Abstract
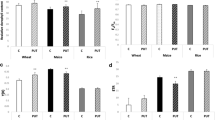
Changes in soluble and cell wall bound peroxidase (POD, EC 1.11.1.7) activity, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL, EC 4.3.1.5) activity, and lignin content in roots of ferulic acid-stressed soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) seedlings and their relationships with root growth were investigated. Three-day-old soybean seedlings were cultivated in half-strength Hoagland nutrient solution containing 1.0 mM ferulic acid for 24–72 hr. Length, fresh weight, and dry weight of roots decreased, while soluble and cell wall bound POD activity, PAL activity, and lignin content increased after ferulic acid treatment. These enzymes probably participate in root growth reduction in association with cell wall stiffening related to the formation of cross-linking among cell wall polymers and lignin production.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Baleroni, C. R. S., Ferrarese, M. L. L., Braccini, A. L., Scapim, C. A., and Ferrarese-Filho, O. 2000. Effects of ferulic and p-coumaric acids on canola (Brassica napus L. cv. Hyola 401) seed germination. Seed Sci. Technol. 28:201–207.
Baziramakenga, R., Leroux, G. D., and Simard, R. R. 1995. Effects of benzoic and cinnamic acids on membrane permeability of soybean roots. J. Chem. Ecol. 21:1271–1285.
Bergmark, C. L., Jackson, W. A., Volk, R. J., and Blum, U. 1992. Differential inhibition by ferulic acid of nitrate and ammonium uptake in Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 98:639–645.
Blum, U. and Rebbeck, J. 1989. Inhibition and recovery of cucumber roots given multiple treatments of ferulic acid in nutrient culture. J. Chem. Ecol. 15:917–928.
Bolwell, G. P. and Wojtaszek, P. 1997. Mechanisms for the generation of reactive oxygen species in plant defense-a broad perspective. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 51:347–366.
Booker, F. L., Blum, U., and Fiscus, E. L. 1992. Short-term effects of ferulic acid on ion uptake and water relations in cucumber seedlings. J. Exp. Bot. 43:649–655.
Cakmak, I. and Horst, W. J. 1991. Effect of aluminum on lipid peroxidation, superoxide-dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities in root tips of soybean (Glycine max). Plant Physiol. 83:463–468.
Chen, S. and Schopfer, P. 1999. Hydroxyl-radical production in physiological reactions. A novel function of peroxidase. Eur. J. Biochem. 260:726–735.
Demos, E. K., Woolwine, M., Wilson, R. H., and McMillan, C. 1975. The effects of ten phenolic compounds on hypocotyl growth and mitochondrial metabolism of mung bean. Am. J. Bot. 62:97–102.
Devi, R. S. and Prasad, M. N. V. 1996. Ferulic acid mediated changes in oxidative enzymes of maize seedlings: Implications in growth. Biol. Plant. 38:387–395.
Doblinski, P. M. F., Ferrarese, M. L. L., Huber, D. A., Scapim, C. A., Braccini, A. L., and Ferrarese-Filho, O. 2003. Peroxidase and lipid peroxidation of soybean roots in response to p-coumaric and p-hydroxybenzoic acids. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 46:193–198.
Einhellig, F. A. 1995. Allelopathy: Current status and future goals, pp. 1–24, in Inderjit, K. M. M. Dakshini, and F. A. Einhellig (eds.). Allelopathy: Organisms, Processes and Applications. ACS Symposium Series 582, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
Einhellig, F. A. and Eckrich, P. C. 1984. Interactions of temperature and ferulic acid stress on grain sorghum and soybeans. J. Chem. Ecol. 10:161–170.
Ferrarese, M. L. L., Ferrarese-Filho, O., and Rodrigues, J. D. 2000a. Ferulic acid uptake by soybean root in nutrient culture. Acta Physiol. Plant. 22:121–124.
Ferrarese, M. L. L., Rodrigues, J. D., and Ferrarese-Filho, O. 2000b. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity in soybean roots extract measured by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Plant Biol. 2:152–153.
Ferrarese, M. L. L., Souza, N. E., Rodrigues, J. D., and Ferrarese-Filho, O. 2001. Carbohydrate and lipid status in soybean roots influenced by ferulic acid uptake. Acta Physiol. Plant. 23:421–427.
Ferrarese, M. L. L., Zottis, A., and Ferrarese-Filho, O. 2002. Protein-free lignin quantification in soybean (Glycine max) roots. Biologia 57:541–543.
Frahry, G. F. and Schopfer, P. 1998. Hydrogen peroxide production by roots and its stimulation by exogenous NADH. Plant Physiol. 103:395–404.
Fry, S. C. 1986. Cross-linking of matrix polymers in the growing cell walls of angiosperms. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 37:165–186.
