Abstract
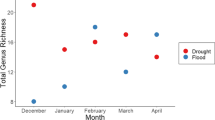
Small dams (height <10 m) have transformed stream networks across the United States. Shopiere Dam was removed from Turtle Creek, a fourth order stream in Southeastern Wisconsin in the fall of 1999. We sampled three sites (upstream of the impoundment, immediately below the dam, and farther downstream) before and after dam removal to identify changes in the invertebrate assemblage following removal. Prior to removal, upstream and downstream sites had similar taxonomic composition. In contrast the dam site had more taxonomic variation. The upstream, dam and downstream sites responded differently to dam removal in analyses of diversity, functional feeding groups, and invertebrate composition. Upstream at the reference site, changes in functional feeding group composition appeared to be associated with a decrease in silt coverage. At the dam site, taxonomic composition changed following dam removal, however diversity and functional feeding groups remained similar. At the downstream site, the invertebrate assemblage remained similar in all analyses. Our observations indicate that the effects of dam removal were not uniform through the stream, rather each site responded in a different way.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball, J. R., R. J. Poff & C. W. Threinen, 1970. Surface Water Resources of Rock County. Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Publication.
Benke, A. C., 1990. A perspective on America's vanishing streams. J. north am. Benthol. Soc. 9: 77–88.
Born, S. M., K. D. Genskow, T. L. Filbert, N. Hernandez-Mora, M. Keefer & K. A. White, 1998. Socioeconomic and institutional dimensions of dam removals: the Wisconsin experience. Environ. Manage. 22: 359–370.
Brown, A. V. & P. P. Brussock, 1991. Comparisons of benthic invertebrates between riffles and pools. Hydrobiologia 220: 99–108.
Dynesius, M. & C. Nilsson, 1994. Fragmentation and flow regulation of river systems in the northern third of the world. Science 266: 753–762.
Gotelli, N. J. & G. L. Entsminger, 2000. EcoSim: Null models software for ecology. Version 5.0. Acquired Intelligence Inc. & Kesey-Bear. http://homepages.together.net/~gentsmin/ecosim.htm.
Hart, D. D. & C. M. Finelli, 1999. Physical-biological coupling in streams: the pervasive effects of flow on benthic organisms. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 30: 363–395.
Heinz Center, 2002. Dam Removal: Science and Decision-Making. Publication of The H. John Heinz III Center for Science, Economics, and the Environment, Washington, DC. 221 pp.
Hilsenhoff, W. L., 1981. Aquatic Insects of Wisconsin. Keys to Wisconsin Genera and Notes on Biology, Distribution and Species. Publication of the Natural History Council, University of Wisconsin, Madison. 60 pp.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1970. The Ecology of Running Waters. University of Toronto Press.
Kanehl, P. D., J. Lyons & J. E. Nelson, 1997. Changes in the habitat and fish community of the Milwaukee River, Wisconsin, following the removal of the Woolen Mills Dam. N. am. J. Fish. Manage. 17: 387–400.
Ligon, F. K., W. E. Dietrich & W. J. Trush, 1995. Downstream ecological effects of dams. BioScience 45: 183–192.
Malmqvist, B. & A. Eriksson, 1995. Benthic insects in Swedish lake-outlet streams: patterns in species richness and assemblage structure. Freshwat. Biol. 34: 285–296.
McCune, B. & M. J. Mefford, 1999. PC-ORD. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data, Version 4. MjM Software Design, Oregon, U.S.A.
Merritt, R. W. & K. W. Cummins (eds), 1998. An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America. 3rd edn. Kendall/Hunt, Dubuque, Iowa. 722 pp.
Minshall, G. W., 1984. Aquatic insect-substratum relationships. In Resh, V. H. & D. M. Rosenberg (eds), The Ecology of Aquatic Insects. Praeger, New York: 358–400.
Petts, G. E., 1984. Impounded Rivers: Perspectives for Ecological Management. Wiley, New York: 326 pp.
Pickett, S. T. A., J. Kolasa & C. G. Jones, 1994. Ecological Understanding, Academic Press, U.S.A.
Poff, N. L. & D. D. Hart, 2002. How dams vary and why it matters for the emerging science of dam removal. Bioscience 52: 659–668.
Quinn, G. P., P. S. Lake & S. G. Schreiber, 1996. Littoral benthos of a Victorian lake and its outlet stream: spatial and temporal variation. Aust. J. Ecol. 21: 292–301.
Schlosser, I. J., 1992. Effects of life-history attributes and stream discharge on filter-feeding colonization. J. n. am. Benthol. Soc. 11: 366–376.
Shuman, J. R., 1995. Environmental considerations for assessing dam removal alternatives for river restoration. Reg. Riv.: Res. Manage. 11: 249–261.
Stanley, E. H., M. A. Luebke, M. W. Doyle & D. W. Marshall, 2002. Short-term changes in channel form and macroinvertebrate communities following low head dam removal. J. n. am. Benthol. Soc. 21: 172–187.
Statzner, B. & B. Higler, 1986. Stream hydraulics as a major determinant of benthic invertebrate zonation. Freshwat. Biol. 16: 127–139.
Thorp, J. H. & A. P. Covich (eds), 1991. Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates. Academic Press. 911 pp.
Wohl, D. L., J. B. Wallace & J. L. Meyer, 1995. Benthic macroinvertebrate community structure, function and production with respect to habitat type, reach and drainage basin in the southern Appalachians (U.S.A.). Freshwat. Biol. 34: 447–464.
Wunderlich, R. C., B. D. Winter & J. H. Meyer, 1994. Restoration of the Elwha River ecosystem. Fisheries 19: 11–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollard, A.I., Reed, T. Benthic invertebrate assemblage change following dam removal in a Wisconsin stream. Hydrobiologia 513, 51–58 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:hydr.0000018164.17234.4f
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:hydr.0000018164.17234.4f