Abstract
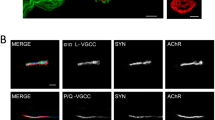
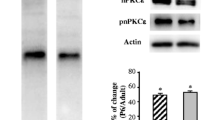
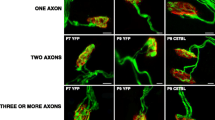
In vertebrate neuromuscular junctions (nmjs), adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) is stored at the motor nerve terminals and is co-released with acetylcholine during neural stimulation. Several lines of evidence suggest that the synaptic ATP can act as a synapse-organizing factor at the nmjs, mediated by metabotropic P2Y1 receptors. P2Y1 receptor mRNAs in chicken and rat muscles are low in embryo but increases markedly in the adult, and decreased after denervation. The P2Y1 receptor protein is restricted to the nmjs and co-localized with AChRs in adult muscles. The activation of P2Y1 receptor by adenine nucleotides in cultured chick myotubes stimulated the accumulation of inositol phosphates, intracellular Ca2+ mobilization, protein kinase C activity and phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases. The receptor activation led to an increase in the expression of transcripts encoding AChE catalytic subunit and AChR subunits. The ATP-induced post-synaptic gene expression is possibly mediated by the activation of signaling cascades of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Therefore, a model is being proposed here that the synaptic ATP has a role of synergy with other regulatory signals, such as neuregulin, which act via their post-synaptic receptors to activate second signaling molecules locally to enhance the transcription of AChR/AChE genes specifically in the adjacent sub-synaptic nuclei during the formation and, especially, the maintenance of post-synaptic specializations at the nmjs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABBRACCHIO, M. P., BOEYNAEMS, J. M., BARNARD, E. A., BOYER, J. L., KENNEDY, C., MIRASPORTUGAL, M. T., KING, B. F., GACHET, C., JACOBSON, K. A., WEISMAN, G. A. & BURNSTOCK, G. (2003) Characterization of the UDP-glucose receptor (re-named here the P2Y14 receptor) adds diversity to the P2Y receptor family. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 24, 5–55.
ALTIOK, N., ALTIOK, S. & CHANGEUX, J.-P. (1997) Heregulin-stimulated acetylcholine receptor gene expression in muscle: Requirement for MAP kinase and evidence fro a parallel inhibitory pathway independent of electrical activity. The EMBO Journal 16, 71–725.
ALTIOK, N. & CHANGEUX, J.-P. (2001) Electrical activity regulates AChR gene expression via JNK, PKC? and Sp1 in skeletal chick muscle. FEBS Letter 487, 33–338.
ANGLISTER, L., STILES, J. R. & SALPETER, M. M. (1994) Acetylcholinesterae density and turnover number at frog neuromuscular junctions, with modeling of their role in synaptic function. Neuron 12, 78–794.
ANGUS, L. M., CHAN, R. Y. & JASMIN, B. J. (2001) Role of intronic E-and N-box motifs in the transcriptional induction of the acetylcholinesterase gene during myogenic differentiation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276, 1760–17609.
ARIKAWA-HIRASAWA, E., ROSSI, S. G., ROTUNDO, R. L. & YAMADA, Y. (2002) Absence of acetylcholinesterase at the neuromuscular junctions of perlecan-null mice. Nature Neuroscience 5, 11–123.
BARNARD, E. A. (1992) Receptor classes and the transmitter-gated ion channels. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 17, 36–374.
BARNARD, E. A. & SIMON, J. (2001) An elusive receptor finally caught: P2Y12, animportant drug target in platelets. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 22, 38–391.
BEN AZIZ-ALOYA, R., SEIDMAN, S., TIMBERG, R., STERNFELD, M., ZAKUT, H. & SOREQ, H. (1993) Expression of a human acetylcholinesterase promoterreporter construct in development neuromuscular junctions of Xenopus embryos. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 90, 247–2475.
BERMAN, H. A., DECKER, M. M. & JO, S. (1987) Reciprocal regulation of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in mammalian skeletal muscle. Developmental Biology 120, 15–161.
BO, X., SCHOEPFER, R. & BURNSTOCK, G. (2000) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel ATP P2X receptor subtype from embryonic chick skeletal muscle. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, 1440–14407.
