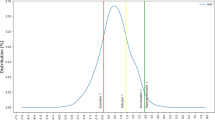
Abstract
The effectiveness of a warm season grass (eastern gamagrass), a cool season grass (annual ryegrass) and a rotation of warm and cool season grasses in the remediation of soil freshly contaminated with trinitrotoluene (TNT) and polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) was evaluated. A total of 96 columns were filled with a Weswood silt loam soil that was mixed with TNT and PBB compounds to a target concentration of 10 mg of each contaminant. Chemical losses during this two-year field lysimeter experiment were similar for all experimental treatments and at all depths. Although higher microbial biomass was found in the rhizosphere soil, enumeration of soil microorganisms revealed a robust population in both the bulk and rhizosphere soils and the microbial growth was not dependent on root exudates only. Microbial degradation rates in the freshly contaminated soil were more affected by soil properties and the chemical characteristics of the contaminant than the presence of roots. The field data collected from the lysimeter experiment was used to calibrate a recently developed phytoremediation model. The phytoremediation computer model successfully simulated TNT soil concentrations in the column lysimeters. The model may be a valuable tool for the selection and optimization of phytoremediation methods at contaminated field sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M.: 1994, Biodegradation and Bioremediation, Academic Press.
Anderson, T.A., Guthrie, E.A. and Walton. B.T.: 1993, ‘Bioremediation in the rhizosphere’, Environ Sci. Technol. 27, 2630–2636.
Aprill, W. and Sims, R.C.: 1990, ‘Evaluation of the use of prairie grasses for simulating polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon treatment in soil’, Chemosphere 20, 253–265.
Boopathy, R.C., Kulpa, C.F., Manning, J. and Montemagno, C.D.: 1994, ‘Biotransformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) by co-metabolism with various co-substrates—a laboratory scale study’, Bioresour. Technol. 47, 205–208.
Brusseau, M.L., Jessup, R.E. and Rao, P.S.C.: 1989, ‘Modeling the transport of solutes influenced by multiprocess nonequilibrium’, Water Resour. Res. 25, 971–988.
Burken, G.J. and Schnoor, J.L.: 1998, ‘Predictive relationships for uptake of organic contaminants by hybrid poplar trees’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 3379–3385.
Corapcioglu, M.Y., Rhykerd, R.L., Munster, C.L., Drew, M.C., Sung, K. and Chang. Y.Y.: 1999, ‘Phytoremediation and modeling of land contaminated by hydrocarbons’, in: A. Leeson and B.C. Alleman (eds.), Phytoremediation and Innovative Strategies for Specialized Remedial Applications, Battelle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 9–14.
Cunningham, S.D. Berti, W.R. and Huang, J.W.: 1995, ‘Phytoremediation of contaminated soils’, Trends Biotechno. 13, 393–397.
Filonow, A.B., Jacob, L.W. and Mortland., M.M.: 1976, ‘Fate of polybrominated biphenyls (PBB’s) in soils. Retention of hexabromobiphenyl in four Michigan soils’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 24, 1201–1204.
Gatliff, E.G.: 1994, ‘Vegetative remediation process offers advantages over traditional pump-and-treat technologies’, Remediation, summer, 343–352.
Glass D.J.: 1997, Evaluating phytoremediation's potential share of the hazardous site remediation market, in: C.A. Thibeault and L.M. Savage (eds.), Phytoremediation, International Business Communications, Inc. Southborough, MA, pp. 7–39.
Harris, J.A., Birch, P., Palmer, J.: 1996, Land Restoration and Reclamation: Principles and Practice, Addison Wesley Longman Ltd.
Imhoff, P.T. and Jaffe, P.R.: 1994, ‘Effect of liquid distribution on gas-water phase mass transfer in an unsaturated sand during infiltration’, J. Cont. Hydrol. 16, 359–380.
Jacobs, L.W., Chou, S. and Tiedje, J.M.: 1978, ‘Field concentrations and persistence of polybrominated biphenyls in soils and solubility of PBB in natural waters’, Environ. Health Perspect. 23, 1–8.
Jacobs, L.W., Chou, S. and Tiedje, J.M.: 1976, ‘Fate of polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) in soil’, J Agric. Food Chem. 24, 1198–1201.
Jacobs, L.W., O’Connor, G.A., Overcash, M.R., Zabik, M.J. and Rygiewicz, P.: 1987, ‘Effects of trace organics in sewage sludge on soil-plant systems and assessing their risk to humans’, in: A.L., Page (ed.), Land Application of Sludge,Lewis Pub. Chelsea, MI, pp. 101–143.
Jenkins, T.F. and Walsh, M.E.: 1992, ‘Development of field screening methods for TNT, 2,4-DNT and RDX in soil’, Talanta 39, 419–428.
