Abstract
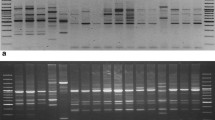
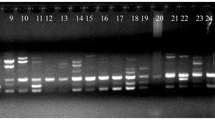
Intra and inter-species ISSR variation and use of ISSR markers in determination of genetic relationship were investigated in an accession collection representing twoperennial and six annual Cicerspecies. Screening of Ciceraccessions with SSR primers revealed highly reproducible amplicon profiles with relatively high multiplex ratios. Many of the primers generated amplicon profiles with which not only the differences among species can readily be identified, but also polymorphisms within species could be detected more efficiently. PCR products at 150 gel positions detected using six SSR primers in Cicer accessions were treated as dominant DNA markers and utilized to compute the distances among accessions and species. Cluster analysis of accessions and species revealed groupings that corroborate our previous studies of relationships based on allozyme and AFLP analysis. Consistent with the AFLP analysis carried out in the same accession collection, ISSR-based groupings indicated that perennial C. incisumis genetically close to the annuals of the second crossability group (C. pinnatifidum,C. bijugum, C. judaicum) while C. reticulatum is the closest wild species to the cultivated chickpea. ISSR-based variation estimates were relatively higher when compared to previous estimates computed from RAPD and AFLP data. Technically, ISSR analysis combines the PCR-based targeting of microsatellite-associated polymorphisms with no prior sequence requirement and stringent PCR conditions. Similarly, when compared to AFLP analysis, it is less technically demanding allowing to survey polymorphic loci in the genome. Thus, ISSR-PCR technology is a reliable, fast, and cost-effective marker system that can be used to study genetic variation and genetic relationships in the genusCicer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, F., 1999. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis reveals genetic relationships among the annual Cicer species. Theor Appl Genet 98: 657–663.
Ahmad, F. & A.E. Slinkard, 1992. Genetic relationships in the genus Cicer L. as revealed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of seed storage proteins. Theor Appl Genet 84: 688–692.
Ahmad, F., P.M. Gaur & A.E. Slinkard, 1992. Isozyme polymorphism and phylogenetic interpretations in the genus Cicer L. Theor Appl Genet 83: 620–627.
Ajibade, S.R., N.F. Weeden & S.M. Chite, 2000. Inter simple sequence repeat analysis of genetic relationships in the genus Vigna. Euphytica 111: 47–55.
Akem, C., S. Caccarelli, W. Erkine & J. Lenne, 2000. Using genetic diversity for disease resistance in agricultural production. Outlook on Agric 29: 25–30.
Akkaya, M.S., A.A. Bhagwat & P.B. Cregan, 1992. Length polymorphisms of simple sequence repeat DNA in soybean. Genetics 132: 1131–1139.
Bart, S., A.E. Melchinger & T. Lübberstedt, 2002. Genetic diversity in Arabidopsis thaliana L. Heynh. investigated by cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) and inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Mol Ecol 11: 495–505.
Bornet, B. & M. Branchard, 2001. Nonanchored inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers: Reproducible and specific tools for genome fingerprinting. Plant Mol Biol Reporter 19: 209–215.
Botstein, D., R.L. White, M.H. Skolnick & R.W. Davis, 1980. Construction of a genetic map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Human Genet 32: 314–331.
Davis, P.H., 1973. The Flora of Turkey. Edinburgh University Press Edinburgh, Vol. 3, pp. 267–273.
Edwards, A., A. Civitello, H.A. Hammond & C.T. Caskey, 1991. DNA typing and genetic mapping with trimeric and tetrameric tandem repeats. Am J Hum Genet 49: 746–756.
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Organization), 2002. FAO Statistics, Internet; www. fao.org.
Gupta, M., J. Chyi, J. Romero-Severson & J.L. Owen, 1994. Amplification of DNA markers from evolutionary diverse genomes using single primers of simple sequence repeats. Theor Appl Genet 89: 998–1006.