BOYER, J. L., ROMERO-AVILA, T., SCHACHTER, J. B. & HARDEN, T. K. (1996) Identification of competitive antagonists of the P2Y1 receptor. Molecular Pharmacology 50, 132–1329.
BURNSTOCK, G. & KENNEDY, C. (1985) Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? General Pharmacology 16, 43–440.
CHAMBERS, J. K., MACDONALD, L. E., SARAU, H. M., AMES, R. S., FREEMAN, K., FOLEY, J. J., ZHU, Y., MCLAUGHLIN, M. M., MURDOCK, P., MCMILLAN, L., TRILL, J., SWIFT, A., AIYAR, N., TAYLOR, P., VAWTER, L., NAHEED, S., SZEKERES, P., HERVIEU, G., SCOTT, C., WATSON, J. M., MURPHY, A. J., DUZIC, E., KLEIN, C., BERGSMA, D. J., WILSON, S. & LIVI, G. P. (2000). A G proteincoupled receptor for UDP-glucose. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, 1076–10771.
CHAN, R. Y. Y., BOUDREAU-LARIVIERE, C., ANGUS, L. M., MANKAL, F. A. & JASMIN, B. J. (1999) An intronic enhancer containing an N-box motif is required for synapse-and tissue-specific expression of the acetylcholinesterase gene in skeletal muscle fibers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 96, 462–4632.
CHENG, A. W. M., KONG, L. W., TUNG, E. K. K., SIOW, N. L., CHOI, R. C. Y., ZHU, S. Q., PENG, H. B. & TSIM, K. W. K. (2003) cDNA encodes Xenopus P2Y1 nucleotide receptor: Expression at the neuromuscular junctions. Neuroreport 14, 35–357.
CHOI, R. C. Y., YUNG, L. Y., DONG, T. T. X., WAN, D. C. C., WONG, Y. H. & TSIM, K. W. K. (1998) The calcitonin gene-related peptide-induced acetylcholinesterase synthesis in cultured chick myotubes is mediated by cyclic AMP. Journal of Neurochemistry 71, 15–160.
CHOI, R. C. Y., SIOW, N. L., ZHU, S. Q. & TSIM, K. W. K. (2000) The cAMP-dependent protein kinase mediates the expression of AChE in chick myotubes. Neuroreport 11, 80–806.
CHOI, R. C. Y., SIOW, N. L., ZHU, S. Q., WAN, D. C. C., WONG, Y. H. & TSIM, K. W. K. (2001a) The cyclic AMP-mediated expression of AChE in myotubes shows contrasting activation and repression between avian and mammalian enzymes. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences 17, 73–745.
CHOI, R. C. Y., MAN, M. L. S., LING, K. K. Y., IP, N. Y., SIMON, J., BARNARD, E. A. & TSIM, K. W. K. (2001b) Expression of the P2Y1 nucleotide receptor in chick muscle: Its functional role in the regulation of acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholine receptor. The Journal of Neuroscience 21, 922–9234.
CHOI, R. C. Y., SIOW, N. L., CHENG, A. W. M., LING, K. K. Y., TUNG, E. K. K., SIMON, J., BARNARD, E. A. & TSIM, K. W. K. (2003) ATP acts via P2Y1 receptors to stimulate acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholine receptor expression: Transduction and transcription control. The Journal of Neuroscience 23, 444–4456.
COLOMAR, A. & AMEDEE, T. (2001) ATP stimulation of P2X7 receptors activates three different ionic conductances on cultured mouse Schwann cells. The European Journal of Neuroscience 14, 92–936.
COMMUNI, D., GONZALEZ, N. S., DETHEUX, M., BREZILLON, S., LANNOY, V., PARMENTIER, M. & BOEYNAEMS, J. M. (2001) Identification of a novel human ADP receptor coupled to Gi. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276, 4147–41485.
DEMPSEY, E. C., NEWTON, A. C., MOCHLY-ROSEN, D., FIELDS, A. P., REYLAND, M. E., INSEL, P. A. & MESSING, R. O. (2000) Protein kinase C isozymes and the regulation of diverse cell responses. American Journal of Physiology—Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 279, L42–L438.