Herrig, V., Ferrarese, M. L. L., Suzuki, L. S., Rodrigues, J. D., and Ferrarese-Filho, O. 2002. Peroxidase and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activities, phenolic acid contents, and allelochemicals-inhibited root growth of soybean. Biol. Res. 35:59–66.
Holappa, L. D. and Blum, U. 1991. Effects of exogenously applied ferulic acid, a potential allelopathic compound, on leaf growth, water utilization, and endogenous abscisic acid levels of tomato, cucumber, and bean. J. Chem. Ecol. 17:865–886.
Iiyama, K., Lam, T. B. T., and Stone, B. A. 1990. Phenolic acid bridges between polysaccharides and lignin in wheat internodes. Phytochemistry 29:733–737.
Kobza, J. and Einhellig, F. A. 1987. The effects of ferulic acid on the mineral nutrition of grain sorghum. Plant Soil 98:99–109.
Kuiters, A. T. 1990. Role of phenolic substances from decomposing forest litter in plant-soil interactions. Acta Bot. Neerl. 39:329–348.
Lyu, S.-W. and Blum, U. 1990. Effects of ferulic acid, an allelopathic compound, on net P, K, and water uptake by cucumber seedlings in a split-root system. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:2429–2439.
Macias, F. A. 1995. Allelopathy in the Search for natural herbicide models, pp. 311–329, in Inderjit, K. M. M. Dakshini, and F. A. Einhellig (eds.). Allelopathy: Organisms, Processes and Applications. ACS Symposium Series 582, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
Ng, P. L. L., Ferrarese, M. L. L., Huber, D. A., Ravagnani, A. L. S., and Ferrarese-Filho, O. 2003. Canola (Brassica napus L.) seed germination influenced by cinnamic and benzoic acids derivatives: Effects on peroxidase. Seed Sci. Technol. 31:39–46
Patterson, D. T. 1981. Effects of allelopathic chemicals on growth and physiological responses of soybean (Glycine max L.). Weed Sci. 29:53–59.
Politycka, B. 1996. Peroxidase activity and lipid peroxidation in roots of cucumber seedlings influenced by derivatives of cinnamic and benzoic acids. Acta Physiol. Plant. 18:365–370.
Politycka, B. 1998. Phenolics and the activities of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, phenol-β-glucosyltransferase and β-glucosidase in cucumber roots as affected by phenolic allelochemicals. Acta Physiol. Plant. 20:405–410.
Politycka, B. 1999. Ethylene-dependent activity of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and lignin formation in cucumber roots exposed to phenolic allelochemicals. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 68:123–127.
Pramanik, M. H. R., Nagai, M., Asao, T., and Matsui, Y. 2000. Effects of temperature and photoperiod on phytotoxic root exudates of cucumber (Cucumis sativus) in hydroponic culture. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:1953–1967.
Ros-BarcelÓ, A., Pomar, F., LÓpez-Serrano, M., MartÍnez, P., and PedreÑo, M. A. 2002. Developmental regulation of the H2O2-producing system and of a basic peroxidase isoenzyme in the Zinnia elegans lignifying xylem. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 40:325–332.
SÁnchez, M., PeÑa, M. J., Revilla, G., and Zarra, I. 1996. Changes in dehydrodiferulic acids and peroxidase activity against ferulic acid associated with cell walls during growth of Pinus pinaster hypocotyl. Plant Physiol. 111:941–946.
Sato, T., Kiuchi, F., and Sankawa, U. 1982. Inhibition of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase by cinnamic and derivatives and related compounds. Phytochemistry 21:845–850.
Shann, J. R. and Blum, U. 1987. The utilization of exogenously supplied ferulic acid in lignin biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 26:2977–2981.
Siqueira, J. O., Nair, M. G., Hammerschmidt, R., and Safir, G. R. 1991. Significance of phenolic compounds in plant-soil-microbial systems. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 10:63–121.
Tan, K. S., Hoson, T., Masuda, Y., and Kamikasa, S. 1992. Effect of ferulic and p-coumaric acids on Oryza coleoptile growth and the mechanical properties of cell walls. J. Plant Physiol. 140:460–465.
Vaughan, D. and Ord, B. 1990. Influence of phenolic acids on morphological changes in roots of Pisum sativum. J. Sci. Food Agric. 52:289–299.
Whetten, R. W., MacKaw, J. J., and Sederoff, R. R. 1998. Recent advances in understanding lignin biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 49:585–609.
Wojtaszek, P. 1997. Oxidative burst: An early plant response to pathogen infection. Biochem. J. 322:681–692.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos, W.D., Ferrarese, M.d.L.L., Finger, A. et al. Lignification and Related Enzymes in Glycine max Root Growth-Inhibition by Ferulic Acid. J Chem Ecol 30, 1203–1212 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOEC.0000030272.83794.f0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOEC.0000030272.83794.f0