Abstract
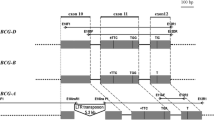
Two overlapping bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clones from the B genome of the tetraploid wheat Triticum turgidum were identified, each of which contains one of the two high-molecular-weight (HMW) glutenin genes, comprising the complex Glu-B1 locus. The complete sequence (285 506 bp of DNA) of this chromosomal region was determined. The two paralogous x-type (Glu-1-1) and y-type (Glu-1-2) HMW-glutenin genes of the complex Glu-B1 locus were found to be separated by ca. 168 000 bp instead of the 51 000 bp separation previously reported for the orthologous Glu-D1 locus of Aegilops tauschii, the D-genome donor of hexaploid wheat. This difference in intergene spacing is due almost entirely to be the insertion of clusters of nested retrotransposons. Otherwise, the orientation and order of the HMW glutenins and adjacent genes were identical in the two genomes. A comparison of these orthologous regions indicates modes and patterns of sequence divergence, with implications for the overall Triticeae genome structure and evolution. A duplicate globulin gene, found 5′ of each HMW-glutenin gene, assists to tentatively define the original duplication event leading to the paralogous x- and y-type HMW-glutenin genes. The intergenic regions of the two loci are composed of different patterns and classes of retrotransposons, indicating that insertion times of these retroelements were after the divergence of the two wheat genomes. In addition, a putative receptor kinase gene near the y-type HMW-glutenin gene at the Glu-B1 locus is likely active as it matches recently reported ESTs from germinating barley endosperm. The presence of four genes represented only in the Triticeae endosperm ESTs suggests an endosperm-specific chromosome domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhunov, E.D., Goodyear, A.W., Geng, S., Qi, L.L., Echalier, B., Gill, B.S., Miftahudin, Gustafson, J.P., Lazo, G., Chao, S., Anderson, O.D., Linkiewicz, A.M., Dubcovsky, J., Rota, M.L., Sorrells, M.E., Zhang, D., Nguyen, H.T., Kalavacharla, V., Hossain, K., Kianian, S.F., Peng, J., Lapitan, N.L., Gonzalez-Hernandez, J.L., Anderson, J.A., Choi, D.W., Close, T.J., Dilbirligi, M., Gill, K.S., Walker-Simmons, M.K., Steber, C., McGuire, P.E., Qualset, C.O. and Dvorak, J. 2003. The organization and rate of evolution of wheat genomes are correlated with recombination rates along chromosome arms. Genome Res. 13: 753–763.
Anderson, O.D. and Greene, F.C. 1989. The characterization and comparative analysis of high-molecular-weight-glutenin genes from genomes A and B of a hexaploid bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 77: 689–700.
Anderson, O.D., Larka, L., Christoffers, M.J., McCue, K.F. and Gustafson, J.P. 2002. Comparison of orthologous and paralogous DNA flanking the wheat high molecular weight glutenin genes: sequence conservation and divergence, transposon distribution, and matrix-attachment regions. Genome 45: 367–380.
Anderson, O.D., Rausch, C., Moullet, O. and Lagudah, E.S. 2003. The wheat D-genome HMW-glutenin locus: BAC sequencing, gene distribution, and retrotransposon clusters. Funct. Integr. Genomics 3: 56–68.
Arumuganathan, K. and Earle, E.D. 1991. Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 9: 208–218.
Bancroft, I. 2001. Duplicate and diverge: the evolution of plant genome microstructure. Trends Genet. 17: 89–93.
Bennetzen, J.L. 2000. Comparative sequence analysis of plant nuclear genomes: microcolinearity and its many exceptions. Plant Cell 12: 1021–1029.
Blechl, A.E. and Anderson, O.D. 1996. Expression of a novel high-molecular-weight glutenin subunit gene in transgenic wheat. Nature Biotechnol. 14: 875–879.
Brooks, S.A., Huang L., Gill, B.S. and Fellers, J.P. 2002. Analysis of 106 kb of contiguous DNA sequence from the D genome of wheat reveals high gene density and a complex arrangement of genes related to disease resistance. Genome 45: 963–972.
Bureau, T.E. and Wessler, S.R. 1994. Stowaway: a new family of inverted repeat elements associated with the genes of both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants. Plant Cell 6: 907–916.
Cenci, A., Chantret, N., Kong, X., Gu, Y.-Q., Anderson, O.D., Fahima, T., Distelfeld, A. and Dubcovsky, J. 2003. Construction and characterization of a half million clone BAC library of durum wheat (Triticum turdigum ssp. durum). Theor. Appl. Genet. 107: 931–939.
Chen, M., SanMiguel, P., de Oliveira, A.C., Woo, S.-S., Zhang, H., Wing, R.A. and Bennetzen, J.L. 1997. Microcolinearity in sh2-homologous regions of the maize, rice, and sorghum genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 3431–3435.
De Bustos, A., Rubio, P. and Jouve, N. 2001. Characterization of two gene subunits on the 1R chromosome of rye as orthologs of each of the Glu-1 genes of hexaploid wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 103: 733–742.
