Abstract
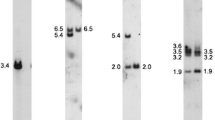
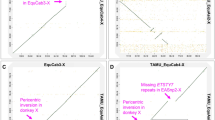
We cloned and mapped the dog and/or sheep homologues of two human pseudoautosomal genes CSF2RA and ANT3. We also cloned and mapped dog and/or sheep homologues of STS and PRKX, which are located nearby on the differential region of the human X and have related genes or pseudogenes on the Y. STS, as well as CSF2RA, mapped to the tips of the short arm of the sheep X and Y (Xp and Yp), and STS and PRKX, as well as ANT3, mapped to the tips of the dog Xp and Y long arm (Yq). These locations within the X-Y pairing regions suggest that the regions containing all these human Xp22.3-Xpter genes are pseudoautosomal in dog and sheep. This supports the hypothesis that a larger pseudoautosomal region (PAR) shared by eutherian groups was disrupted by chromosomal rearrangements during primate evolution. The absence of STS and ANT3 from the sex chromosomes in two prosimian lemur species must therefore represent a recent translocation from their ancestral PAR, rather than retention of a smaller ancestral PAR shared by mouse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affara NA, Ferguson-Smith MA (1994) DNA Sequence Homology Between the Human Sex Chromosomes. In: Wachtel SS, ed. Molecular Genetics of Sex Determination London: Academic Press, Chapter 11, pp 225–226.
Affara NA, Chambers D, O'Brian J et al. (1989) Evidence for distinguishable transcipts of the putative testis determining gene (ZFY) and mapping of homologous cDNA sequences to chromosome X, Y and 9. Nucleic Acids Res 17: 2987–2999.
Bardoni G, Zuffardi O, Guioli S et al. (1991) A deletion map of the human Yq11 region: implications for the evolution of the Y chromosome and tentative mapping of a locus involved in spermatogenesis. Genomics 11: 443–451.
Dai K, Dollin AE, Gillies CB (1994) Synaptonemal complex analysis of domestic sheep (Ovis aries) with Robertsonian translocations. I. Pachytene karyotype substaging of normal sheep. Genome 37: 672–678.
del Castillo J, Cohen-Salmon M, Blanchard S, Lutfalla G, Petit C (1992) Structure of the X-linked Kallmann syndrome gene and its homologous pseudogene on the Y chromosome. Nature Genet 2: 305–310.
Ellis N, Goodfellow PN (1989) The mammalian pseudoautosomal region. Trends Genet 5: 406–410.
Franco B, Guioli S, Pragliola A et al. (1991) A gene deleted in Kallmann's syndrome shares homology with neural cell adhesion and axonal path-finding molecules. Nature 353: 529–536.
Graves JAM (1995) The origin and function of the mammalian Y chromosome and Y-borne genes - an evolving understanding. BioEssays 17: 311–320.
Holm PB, Rasmussen SW (1983) Human meiosis. VII. Chiasma formation in human spermatocytes. Carlsberg Res Commun 48: 415–456.
Incerti B, Guioli S, Pragliola A et al. (1992) Kallmann syndrome gene on the X and Y chromosomes: implications for evolutionary divergence of human sex chromosomes. Nature Genet 2: 311–314.
Keitges E, Rivest M, Siniscalco M, Gartler SM (1985) X-linkage of steroid sulfatase in the mouse is evidence for a functional Y-linked allele. Nature 315: 226–227.
Klink A, Schiebel K, Winkelmann M et al. (1995) The human protein kinase gene PKX1 on Xp22.3 displays Xp/Yp homology and is a site of chromosomal instability. Hum Mol Genet 4: 869–878.
Koller PC, Darlington CD (1934) The genetical and mechanical properties of the sex chromosomes. I. Rattus norvegigus. J Genet 29: 159–173.
Kunkel LM, Smith KD, Boyer SH et al. (1977) Analysis of human Y chromosome specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 1245–1249.
Legouis R, Hardelin J-P, Levillier J et al. (1991) The candidate gene for the X-linked Kallmann syndrome encodes a protein related to adhesion molecules. Cell 67: 423–435.
