Abstract
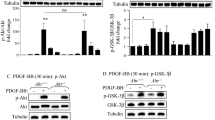
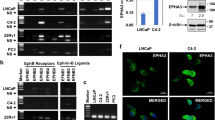
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), or dioxin receptor, is a transcription factor that induces adaptive metabolic pathways in response to environmental pollutants. Recently, other pathways were found to be altered by AhR and its ligands. Indeed, developmental defects elicited by AhR ligands suggest that additional cellular functions may be targeted by this receptor, including cell migration and plasticity. Here, we show that dioxin-mediated activation of Ahr induces Nedd9/Hef1/Cas-L, a member of the Cas protein family recently identified as a metastasis marker. The Hef1 gene induction is mediated by two xenobiotic responsive elements present in this gene promoter. Moreover, using RNA interference, we show that Nedd9/Hef1/Cas-L mediates the dioxin-elicited changes related to cell plasticity, including alterations of cellular adhesion and shape, cytoskeleton reorganization, and increased cell migration. Furthermore, we show that both E-cadherin repression and Jun N-terminal kinases activation by dioxin and AhR also depend on the expression of Nedd9/Hef1/Cas-L. Our study unveils, for the first time, a link between pollutants exposure and the induced expression of a metastasis marker and shows that cellular migration and plasticity markers are regulated by AhR and its toxic ligands.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre-Ghiso JA . (2007). Models, mechanisms and clinical evidence for cancer dormancy. Nat Rev Cancer 7: 834–846.
Crews ST, Brenman JE . (2006). Spineless provides a little backbone for dendritic morphogenesis. Genes Dev 20: 2773–2778.
Diry M, Tomkiewicz C, Koehle C, Coumoul X, Bock KW, Barouki R et al. (2006). Activation of the dioxin/aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) modulates cell plasticity through a JNK-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 25: 5570–5574.
Downie D, McFadyen MC, Rooney PH, Cruickshank ME, Parkin DE, Miller ID et al. (2005). Profiling cytochrome P450 expression in ovarian cancer: identification of prognostic markers. Clin Cancer Res 11: 7369–7375.
Frueh FW, Hayashibara KC, Brown PO, Whitlock Jr JP . (2001). Use of cDNA microarrays to analyze dioxin-induced changes in human liver gene expression. Toxicol Lett 122: 189–203.
Haas S, Pierl C, Harth V, Pesch B, Rabstein S, Bruning T et al. (2006). Expression of xenobiotic and steroid hormone metabolizing enzymes in human breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer 119: 1785–1791.
Huang C, Jacobson K, Schaller MD. . (2004). A role for JNK-paxillin signaling in cell migration. Cell Cycle 3: 4–6.
Ji H, Ramsey MR, Hayes DN, Fan C, McNamara K, Kozlowski P et al. (2007). LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature 448: 807–810.
Kim M, Gans JD, Nogueira C, Wang A, Paik JH, Feng B et al. (2006). Comparative oncogenomics identifies NEDD9 as a melanoma metastasis gene. Cell 125: 1269–1281.
Kohle C, Bock KW . (2007). Coordinate regulation of Phase I and II xenobiotic metabolisms by the Ah receptor and Nrf2. Biochem Pharmacol 73: 1853–1862.
Kumarakulasingham M, Rooney PH, Dundas SR, Telfer C, Melvin WT, Curran S et al. (2005). Cytochrome p450 profile of colorectal cancer: identification of markers of prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 11: 3758–3765.
Law SF, Estojak J, Wang B, Mysliwiec T, Kruh G, Golemis EA . (1996). Human enhancer of filamentation 1, a novel p130cas-like docking protein, associates with focal adhesion kinase and induces pseudohyphal growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 16: 3327–3337.
Law SF, O’Neill GM, Fashena SJ, Einarson MB, Golemis EA . (2000). The docking protein HEF1 is an apoptotic mediator at focal adhesion sites. Mol Cell Biol 20: 5184–5195.
Ma Q, Whitlock Jr JP . (1996). The aromatic hydrocarbon receptor modulates the Hepa 1c1c7 cell cycle and differentiated state independently of dioxin. Mol Cell Biol 16: 2144–2150.