DEUCHARS, S. A., ATKINSON, L., BROOKE, R. E., MUSA, H., MILLIGAN, C. J., BATTEN, T. F., BUCKLEY, N. J., PARSON, S. H. & DEUCHARS, J. (2001) Neuronal P2X7 receptors are targeted to presynaptic terminals in the central and peripheral nervous systems. The Journal of Neuroscience 21, 714–7152.
DUDLEY, D. T., PANG, L., DECKER, S. J., BRIDGES, A. J. & SALTIEL, A. R. (1995) A synthetic inhibitor of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 92, 768–7689.
EKSTRÖM, T. J., KLUMP, W. M., GETMAN, D., KARIN, M. & TAYLOR, P. (1993) Promoter elements and transcriptional regulation of the acetylcholinesterase gene. DNA and Cell Biology 12, 6–72.
FAVATA, M. F., HORIUCHI, K. Y., MANOS, E. J., DAULERIO, A. J., STRADLEY, D. A., FEESER, W. S., VAN DYK, D. E., PITTS, W. J., EARL, R. A., HOBBS, F., COPELAND, R. A., MAGOLDA, R. L., SCHERLE, P. A. & TRZASKOS, J. M. (1998) Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 1862– 18632.
FERTUCK, H. C. & SALPETER, M. M. (1974) Localization of acetylcholine receptor by I125-labeled ?-bungartoxin binding at mouse endplates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 71, 137–1378.
FILIPPOV, A. K., BROWN, D. A. & BARNARD, E. A. (2000) The P2Y1 receptor closes the N-type Ca2+ channel in neurones, with both adenosine triphosphates and diphosphates as potent agonists. British Journal of Pharmacology 129, 106–1066.
FU, W. M., CHAN, Y. H., LEE, K. F. & LIOU, J. C. (1997) Regulation of quantal transmitter secretion by ATP and protein kinase at developing neuromuscular synapses. The European Journal of Neuroscience 9, 67–685.
FUENTES, M. E. & TAYLOR, P. (1993) Control of acetylcholinesterase gene expression during myogenesis. Neuron 10, 67–687.
GEE, S. H., MADHAVAN, R., LEVINSON, S. R., CALDWELL, J. H., SEALOCK, R. & FROEHNER, S. C. (1998) Interaction of muscle and brain sodium channels with multiple members of the syntrophin family of dystrophin-associated proteins. The Journal of Neuroscience 18, 12–137.
HÄGGBLAD, J. & HEILBRONN, E. (1988) P2-receptorstimulated phosphoinositide turnover in chick myotubes. FEBS Letters 235, 13–136.
HALL, R. A., OSTEDGAARD, L. S., PREMONT, R. T., BLITZER, J. T., RAHMAN, N., WELSH, M. J. & LEFKOWITZ, R. J. (1998) A C-terminal motif found in the beta2-adrenergic receptor, P2Y1 receptor and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator determines binding to theNa+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor family of PDZ proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95, 849–8501.
HENNING, R. H., DUIN, M., DEN HERTOG, A. & NELEMANS, A. (1993) Activation of the phospholipase C pathway by ATP is mediated exclusively through nucleotide type P2-purinoceptors in C2C12 myotubes. British Journal of Pharmacology 110, 74–752.
HENNING, R. H. (1997) Purinoceptors in neuromuscular transmission. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 74, 11–128.
HILGENBERG, L., YEARWOOD, S., MILSTEIN, S. & MILES, K. (1996) Neural influence on protein kinase C isoform expression in skeletal muscle. The Journal of Neuroscience 16, 499–5003.
HOLLOPETER, G., JANTZEN, H. M., VINCENT, D., LI, G., ENGLAND, L., RAMAKRISHNAN, V., YANG, R. B., NURDEN, P., NURDEN, A., JULIUS, D. & CONLEY, P. B. (2001) Identification of the platelet ADP receptor targeted by antithrombotic drugs. Nature 409, 20–207.
ISRAEL, M. & DUNANT, Y. (1998) Acetylcholine release and the cholinergic genomic locus. Molecular Neurobiology 16, –20.
JO, Y. H. & SCHLICHTER, R. (1999) Synaptic corelease of ATP and GABA in cultured spinal neurons. Nature Neuroscience 2, 24–245.
KERESZTES, M., HÄGGBLAD, J. & HEILBRONN, E. (1991) Basal and ATP-stimulated phosphoinositol metabolism in fusing rat skeletal muscle cells in culture. Experimental Cell Research 196, 36–364.