Hamrick, J.L., 1989. Isozymes and the analysis of genetic structure in plant populations. In: D.E. Soltis & P.S. Soltis (Eds.), Isozymes in Plant Biology, pp. 87–105. Discorides Press, Portland, Ore.
Huttel, B., P. Winter, W. Choumane, F. Weigand & G. Kahl, 1999. Sequence-tagged site markers for chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Genome 42: 210–217.
Iruela, M., J. Rubio, J.I. Cubero, J. Gil & T. Millán, 2002. Phylogenetic analysis in the genus Cicer and cultivated chickpea using RAPD and ISSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 104: 643–651.
Jacob, H.J., K. Lindpaintner, S.E. Lincoln, K. Kusumi, R.K. Bunker, Yi-Pei Mao, D. Ganten, V.J. Dzau & E.S. Lander, 1991. Genetic mapping of a gene causing hypertensive rat. Cell 67: 213–224.
Kazan, K. & F.J. Muehlbauer, 1991. Allozyme variation and phylogeny in annual species of Cicer (Leguminosae). Plant Syst Evol 175: 11–21.
Kovach, W.L., 2000. Multi-Variate Statistical Package (MVSP). Ver. 3.1h; Kovach Computing Services, Wales, U.K. http://www.kovcomp.com.
Kumar, L.S., 1999. DNA markers in plant improvement: An overview. Biotechnol Advances 17: 143–182.
Labdi, M., L.D. Robertson, K.B. Singh & A. Charrier, 1996. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships among the annual Cicer species as revealed by isozyme polymorphisms. Euphytica 88: 181–188.
Ladizinsky, G. & A. Adler, 1976. Genetic relationships among the annual species of Cicer L. Theor Appl Genet 48: 197–203.
Litt, M. & J.A. Luty, 1989. A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet 44: 397–401.
McGregor, C.E., C.A. Lambert, M.M. Greyling, J.H. Louw & L. Warnich, 2000. A comparative assessment of DNA fingerprinting techniques (RAPD, ISSR, AFLP and SSR) in tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) germplasm. Euphytica 113: 135–144.
Muehlbauer, F.J., W.J. Kaiser & C.J. Simon, 1994. Potential for wild species in cool seasion food legume breeding. Euphytica 73: 109–114.
Mullis, K.B., 1987. Prosess for Amplifying Nucleic Acid Sequences. US Patent 4,683,202. Filed 10-25-85; Issued 7-28-87.
Nagaoka, T. & Y. Ogihara, 1997. Applicability of inter-simple sequence repeat polymorphisms in wheat for use as DNA markers in comparison to RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 94: 597–602.
Nei, M. & W.H. Li, 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 5269–5273.
Nybom, H. & I.V. Bartish, 2000. Effects of life history traits and sampling strategies on genetic diversity estimates obtained with RAPD marker in plants. Persp Plant Ecol, Evol & Syst 3(2): 93–114.
Rafalski, J.A., J.M. Vogel, M. Morgante, W. Powell, C. Andre & S.V. Tingey, 1996. Generating and using DNA markers in plants. In: B. Brain & E. Lai (Eds.), Nonmammalian Genomic Analysis: A Practical Guide, pp. 75-134. Academic Press.
Raina, S.N., V. Rani, T. Kojima, Y. Ogihara, K.P. Singh & R.M. Devarumath, 2001. RAPD and ISSR fingerprints as useful genetic markers for analysis of genetic diversity, varietal identification and phylogenetic relationships in peanut (Arachis hypogaea) cultivars and wild species. Genome 2001 44: 763–772.
Ratnaparkhe, M.B., M. Tekeoglu & F.J. Muehlbauer, 1998. Intersimple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphisms are useful for finding markers associated with disease resistance gene clusters. Theor Appl Genet 97: 515–519.
Sharma, P.C., P. Winter, T. Bunger, B. Huttel, F. Weigand, K. Weising & G. Kahl, 1995. Abundance and polymorphism of di-, triand tetra-nucleotide tandem repeats in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Theor Appl Genet 90: 90–96.