Marchand A, Tomkiewicz C, Marchandeau JP, Boitier E, Barouki R, Garlatti M . (2005). 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induces insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 gene expression and counteracts the negative effect of insulin. Mol Pharmacol 67: 444–452.
McMillan BJ, Bradfield CA . (2007). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is activated by modified low-density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 1412–1417.
Mulero-Navarro S, Pozo-Guisado E, Perez-Mancera PA, Alvarez-Barrientos A, Catalina-Fernandez I, Hernandez-Nieto E et al. (2005). Immortalized mouse mammary fibroblasts lacking dioxin receptor have impaired tumorigenicity in a subcutaneous mouse xenograft model. J Biol Chem 280: 28731–28741.
Natarajan M, Stewart JE, Golemis EA, Pugacheva EN, Alexandropoulos K, Cox BD et al. (2006). HEF1 is a necessary and specific downstream effector of FAK that promotes the migration of glioblastoma cells. Oncogene 25: 1721–1732.
O’Neill GM, Golemis EA . (2001). Proteolysis of the docking protein HEF1 and implications for focal adhesion dynamics. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5094–5108.
Puga A, Tomlinson CR, Xia Y . (2005). Ah receptor signals cross-talk with multiple developmental pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 69: 199–207.
Pugacheva EN, Golemis EA . (2005). The focal adhesion scaffolding protein HEF1 regulates activation of the Aurora-A and Nek2 kinases at the centrosome. Nat Cell Biol 7: 937–946.
Pugacheva EN, Golemis EA . (2006). HEF1-aurora A interactions: points of dialog between the cell cycle and cell attachment signaling networks. Cell Cycle 5: 384–391.
Pugacheva EN, Jablonski SA, Hartman TR, Henske EP, Golemis EA . (2007). HEF1-dependent Aurora A activation induces disassembly of the primary cilium. Cell 129: 1351–1363.
Qin H, Zhai Z, Powell-Coffman JA . (2006). The Caenorhabditis elegans AHR-1 transcription complex controls expression of soluble guanylate cyclase genes in the URX neurons and regulates aggregation behavior. Dev Biol 298: 606–615.
Regelmann AG, Danzl NM, Wanjalla C, Alexandropoulos K . (2006). The hematopoietic isoform of Cas-Hef1-associated signal transducer regulates chemokine-induced inside-out signaling and T cell trafficking. Immunity 25: 907–918.
Seo S, Ichikawa M, Kurokawa M . (2006). Structure and function of cas-L and integrin-mediated signaling. Crit Rev Immunol 26: 391–406.
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP . (2006). Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 131–142.
Wernet MF, Mazzoni EO, Celik A, Duncan DM, Duncan I, Desplan C . (2006). Stochastic spineless expression creates the retinal mosaic for colour vision. Nature 440: 174–180.
Ziegler WH, Liddington RC, Critchley DR . (2006). The structure and regulation of vinculin. Trends Cell Biol 16: 453–460.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by AFSSET (Agence Française de Sécurité Sanitaire de l’Environnement et du Travail; all authors); ANR (Agence Nationale de la Recherche, 06SEST26, Oncopop; all authors); ARC (Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer, 3927; all authors); Fondation pour la Recherche Medicale (Bourse postdoctorale, Linh-Chi Bui); INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale; all authors); Ligue contre le Cancer (Bourse postdoctorale, Linh-Chi Bui); Ministère de l’enseignement supérieur et de la recherche (Bourse doctorale, Aline Chevallier); Région Ile de France (bourse doctorale, Stéphane Pierre); Université Paris Descartes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bui, LC., Tomkiewicz, C., Chevallier, A. et al. Nedd9/Hef1/Cas-L mediates the effects of environmental pollutants on cell migration and plasticity. Oncogene 28, 3642–3651 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.224
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.224
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Persistent organic pollutants promote aggressiveness in prostate cancer
Oncogene (2023)
-
miR-107 is involved in the regulation of NEDD9-mediated invasion and metastasis in breast cancer
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
Environmental chemicals, breast cancer progression and drug resistance
Environmental Health (2020)
-
Overexpression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) signalling pathway in human meningioma
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2018)
-
Novel roles for AhR and ARNT in the regulation of alcohol dehydrogenases in human hepatic cells
Archives of Toxicology (2017)