KING, B. F. & TOWNSEND-NICHOLSON, A. (2000) Recombinant P2Y receptors: The UCL experience. Journal of the Autonomic Nervous System 81, 16–170.
KOLB, H. A. & WAKELAM, M. J. (1983) Transmitter-like action of ATP on patched membranes of cultured myoblasts and myotubes. Nature 303, 62–623.
KORNAU, H. C., SCHENKER, L. T., KENNEDY, M. B. & SEEBURG, P. H. (1995) Domain interaction between NMDA receptor subunits and the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95. Science 269, 173–1740.
LANUZA, M. A., LI, M. X., JIA, M., KIM, S., DAVENPORT, R., DUNLAP, V. & NELSON, P. G. (2000) Protein kinase C-mediated changes in synaptic efficacy at the neuromuscular junction in vitro: The role of postsynaptic acetylcholine receptors. Journal of Neuroscience Research 61, 61–625.
LAUFER, R., KLARSFELD, A. & CHANGEUX, J.-P. (1991) Phorbol esters inhibit the activity of the chicken acelycholine receptor alpha-subunit gene promoter. Role of myogenic regulators. European Journal of Biochemistry 202, 81–818.
LEGAY, C., MANKAL, F. A., MASSOULIÉ, J. & JASMIN, B. J. (1999) Stability and secretion of acetylcholinesterase forms in skeletal muscle cells. The Journal of Neuroscience 19, 825–8259.
LÉON, C., HECHLER, B., FREUND, M., ECKLY, A., VIAL, C., OHLMANN, P., DIERICH, A., LEMEUR, M., CAZENAVE, J. P., GACHET, C. (1999) Defective platelet aggregation and increased resistance to thrombosis in purinergic P2Y1 receptor-null mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 104, 173–1737.
LU, B. & FU, W. M. (1995) Regulation of post-synaptic response by calcitonin gene related peptide and ATP at developing neuromuscular junctions. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 73, 105–1056.
LU, Z. & SMITH, D. O. (1991) Adenosine 5' triphosphate increases acetylcholine channel opening frequency in rat skeletal muscle. The Journal of Physiology 436, 4–56.
LUSTIG, K. D., SHIAU, A. K., BRAKE, A. J. & JULIUS, D. (1993) Expression cloning of anATP receptor frommouse neuroblastoma cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 90, 511–5117.
MACPHERSON, P., KOSTROMINOVA, T., TANG, H. & GOLDMAN, D. (2002) Protein kinase C and calcium/calmodulin-activated protein kinase II (CaMK II) suppress nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene expression in mammalian muscle. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277, 1563–15646.
MASSOULIÉ, J., PEZZEMENTI, L., BON, S., KREJCI, E. & VALLETTE, F.-M. (1993) Molecular and cellular biology of cholinesterases. Progress in Neurobiology 41, 3–91.
MCMAHAN, U. J., SANES, J. R. & MARSHALL, L. M. (1978) Cholinesterase is associated with the basal lamina at the neuromuscular junction. Nature 271, 17–174.
MEYER, M. P., GRÖSCHEL-STEWART, U., ROBSON, T. & BURNSTOCK, G. (1999) Expression of two ATPgated ion channels, P2X5 and P2X6, in developing chick skeletal muscle. Developmental Dynamics 216, 44–449.
MOORE, D., CHAMBERS, J., WALDVOGEL, H., FAULL, R. & EMSON, P. (2000) Regional and cellular distribution of the P2Y(1) purinergic receptor in the human brain: Striking neuronal localisation. The Journal of Comparative Neurology 421, 37–384.
MUTERO, A., CAMP, S. & TAYLOR, P. (1995) Promoter elements of the mouse acetylcholinesterase gene: Transcriptional regulation during muscle differentiation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 270, 186–1872.
NG, Y. P., PUN, S., YANG, J. F., IP, N. Y. & TSIM, K. W. K. (1997) Chick muscle expresses various ARIA isoforms: Regulation during development, denervation and regeneration. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences 9, 13–143.
NORTH, R. A. & BARNARD, E. A. (1997) Nucleotide receptors. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 7, 34–357.