Jenkinson, D.S. and Powlson, D. S.: 1976, ‘The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil-V: A method for measuring soil biomass’, Soil Biol. Biochem. 8, 209–213.
Kaplan, D.L. and Kaplan, A.M.: 1982, ‘2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene-surfactant complexes: Decomposition, mutagenicity and soil leaching studies’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 566–571.
Klausmeier, R.E., Osman, J.L. and Walls, D.R.: 1973, ‘The effects of trinitrotoluene on microorganisms’, Dev. Ind. Microbiol. 15, 309–317.
McCormick, N.G., Cornell, J.H. and Kaplan, A.M.: 1981, ‘Biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine’, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 42, 817–823.
Mendoza, C.A. and Friend, E.O.: 1990, ‘Advective-dispersive transport of dense organic vapor in the unsaturated zone. 1. Model development’, Water Resour. Res. 26, 379–387.
Newman, E. and Watson, A.: 1977, ‘Microbial abundance in the rhizosphere: A computer model’, Plant Soil 48, 17–56
Rieger, P.G. and Knackmuss, H.J.: 1995, ‘Basic knowledge and perspectives on biodegradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene and related nitroaromatic compounds in contaminated soil’, in: J.C. Spain (ed.), Biodegradation of Nitroaromatic Compounds, Environ. Res. Ser. 49, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 1–18.
Roberts, C. and Kallenbach, R.: 1999, Eastern Gamagrass, MU Extension, University Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO.
Rusling, J.R. and Miaw, C.L.: 1989, ‘Kinetic estimation of standard reduction potentials of polyhalogenated biphenyls’ Environ. Sci. Technol. 23, 476–479.
Russell, R.S.: 1977, Plant and Root Systems: Their Function and Interaction with the Soil, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 298 pp.
Salt, D.E., Smith, R.D. and Raskin, I.: 1998, ‘Phytoremediation’, Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 49, 643–668.
Schnoor, J.L.: 1997, Phytoremediation,Technology Evaluation Report, TE–98–01, Ground-water Remediation Technologies Analysis Center, Pittsburgh, PA.
Schnoor, J.L., Light, L.A., McCutcheon, S.C., Wolfe, N.L. and Carreira, L.H.: 1995, ‘Phytoremediation of organic and nutrient contaminants’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 318–323.
Schwab, A.P. and Banks, M.K.: 1994, ‘Biologically mediated dissipation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the root zone’, in: T.E. Anderson and J.R. Coats (eds.), Bioremediation Through Rhizosphere Technology American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp. 132–141.
Sittig, M.: 1985, Handbook of Toxic and Hazardous Chemicals and Carcinogens, 2nd edn., Noyes Publ., Park Ridge, NJ., 899 pp.
Stayner, L.T., Dannenberg, A.L., Bloom, T. and Thun, M.: 1993, ‘Excess hepatobiliary cancer mortality among munitions workers exposed to dinitrotoluene’, J. Occup. Med. 35, 291–296.
Sung, K.: 2000, ‘Phytoremediation and Bioremediation of Hydrocarbons: Modeling and Field application’, Ph.D. Dissertation, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, 245 pp.
Sung, K., Corapcioglu, M.Y., Drew, M.C. and Munster, C.L.: 2001, ‘Plant contamination by organic pollutants in phytoremediation’, J. Environ. Qual. 30, 2081–2090.
Sung, K., Corapcioglu, M.Y. and Drew, M.C.: 2002a, ‘Heat and mass transfer in the vadose zone with plant roots’, J. Contaminant Hydrol 57, 99–127
Sung, K., Munster, C.L., Rhykerd, R., Drew, M.C. and Corapcioglu, M.Y.: 2002b, ‘The use of box lysimeter with freshly contaminated soils to study the phytoremediation of recalcitrant organic contaminates’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 2249–2255.
Sung, K., Munster, C.L., Rhykerd, R., Drew, M.C. and Corapcioglu, M.Y.: 2003, ‘The use of vegetation to remediate soil freshly contaminated by recalcitrant hydrocarbons’, Water Res. 10, 2408–2418.
Trapp, S., Matthies, M., Scheunert, I. and Topp, E.M.: 1990, ‘Modeling the bioconcentration of organic chemicals in plants’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 24, 1246–1252.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for toxic substances and diseases registry: 2002a, Draft Toxicological Profiles for Polybrominated Biphenyls and Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Toxicology Program: 2002b,Report on Carcinogens, 10th edn.
Weber, E.J. and Wolfe, N.L.: 1987, ‘Kinetic studies of reduction of aromatic compounds in anaerobic sediment/water systems’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 6, 911–919.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, K., Munster, C.L., Corapcioglu, M.Y. et al. Phytoremediation and Modeling of Contaminated Soil using Eastern Gamagrass and Annual Ryegrass. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 159, 175–195 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000049174.34594.08
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000049174.34594.08