Devos, K.M, and Gale, M.D. 2000. Genome relationships: the grass model in current research. Plant Cell 12: 637–646.
Devos, K.M., Dubcovsky, J., Dvorak, J., Chinoy, C.N. and Gale, M.D. 1995 Structural evolution of wheat chromosomes 4A, 5A, and 7B and its impact on recombination. Theor. Appl. Genet. 91: 282–288.
Devos, K.M., Brown, J.K.M. and Bennetzen, J.L. 2002. Genome size reduction through illegitimate recombination counteracts genome expansion in Arabidopsis. Genome Res 12: 1075–1079.
Dubcovsky, J., Ramakrishna, W., SanMiguel, P.J., Busso, C.S., Yan, L, Shiloff, B.A. and Bennetzen, J.L. 2001. Comparative sequence analysis of colinear barley and rice bacterial artificial chromosomes. Plant Physiol. 125: 1342–1353.
Dvorak, J. 1998. Genome analysis in the Triticum-Aegilops alliance. In: A.E. Slinkard (Ed.) Proceedings of the 9th International Wheat Genetics Symposium (Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada), University Extension Press, University of Saskatchewan, vol. 1, pp. 8–11.
Ellis, J., Dodds, P. and Pryor, T. 2000. Structure, function and evolution of plant disease resistance genes. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 3: 278–284.
Feldman, M., Lupton, F.G.H., and Millers, T.E. 1995. Wheats. In: J. Smartt, N.W and Simmonds (Eds.) Evolution of Crops, Longman Scientific, London, pp. 184–192.
Feschotte, C., Jiang, N. and Wessler, S.R. 2002. Plant transposable elements: where genetics meets genomics. Nature Rev. Genet. 3: 329–341.
Feuillet, C. and Keller, B. 2002. Comparative genomics in the grass family: molecular characterization of grass genome structure and evolution. Ann. Bot. 89: 3–10.
Gaut, B.S. 2002. Evolutionary dynamics of grass genomes. New Phytol. 154: 15–28.
Gu, Y.-Q., Anderson, O.D., Londeore, C., Kong, X., Chibbar, R.N. and Lazo, G.R. 2003. Structural organization of the barley D-hordein locus in comparison with its orthologous regions of wheat genomes. Genome 46: 1087–1097.
Halford, N.G., Forde, J., Anderson, O.D., Greene, F.C. and Shewry, P.R. 1987. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of an HMW glutenin subunit gene from chromosome IB of bread wheat (Triticum aestirum L) and comparison with those of genes from chromosomes IA and ID. Theor. Appl. Genet. 75: 117–126.
Huang, S., Sirikhachornkit, A., Su, X., Faris, J., Gill, B., Haselkorn, R. and Gornicki, P. 2002. Genes encoding plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase and 3-phosphoglycerate kinase of the Triticum/Aegilops complex and the evolutionary history of polyploid wheat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99: 8133–8138.
Hulbert, S., Webb, C.A., Smith, S.M. and Sun, Q. 2001. Resistance gene complexes: evolution and utilization. Annu. Rev. Phytopath. 39: 285–312.
Kumar, A. and Bennetzen, J.L. 1999. Plant retrotransposons. Annu. Rev. Genet. 33: 479–532.
Lafiandra, D., D'Ovidio, R., Porceddu, E., Margiotta, B. and Colaprico, G. 1993. New data supporting high Mr glutenin subunit 5 as the determinant of quality differences among the pairs 5+10 vs. 2+12. J. Cereal Sci. 18: 197–205.
Li, W.-H. 1997. Molecular Evolution. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA.
Lynch, M. and Conery, J.S. 2000. The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science 290: 1151–1155.
MacFadden, E.S. and Sears, E.R. 1946. The artificial synthesis of Triticum spelta. Rec. Soc. Genet. Am. 13: 26–27.
Nakase, M., Hotta, H., Adachi, T., Aoki, N., Nakamura, R., Masumura, T., Tanaka, K. and Matsuda, T. 1996. Cloning of the rice seed alpha-globulin-encoding gene: sequence similarity of the 5′-flanking region to those of the genes encoding wheat high-molecular-weight glutenin and barley D hordein. Gene 170: 223–226.
Nelson, J.C., Sorrells, M.E., Van Denze, A.E., Lu, Y.H., Atkinson, M., Bernard, M., Leroy, P., Faris, J.D. and Anderson, J.A. 1995. Molecular mapping of wheat: major genes and rearrangements in homoeologous groups 4, 5, and 7. Genetics 141: 721–731.
Oh, K.C., Hardeman, K., Ivanchenko, M.G., Ellard-Ivey, M., Nebenführ, A., White, T.J. and Lomax, T.L. 2002. Fine mapping in tomato using microsynteny with the Arabidopsis genome: the Diageotropica (Dgt) locus. Genome Biol. 3(9): research0049.1–0049.11.
Panstruga, R., Buschges, R., Piffanelli, P. and Schulze-Lefert, P. 1998. A contiguous 60 kb genomic stretch from barley reveals molecular evidence for gene islands in a monocot genome. Nucl. Acids Res. 26: 1056–1062.