Simon, C.J. & F.J. Muehlbauer, 1997. Construction of a chickpea linkage map and its comparison with map of pea and lentil. J Hered 88: 115–119.
Singh, K.B., 1997. Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Field Crop Res 53: 161–170.
Singh, K.B. & B. Ocampo, 1997. Exploitation of wild Cicer species for yield improvement in chickpea. Theor Appl Genet 95: 418–423.
Singh, K.B., R.S. Malhotra, M.H. Halila, E.J. Knights & M.M. Verma, 1994. Current status and future strategy in breeding for resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Euphytica 73: 137–149.
Staginnus, C., P. Winter, C. Desel, T. Schmidt & G. Kahl, 1999. Molecular structure and chromosomal localization of major repetitive DNA families in the chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genome. Plant Mol Biol 39: 1037–1050.
Sudupak, M.A. & A. Kence, 2003. Genetic relationships among perennial and annual Cicer species growing in Turkey as revealed by allozymes. Genet Res & Crop Evol (in press).
Sudupak, M.A., M.S. Akkaya & A. Kence, 2002. Analysis of genetic relationships among perennial and annual Cicer species growing in Turkey using RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 105: 1220–1228.
Tautz, D., 1989. Hypervariablity of simple sequences as a general source of polymorphic DNA markers. Nucleic Acids Res 17: 6463–6471.
Tauz, D. & M. Renz, 1984. Simple sequences are ubiquitous components of eukaryotic genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 12: 4127–4138.
Tayyar, R.I. & J.G. Waines, 1996. Genetic relationships among annual species of Cicer (Fabaceae) using isozyme variation. Theor Appl Genet 92: 245–254.
Udupa, S.M., L.D. Roberson, F. Weigand, M. Baum & G. Kahl, 1999. Allelic variation at (TAA)(II) microsatellite loci in a world collection of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) germplasm. Mol and Gen Genet 261: 354–363.
van der Maesen, L.J.G., 1987. Origin, history and taxonomy of chickpea. In: M.C. Saxena & K.B. Singh (Eds.), The Chickpea, pp. 11–34. CAB Int Publ, UK.
Vos, P., R. Hogers, M. Bleeker, M. Reijans, T. Van de Lee, M. Hornes, A. Frijters, J. Potet, J. Pelemen, M. Kuiper & M. Zebeau, 1995. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23: 4407–4414.
Weising, K., D. Kaemmer, F. Weigand, T.J. Epplen & G. Kahl, 1992. Oligonucleotide fingerprinting reveals various probe-dependent levels of informativeness in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Genome 35: 436–442.
Williams, J.G.K., A.R. Kubelik, K.J. Livak, J.A. Rafalski & S.V. Tingeyl, 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 6531–6535.
Winter, P., T. Pfaff, S.M. Udupa, B. Hüttel, P.C. Sharma, S. Sahi, R. Arreguin-Espinoza, F. Weigand, F.J. Muehlbauer & G. Kahl, 1999. Characterization and mapping of sequence-tagged microsatellite sites in the chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genome. Mol Gen Genet 262: 90–101.
Yang,W., A.C. de Oliveira, I. Godwin, K. Schertz & J.L. Bennetzen, 1996. Comparison of DNA marker technologies in characterizing plant genome diversity: variability in Chinese sorghums. Crop Sci 36: 1669–1676.
Yeh, F.C., R.C. Yang, T.J.B. Boyle, Z.H. Ye & J.X. Mao, 1997. POPGENE, the user-friendly shareware for population genetic analysis. Ver. 1.32. Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Center, University of Alberta, Canada.
Zietkiewicz, E., J.A. Rafalski & D. Labuda, 1994. Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20: 176–183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sudupak, M.A. Inter and intra-species Inter Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) variations in the genus Cicer . Euphytica 135, 229–238 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EUPH.0000014938.02019.f3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EUPH.0000014938.02019.f3