, Maringa M, Propping P, Mansour S, Pollitt C et al. (2000). Dominant mutations in ROR2, encoding an orphan receptor tyrosine kinase, cause brachydactyly type B. Nat Genet 24: 275–278.
Pfeiffer S, Ricardo S, Manneville JB, Alexandre C, Vincent JP . (2002). Producing cells retain and recycle Wingless in Drosophila embryos. Curr Biol 12: 957–962.
Romanowska M, Evans A, Kellock D, Bray SE, McLean K, Donandt S et al. (2009). Wnt5a exhibits layer-specific expression in adult skin, is upregulated in psoriasis, and synergizes with type 1 interferon. PLoS One 4: e5354.
Safholm A, Leandersson K, Dejmek J, Nielsen CK, Villoutreix BO, Andersson T . (2006). A formylated hexapeptide ligand mimics the ability of Wnt-5a to impair migration of human breast epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 281: 2740–2749.
Safholm A, Tuomela J, Rosenkvist J, Dejmek J, Harkonen P, Andersson T . (2008). The Wnt-5a-derived hexapeptide Foxy-5 inhibits breast cancer metastasis in vivo by targeting cell motility. Clin Cancer Res 14: 6556–6563.
Saldanha J, Singh J, Mahadevan D . (1998). Identification of a Frizzled-like cysteine rich domain in the extracellular region of developmental receptor tyrosine kinases. Protein Sci 7: 1632–1635.
Sen M, Chamorro M, Reifert J, Corr M, Carson DA . (2001). Blockade of Wnt-5A/frizzled 5 signaling inhibits rheumatoid synoviocyte activation. Arthritis Rheum 44: 772–781.
Song E, Lee SK, Wang J, Ince N, Ouyang N, Min J et al. (2003). RNA interference targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis. Nat Med 9: 347–351.
van Bokhoven H, Celli J, Kayserili H, van Beusekom E, Balci S, Brussel W et al. (2000). Mutation of the gene encoding the ROR2 tyrosine kinase causes autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome. Nat Genet 25: 423–426.
Weeraratna AT, Arnold JT, George DJ, DeMarzo A, Isaacs JT . (2000). Rational basis for Trk inhibition therapy for prostate cancer. Prostate 45: 140–148.
Weeraratna AT, Dalrymple SL, Lamb JC, Denmeade SR, Miknyoczki S, Dionne CA et al. (2001). Pan-trk inhibition decreases metastasis and enhances host survival in experimental models as a result of its selective induction of apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 7: 2237–2245.
Weeraratna AT, Jiang Y, Hostetter G, Rosenblatt K, Duray P, Bittner M et al. (2002). Wnt5a signaling directly affects cell motility and invasion of metastatic melanoma. Cancer Cell 1: 279–288.
Yamamoto H, Yoo SK, Nishita M, Kikuchi A, Minami Y . (2007). Wnt5a modulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 to induce phosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2. Genes Cells 12: 1215–1223.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms Ana Lustig for assistance with animal experiments. This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Aging, Baltimore, MD 21224, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Connell, M., Fiori, J., Xu, M. et al. The orphan tyrosine kinase receptor, ROR2, mediates Wnt5A signaling in metastatic melanoma. Oncogene 29, 34–44 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.305
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.305
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of the Ror family receptors in Wnt5a signaling
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2024)
-
ROR2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by hyperactivating ERK in melanoma
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
WNT5A-ROR2 axis mediates VEGF dependence of BRAF mutant melanoma
Cellular Oncology (2023)
-
ROR2 increases the chemoresistance of melanoma by regulating p53 and Bcl2-family proteins via ERK hyperactivation
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2022)
-
ROR2, a driver of “phenotype switching” in melanoma?
Cancer Cell International (2022)