Pereira, A., Cuypers, H., Gierl, A., Sommer, Z.S. and Saedler, H. 1986. Molecular analysis of the En/spm transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 5: 835–841.
Ramakrishna, W., Dubcovsky, J., Park, Y.-J., Busso, C., Emberton, J., SanMiguel, P. and Bennetzen, J.L. 2002. Different types and rates of genome evolution detected by comparative sequence analysis of orthologous segments from four cereal genomes. Genetics 162: 1389–1499.
Roberts, M.A., Reader, S.M., Dalgliesh, C., Miller, T.E., Foote, T.N., Fish, L.J., Snape, J.W. and Moore, G. 1999. Induction and characterization of Ph1 wheat mutants. Genetics 153: 1909–1918.
Rooke, L., Bekes, F., Fido, R., Barro, F., Gras, P., Tatham, A.S., Barcelo, P.A., Lazzeri, P. and Shewry, P.R. 1999. Overexpresssion of a gluten protein in transgenic wheat results in greatly increased dough strength. J. Cereal Sci. 30: 115–120.
SanMiguel, P., Ramakrishna, W., Bennetzen, J.L., Busso, C.S. and Dubcovsky, J. 2002. Transposable elements, genes and recombination in a 215-kb contig from wheat chromosome 5Am. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2: 70–80.
Schmidt, R. 2000. Synteny: recent advances and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 3: 97–102.
Shewry, P.R., Halford, N.G. and Tatham, A.S. 1992. High molecular weight subunits of wheat glutenin. J. Cereal Sci. 15: 105–120.
Shorrosh, B.S., Wen, L., Kuo-Chang, Z., Huang, J.-K., Pan, J.S., Hermodson, M.A., Tanaka, K., Muthukrishnan, S. and Reeck, G.R. 1992. A novel cereal storage protein: molecular genetics of the 19 kDa globulin of rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 18: 151–154.
Soderlund, C., Humphreys, S., Dunham, A. and French, I. 2000. Contigs built with fingerprints, markers, and FPC V4.7. Genome Res. 10: 1772–1787.
Song, R., Llaca, V., Linton, E. and Messing, J. 2001. Sequence, regulation, and evolution of the maize 22-kD alpha zein gene family. Genome Res. 11: 1817–1825.
Song, R., Llaca, V. and Messing, J. 2002. Mosaic organization of orthologous sequences in grass genomes. Genome Res. 12: 1549–1555.
Song, W.Y., Pi, L.Y., Wang, G.L., Gardner, J., Holsten, T. and Ronald, P.C. 1997. Evolution of the rice Xa21 disease resistance gene family. Plant Cell 9: 1279–1287.
Tikhonov, A.P., SanMiguel, P.J., Nakajima, Y., Gorenstein, N.D., Bennetzen, J.L. and Avramova, Z. 1999. Colinearity and its exceptions in orthologous adh regions of maize and sorghum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 7409–7414.
Vasil, I.K. and Anderson, O.D. 1997. Genetic engineering of wheat gluten. Trends Plant Sci. 8: 292–297.
Wang, G.-L., Ruan, D.-L., Song, W.-Y., Sideris, S., Chen, L., Pi, L.-Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, Z., Fauquet, C., Gaut, B.S., Whalen, M.C. and Ronald, P.C. 1998. Xa21D encodes a receptor-like molecule with a leucine-rich repeat domain that determines race-specific recognition and is subject to adaptive evolution. Plant Cell 10: 765–779.
Wei, F., Wing, R.A. and Wise, R.P. 2002. Genome dynamics and evolution of the Mla (powdery mildew) resistance locus in barley. Plant Cell 14: 1903–1917.
Wicker, T., Stein, N., Albar, L., Feuillet, C., Schlagenhauf, E. and Keller, B. 2001. Analysis of a contiguous 211 kb sequence in diploid wheat (Triticum monococcum L.) reveals multiple mechanisms of genome evolution. Plant J. 26: 307–316.
Wicker, T., Yahiaoui, N., Guyot, R., Schlagenhauf, E., Liu, Z.D., Dubcovsky, J. and Keller, B. 2003a. Rapid genome divergence at orthologous low molecular weight glutenin loci of the A and Am genomes of wheat. Plant Cell 15: 1186–1197.
Wicker, T., Guyot, R., Yahiaoui, N. and Keller, B. 2003b. CACTA transposons in Triticeae. A diverse family of high-copy repetitive elements. Plant Physiol. 132: 52–63.
Woo, Y.M., Hu, D.W., Larkins, B.A. and Jung, R. 2001. Genomics analysis of genes expressed in maize endosperm identifies novel seed proteins and clarifies patterns of zein gene expression. Plant Cell 13: 2297–2317.
Yan, L., Loukoianov, A., Tranquilli, G., Helguera, M., Fahima, T. and Dubcovsky, J. 2003. Positional cloning of the wheat vernalization gene VRN1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 6263–6268.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, XY., Gu, Y.Q., You, F.M. et al. Dynamics of the evolution of orthologous and paralogous portions of a complex locus region in two genomes of allopolyploid wheat. Plant Mol Biol 54, 55–69 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLAN.0000028768.21587.dc
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLAN.0000028768.21587.dc