O'MALLEY, J. P., MOORE, C. P. & SALPETER, M. M. (1997) Stabilization of acetylcholine receptors by exogenous ATP and its reversal by cAMP and calcium. The Journal of Cell Biology 138, 15–165.
PARR, C. E., SULLIVAN, D. M., PARADISO, A. M., LAZAROWSKI, E. R., BURCH, L. H., OLSEN, J. C., ERB, L., WEISMAN, G. A., BOUCHER, R. C. & TURNER, J. T. (1995) Cloning and expression of a human P2U nucleotide receptor, a target for cystic fibrosis pharmacology. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 91, 327–3279.
PENG, H. B., XIE, H., ROSSI, S. G. & ROTUNDO, R. L. (1999) Acetylcholinesterase clustering at the neuromuscular junction involves perlecan and dystroglycan. The Journal of Cell Biology 145, 91–921.
PERKINS, G. A., WANG, L., HUANG, L. J., HUMPHRIES, K., YAO, V. J., MARTONE, M., DEERINCK, T. J., BARRACLOUGH, D. M., VIOLIN, J. D., SMITH, D., NEWTON, A., SCOTT, J. D., TAYLOR, S. S. & ELLISMAN, M. H. (2001) PKA, PKC, and AKAP localization in and around the neuromuscular junction. BMC Neuroscience 2, 1–35.
PORTER, C. W. & BARNARD, E. A. (1976) Ultrastructural studies on the acetylcholine receptor at motor end plates of normal and pathologic muscles. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 274, 8–107.
PUN, S. & TSIM, K. W. K. (1995) Truncated form of proacetylcholine receptor-inducing activity (ARIA) induces AChR alpha-subunit but not AChE transcripts in cultured chick myotubes. Neuroscience Letters 198, 10–110.
RALEVIC, V. & BURNSTOCK, G. (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacological Reviews 50, 41–492.
ROTUNDO, R. L. (1988) Biogenesis of acetylcholinesterase molecular forms in muscle. Evidence for a rapidly turning over, catalytically inactive precursor pool. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 263, 1939–19406.
RYTEN, M., HOEBERTZ, A. & BURNSTOCK, G. (2001) Sequential expression of three receptor subtypes of extracellular ATP in developing rat skeletal muscle. Developmental Dynamics 221, 33–341.
RYTEN, M., DUNN, P. M., NEARY, J. T. & BURNSTOCK, G. (2002) ATP regulates the differentiation of mammalian skeletal muscle by activation of a P2X5 receptor on satellite cells. The Journal of Cell Biology 158, 34–355.
SALPETER, M. M. (1987) Vertebrate neuromuscular junctions: General morphology, molecular organization, and functional consequences. In Vertebrate Neuromuscular Junction (edited by SALPETER, M. M.) pp. –54. New York: Alan R. Liss Inc.
SANES, J. R. & LICHTMAN, J. W. (1999) Development of the vertebrate neuromuscular junction. Annual Review of Neuroscience 22, 38–442.
SCHAEFFER, L., DE KERCHOVE D'EXAERDE, A. & CHANGEUX, J. P. (2001) Targeting transcription to the neuromuscular synapse. Neuron 31, 1–22.
SELLERS, L. A., SIMON, J., LUNDAHL, T. S., COUSENS, D. J., HUMPHREY, P. P. A. & BARNARD, E. A. (2001) Adenosine nucleotides acting at the human P2Y1 receptor stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinases and induce apoptosis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276, 1637–16390.
SI, J. & MEI, L. (1999) ERK MAP kinase activation is required for acetylcholine receptor inducing activity-induced increase in all five acetylcholine receptor subunit mRNAs as well as synapse-specific expression of acetylcholine receptor ?-transgene. Molecular Brain Research 67, 1–27.
SI, J., WANG, Q. & MEI, L. (1999) Essential roles of c-JUN and c-JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK) in neuregulinincreased expression of the acetylcholine receptor epsilon-subunit. The Journal of Neuroscience 19, 849–8508.
SILMAN, I., DI GIAMBERARDINO, L., LYLES, L., COURAUD, J. Y. & BARNARD, E. A. (1979) Parallel regulation of acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase in normal, denervated and dystrophic chicken skeletal muscle. Nature 280, 16–162.
SILINSKY, E. M. & REDMAN, R. S. (1996) Synchronous release of ATP and neurotransmitter within milliseconds of a motor nerve impulse in the frog. The Journal of Physiology 492, 81–822.