Meroni G, Franco B, Archidiacono N et al. (1996) Characterization of a cluster of sulfatase genes on Xp22.3 suggests gene duplications in ancestral pseudoautosomal region. Hum Mol Genet 5: 423–431.
Moses MJ, Karatsis PA, Hamilton AE (1979) Synaptonemal complex analysis of heteromorphic bivalents in Lemur hybrids. Chromosoma 70: 141–160.
Müller U, Schempp W (1982) Homologous early replication patterns of the distal short arms of prometaphasic X and Y chromosomes. Hum Genet 60: 274–275.
Müller G, Schempp W (1989) Mapping the human ZFX locus to Xp21 by in situ hybridisation. Hum Genet 82: 82–84.
Novacek MJ (1992) Mammalian phylogeny: shaking the tree. Nature 356: 121–125.
Ohno S (1967) Sex Chromosomes and Sex-linked Genes. Berlin: Springer.
Pathak S, Van Tuinen P, Merry DE (1982) Heterochromatin, synaptonemal complex, and NOR activity in the somatic and germ cells of a male domestic dog, Canis familiaris (Mammalia, Canidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 34: 112–118.
Rappold GA (1993) The pseudoautosomal regions of the human sex chromosomes. Hum Genet 92: 315–324.
Salido EC, Yen PH, Koprivnikar K, Yu L-C, Shapiro LJ (1992) The human enamel protein gene amelogenin is expressed from both the X and Y chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet 50: 303–316.
Salido EC, Li XM, Yen PH, Martin N, Mohandas TK, Shapiro LJ (1996) Cloning and expression of the mouse pseudoautosomal steroid sulphatase gene Sts. Nature Genet 13: 83–86.
Schemp W, Meer B (1983) Cytologic evidence for three X-chromosomal segments escaping inactivation. Hum Genet 63: 171–174.
Schempp W, Toder R (1993) Molecular cytogenetic studies on the evolution of sex chromosomes in primates In: Graves JAM, Reed K, eds. Sex Chromosomes and Sex-determining Genes. New York: Harwood Academic, Chapter 11, pp 137–151.
Schneider-Gädicke A, Beer-Romero P, Brown LG, Nussbaum R, Page DC (1989) ZFX has a gene structure similar to ZFY, the putative sex determinant, and escapes X-inactivation. Cell 57: 1247–1258.
Solari AJ (1974) The behavior of the XY pair in mammals. Int Rev Cytol 38: 273–317.
Svironski M, Reimann N, Bosma AA, Long S, Pienkowska, Morena-Milan MM, Fischer P (1996) Report on the progress of standardization of the G-banded canine (Canis familiaris) karyotype. Chrom Res 4: 306–309.
Toder R, Rappold GA, Schiebel K, Schempp W (1995) ANT3 and STS are autosomal in prosimian lemurs: implications for the evolution of the pseudoautosomal region. Hum Genet 95: 22–28.
Toder R, Wilcox SA, Smithwick M, Graves JAM (1996) The human/mouse imprinted genes IGF2, H19, SNRPN and ZNF127 map to two conserved autosomal clusters in a marsupial. Chrom Res 4: 295–300.
Wolf U, Schempp W, Scherer G (1992) Molecular biology of the human Y chromosome. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 121: 147–213.
Yen PH, Marsh B, Allen E et al. (1988) The human X-linked steroid sulfatase gene and a Y-encoded pseudogene: evidence for an inversion of the Y chromosome during primate evolution. Cell 55: 1123–1135.
Yen P, Tsai S-P, Wenger SL, Steele MW, Mohandas TK, Shapiro LJ (1991) X/Y translocations resulting from recombination between homologous sequences on Xp and Yq. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 8944–8948
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toder, R., Gläser, B., Schiebel, K. et al. Genes Located In and Near the Human Pseudoautosomal Region are Located in the X-Y Pairing Region in Dog and Sheep. Chromosome Res 5, 301–306 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CHRO.0000038760.84605.0d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CHRO.0000038760.84605.0d