SIMON, J., VIGNE, P., EKLUND, K. M., MICHEL, A. D., FRELIN, C. & BARNARD, E. A. (2001) Activity of adenosine diphosphates and triphosphates on a P2YT receptor in brain capillary endothelial cells. British Journal of Pharmacology 132, 17–182.
SIOW, N. L., CHOI, R. C. Y., CHENG, A. W. M., JIANG, J. X. S., WAN, D. C. C., ZHU, S. Q. & TSIM, K. W. K. (2002) A cyclic AMP-dependent pathway regulates the expression of acetylcholinesterase during myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277, 3612–36136.
TASSIN, A. M., HÄGGBLAD, J. & HEILBRONN, E. (1990) Receptor-triggered polyphosphoinositide turnover produces less cytosolic free calcium in cultured dysgenic myotubes than in normal myotubes. Muscle Nerve 13, 14–145.
TSIM, K. W. K., RANDALL, W. R. & BARNARD, E. A. (1988) An asymmetric form of muscle acetylcholinesterase contains three subunits types and two enzymic activities in one molecule. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 85, 126–1266.
TSIM, K. W. K. & BARNARD, E. A. (2002) The signaling pathways mediated by P2Y nucleotide receptors in the formation and maintenance o the skeletal neuromuscular junction. NeuroSignals 11, 5–64.
WAN, D. C. C., CHOI, R. C. Y., SIOW, N. L. & TSIM, K. W. K. (2000) The promoter of human acetylcholinesterase is activated by a cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate-dependent pathway in cultured NG108-15 neuroblastoma cells. Neuroscience Letters 288, 8–85.
WEBB, T. E., SIMON, J., KRISHEK, B. J., BATESON, A. N., SMART, T. G., KING, B. F., BURNSTOCK, G. & BARNARD, E. A. (1993) Cloning and functional expression of a brain G-protein-coupled ATP receptor. FEBS Letters 324, 21–225.
WEBB, T. E., HENDERSON, D., KING, B. F., WANG, S., SIMON, J., BATESON, A. N., BURNSTOCK, G. & BARNARD, E. A. (1996) A novel G protein-coupled P2 purinoceptor (P2Y3) activated preferentially by nucleoside. Molecular Pharmacology 50, 25–265.
WEBB, T. E., HENDERSON, D. J., ROBERTS, J. A. & BARNARD, E. A. (1998) Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat P2Y4 receptor. Journal of Neurochemistry 71, 134–1357.
YANG, J. F., ZHOU, H., PUN, S., IP, N. Y., PENG, H. B. & TSIM, K. W. K. (1998) Cloning ofcDNAsencoding Xenopus neuregulin: Expression in myotomal muscle during embryo development. Molecular Brain Research 58, 5–73.
YANG, J. F., ZHOU, H., CHOI, R. C. Y., IP, N. Y., PENG, H. B. & TSIM, K. W. K. (1999) A cysteine-rich form of Xenopus neuregulin induces the expression of acetylcholine receptors in cultured myotubes. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences 13, 41–429.
ZHANG, F. L., LUO, L., GUSTAFSON, E., LACHOWICZ, J., SMITH, M., QIAO, X., LIU, Y. H., CHEN, G., PRAMANIK, B., LAZ, T. M., PALMER, K., BAYNE, M. & MONSMA F. J. JR. (2001) ADP is the cognate ligand for the orphan G protein-coupled receptor SP1999. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276, 860–8615.
ZHANG, F. L., LUO, L., GUSTAFSON, E., PALMER, K., QIAO, X., FAN, X., YANG, S., LAZ, T. M., BAYNE, M. & MONSMA, F. L. JR. (2002) P2Y13: Identification and characterization of a novel G?i-coupled ADP receptor from human and mouse. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 301, 70–713.
ZIMMERMANN, H. (1999) Two novel families of ectonucleotidases: Molecular structures, catalytic properties and a search for function. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 20, 23–236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsim, K.W.K., Choi, R.C.Y., Siow, N.L. et al. ATP induces post-synaptic gene expressions in vertebrate skeletal neuromuscular junctions. J Neurocytol 32, 603–617 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEUR.0000020613.25367.78
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEUR.0000020613.25367.78